

Quick Summary
In today’s world of hybrid teams, rapid innovation, and dynamic work cultures, leadership isn’t a static concept—it’s a living force that shapes how people engage, collaborate, and succeed. Whether leading a small project team or an entire organization, your leadership style affects more than results—it defines how people experience their work.
Like feedback in communication, leadership styles act as a framework through which we express vision, enable performance, and foster trust. This blog is a great starting point, but there’s room to make it more powerful, actionable, and relevant to today’s professionals. This enhanced version brings real-world insights, additional styles, strategic comparisons, and practical tools to help readers lead with intention and impact.

Leadership and leadership styles refer to how a leader guides, influences, and motivates their team. It shapes how strategies are planned and executed, ultimately affecting team performance, stakeholder expectations, and overall success.
Key insights about leadership styles:
Knowing your leadership style is essential for becoming a successful leader. It helps you see how your approach influences your team, recognize your strengths, and identify areas for improvement.
While some leaders can easily define their leadership styles, many naturally display traits from multiple leadership styles. Understanding your dominant style can help you assess its effectiveness and how your team perceives your leadership.
One of the best ways to gain clarity on your leadership style is through honest feedback from your team. Encouraging open discussions allows you to refine your approach and make necessary adjustments to become a more effective and supportive leader.
Various factors, including personality, life experiences, emotional intelligence, family background, and mindset shape a leader’s style. Understanding these influences helps leaders refine their approach and become more effective.
At Adobe, leaders adopted transformational practices by eliminating annual performance reviews and shifting to continuous feedback. This change boosted engagement and innovation across teams.
Many banks adopted autocratic strategies during the 2008 financial meltdown to stabilize operations. While not ideal in the long term, it helped execute swift decisions under pressure.
BYJU uses a coach-style model to guide educators and content creators, resulting in better student outcomes and rapid platform scaling.
When leaders recognize and adapt their leadership style to different situations, they can achieve:
Leaders can use a 2×2 matrix based on level of control vs. team autonomy to identify their dominant style.
| High Control | Low Control | |
| High Autonomy | Coaching | Laissez-Faire |
| Low Autonomy | Autocratic | Bureaucratic |
This matrix helps determine which style to use based on team maturity and task complexity.
Understanding how leadership styles impact decision-making can improve organizational efficiency.
| Style | Speed of Decision | Collaboration | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autocratic | Very Fast | Low | Crisis response, time-sensitive ops |
| Democratic | Slow | High | Creative brainstorming, team buy-in |
| Laissez-Faire | Moderate | Variable | Skilled, self-managing teams |
| Transformational | Moderate | High | Innovation, high-growth strategy |
| Transactional | Fast | Low | Performance-based tasks |
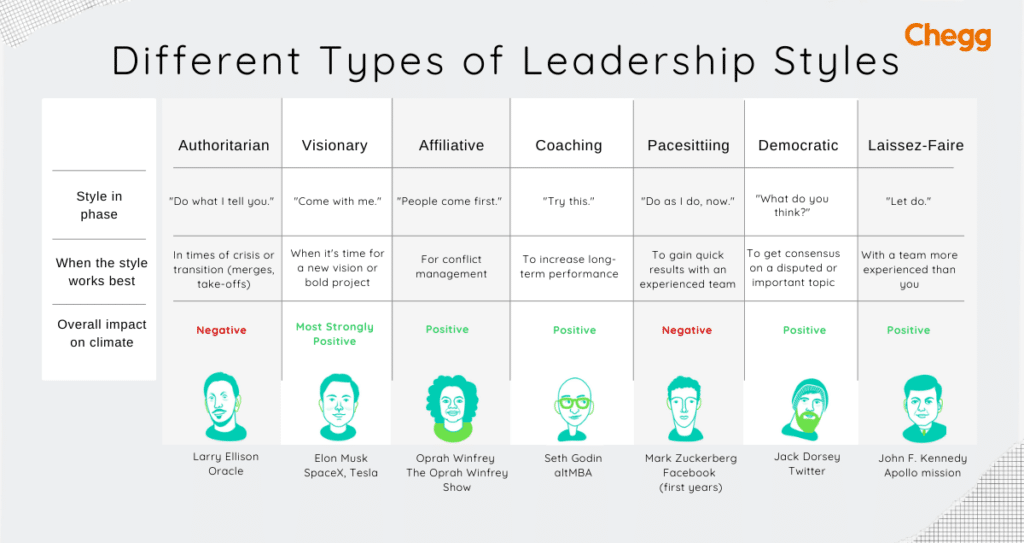
Authoritarian leaders make decisions independently, without input from others. They expect subordinates to follow orders without question. Larry Ellison, the co-founder of Oracle, exemplifies this style. Known for his decisive leadership and hands-on approach, Ellison drives his vision relentlessly, often taking bold actions with little consultation.
Visionary leaders inspire others with their long-term goals and clear vision for the future. Elon Musk, the CEO of Tesla and SpaceX, is a classic example. His ability to foresee the future of electric cars, space travel, and renewable energy has revolutionized industries and rallied teams around his bold ideas.
Affiliative leaders prioritize emotional connections and harmony within the team. Oprah Winfrey is a great example, with her empathetic and compassionate approach. She builds strong relationships with her team, fostering a supportive, trusting environment that encourages creativity and personal growth.
Coaching leaders focus on their employees’ personal and professional development, guiding them toward achieving their potential. Seth Godin, a renowned author and entrepreneur, embodies this style by mentoring others through his workshops, books, and blogs, encouraging people to think critically and develop their unique strengths.
Pacesetting leaders set high standards and lead by example, pushing their teams to meet demanding targets. Mark Zuckerberg, the founder of Facebook (Meta), is known for his fast-paced, high-expectation leadership. He pushes his teams to innovate rapidly, often pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
Democratic leadership is a collaborative approach where leaders seek input from their team before making decisions. While everyone contributes, the leader holds the final responsibility for decision-making.
Jack Dorsey, co-founder of Twitter, is known for his transparent and collaborative leadership style. He encourages open discussions, values team input, and empowers employees to take ownership of their work.
Laissez-faire leadership is a hands-off approach where leaders provide resources, tools, and guidance but allow team members to work independently. Employees are free to plan, organize, make decisions, and solve problems without constant supervision.
John F. Kennedy practiced laissez-faire leadership by trusting his advisors and cabinet members to manage their departments with minimal interference, relying on their expertise and decision-making abilities.
Autocratic leadership is the opposite of democratic leadership. In this approach, the leader makes all decisions without seeking input from the team. The leader holds complete authority, and employees are expected to follow orders without discussion.
Useful in emergencies where quick decisions are needed.
Works well when the leader has expert knowledge of the situation.
Suitable when team input is unnecessary for a successful outcome.
Although autocratic leadership is sometimes efficient, overuse can create a rigid and demotivating work environment.
Transformational leadership focuses on inspiring and motivating teams to exceed their limits and achieve more than they thought possible. These leaders push for continuous improvement, driving personal, professional, and organizational growth.
Transformational leadership is commonly seen in fast-growing organizations prioritizing innovation and pushing boundaries for long-term success.
Transactional leadership is a structured, short-term approach based on a clear exchange: employees perform their tasks in return for compensation. It follows a “give and take” system where rewards are given for meeting targets, making it common in sales and marketing roles.
While transactional leadership is effective for achieving short-term goals and maintaining order, it may not be suitable for environments that require flexibility and innovation.
Bureaucratic leadership follows strict policies, procedures, and regulations without flexibility. Leaders ensure that all tasks are completed according to set rules, and while employee input may be considered, it is often rejected if it does not align with organizational policies. This leadership style operates within a hierarchical structure where authority flows from top to bottom.
Bureaucratic leadership is most effective in well-established organizations where stability and risk management are prioritized over creativity and rapid change.
Servant leadership focuses on prioritizing the team’s needs over the leader’s own. A servant leader leads by example and helps team members grow, develop, and achieve success.
Coach-style leaders focus on developing individual strengths and helping team members grow through guidance and feedback. They foster long-term improvement by investing in professional and personal development.
Key Features:
Benefits:
Example: Leaders in education and startup incubators often use this style to nurture talent.
Charismatic leaders influence people through charm, communication, and confidence. They lead by vision and emotional connection, often becoming the face of the organization.
Key Features:
Benefits:
Challenges:
For example, Steve Jobs is a well-known charismatic leader.
Strategic leaders balance long-term vision with day-to-day operations. They align team efforts with organizational goals and often operate across multiple departments.
Key Features:
Benefits:
Example: Satya Nadella’s leadership at Microsoft embodies strategic thinking and transformation.
When It Works Best:
When It Doesn’t:
There is no single leadership style that works for every organization or situation. Effective leadership requires flexibility, and leaders may need to adapt their approach based on different circumstances. Understanding various leadership styles and their advantages and disadvantages is essential for making the right choice.
By considering these factors, leaders can choose the most effective leadership style or a combination of styles to support their team and organizational goals best.
Great leaders adjust their leadership style based on the situation, whether it’s workplace changes, organizational shifts, or evolving business needs. Awareness, adaptability, and understanding the impact of actions on others are key to effective leadership.
Adapting as Your Role Grows
Leadership needs to evolve with changing roles:
During Crisis:
During Growth or Innovation Phases:
Every leadership style has its time and workplace. The best leaders often adapt their approach depending on the situation and the people they lead. While one leadership style may work in high-pressure environments, a democratic or transformational style might be better for a creative or growth-focused organization. Understanding these leadership styles can help leaders and team members work better together to achieve their goals.
Ultimately, the best leaders are flexible, open to feedback, and willing to grow with their teams. Whether you’re leading a small group or a large company, finding the right style for the moment can make all the difference.

Ans. The most commonly used leadership styles include autocratic, democratic, laissez-faire, and transformational. Each style has its approach to decision-making, team management, and motivation, making them suitable for different situations and organizational needs.
Ans. The 4 C’s of leadership—competence, commitment, courage, and candour—are essential qualities for strong and effective leadership. These core values help leaders make informed decisions, stay dedicated to their goals, face challenges with confidence, and communicate with honesty at all levels.
Ans. A leadership style is how a leader guides, plans, and motivates a team. In 1939, psychologist Kurt Lewin identified three main styles: Autocratic (Authoritarian), Democratic (Participative), and Laissez-Faire (Delegative).
Ans. The seventh leadership principle emphasizes the importance of clear communication, proper supervision, and successful task completion.
Ans. The 4 Ps of leadership—perception, process, people, and projection—provide a framework that helps leaders consider both internal and external factors in their approach.

Authored by, Mansi Rawat
Career Guidance Expert
Mansi crafts content that makes learning engaging and accessible. For her, writing is more than just a profession—it’s a way to transform complex ideas into meaningful, relatable stories. She has written extensively on topics such as education, online teaching tools, and productivity. Whether she’s reading, observing, or striking up a conversation while waiting in line, she’s constantly discovering new narratives hidden in everyday moments.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.