

Quick Summary
Computer skills are abilities that allow you to use computers and digital technology to complete tasks. These skills range from basic to advanced. Basic skills include typing, using operating systems like Windows or macOS, browsing the internet, and using email and simple office software. Advanced skills can involve programming, graphic design, data analysis, network management, and cybersecurity.
There are several reasons why learning computer skills is essential for career growth. Perhaps the most obvious reason is that most jobs now require at least some level of computer literacy. In addition, learning computer skills can help you be more productive and efficient in your current position. So, if you want to improve your career prospects, learning computer skills is a great place to start.
Basic computer skills include opening and closing programs, navigating menus and windows, understanding file formats and extensions, and copying, pasting, and deleting files. Additionally, users should be familiar with using a web browser to surf the internet, including opening and closing tabs and navigating different websites.
For those who want to go beyond the basics, several intermediate and advanced computer skills can be learned, such as creating and formatting documents, using different software programs, and troubleshooting common computer issues.
In 2025, computer skills will be essential across nearly every industry due to the growing reliance on technology, automation, and AI tools. As businesses adopt AI-driven platforms, cloud-based tools, and advanced data systems, employees are expected to be digitally fluent. A baseline requirement is proficiency in tools like Microsoft Excel, Google Workspace, ChatGPT, Notion, and AI content generators.
With the rise of the hybrid work culture, strong computer skills enable seamless communication, remote collaboration, and digital productivity. From virtual meetings to cloud file sharing, tech-savvy professionals are better equipped to thrive. Moreover, job roles are evolving—even non-tech positions require digital literacy, making computer skills a key employability factor in today’s competitive job market.

Computer skills and tools are essential for anyone looking to enter or advance in the modern workforce. Basic computer proficiency skills for students include typing fast and accurately, basic understanding of standard software programs (such as word processors, spreadsheets, and presentation software), and being comfortable using the internet and email. Additionally, more advanced skills (such as coding, graphic design, and web development) can give individuals a competitive edge in the job market.
Basic computer skills are foundational to operating a computer or digital device. These include turning the computer on and off, understanding how to use a mouse and keyboard, and navigating the desktop or file system. For instance, users should be able to create, save, rename, or delete files and folders. Familiarity with file formats like .docx, .pdf, .jpg, and .xlsx is also essential. These skills form the base for more advanced computer operations.
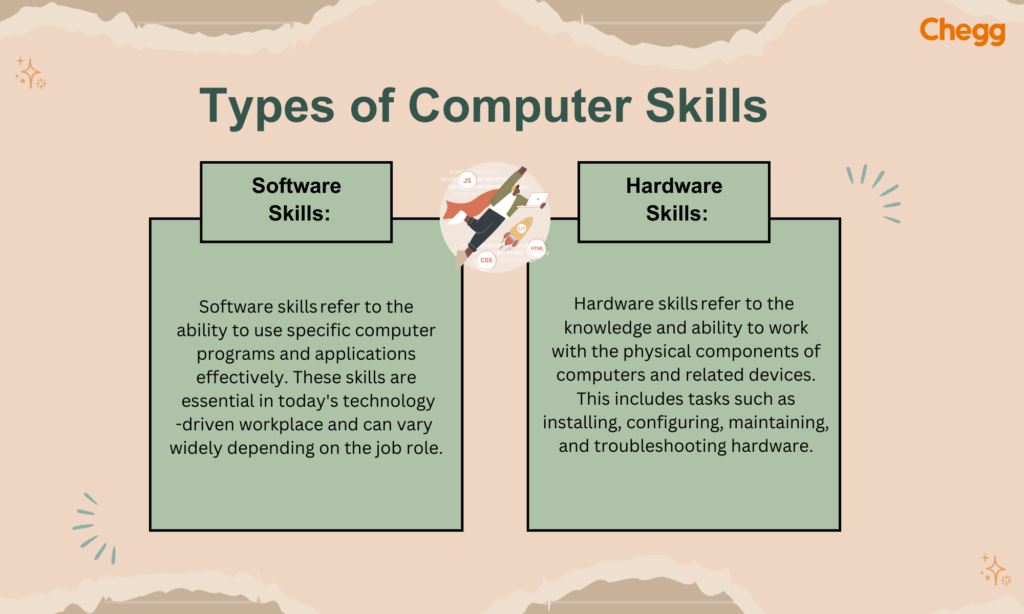
Software skills refer to the ability to use various programs and applications efficiently. In most workplaces, employees must work with productivity tools such as Microsoft Office (Word, Excel, PowerPoint) or Google Workspace (Docs, Sheets, Slides). Additionally, familiarity with communication tools like Slack, Zoom, or Microsoft Teams is often required. Software like Canva, Adobe Photoshop, or AI tools like Grammarly and ChatGPT are essential for content creation or design roles. Mastery of software tools improves efficiency and productivity in individual and collaborative tasks.
Hardware skills involve understanding and working with the physical components of a computer. While advanced tasks like motherboard replacement are typically for IT professionals, all users benefit from basic knowledge such as connecting a printer, installing a webcam, or troubleshooting hardware like a non-responsive mouse. Knowing how to handle cables, ports, and external storage devices also falls under this category. These skills help minimize dependency on technical support for everyday issues.
Using the internet and email effectively is crucial in the digital workplace. Internet skills include browsing with different search engines, using bookmarks, and conducting efficient online research. Email skills cover creating and managing email accounts, sending attachments, understanding email etiquette, and using tools like CC, BCC, and folders for organization. Familiarity with cloud storage (Google Drive, Dropbox) also enhances your ability to share and manage files online.
Operating system (OS) knowledge helps users interact smoothly with computer systems. Whether using Windows, macOS, or Linux, understanding basic OS functions—like file management, system settings, and installing or uninstalling software—is vital. For example, knowing how to use Windows Explorer or macOS Finder to locate files or change system preferences like time zones or printer settings is an expected skill in most professional environments.
Typing and word processing skills are core to most administrative or content-driven roles. Writing at 40+ words per minute (WPM) with accuracy saves time and enhances productivity. Using Microsoft Word or Google Docs to create and format reports, resumes, or letters is standard. Word processing tasks may include setting page layouts, inserting tables or images, and using spell check and grammar tools.
Spreadsheets are essential for data entry, tracking, and analysis. Proficiency in Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets includes creating formulas (SUM, AVERAGE), using functions (VLOOKUP, IF), and building charts and pivot tables. These skills are invaluable in finance, operations, and project management roles, where data needs to be visualized and interpreted.
Presentation software like PowerPoint or Google Slides is widely used for communicating ideas in meetings, webinars, and training sessions. Key skills include designing visually appealing slides, inserting animations or transitions, using charts and images effectively, and presenting in slideshow mode. The ability to convey information clearly and confidently through presentations is a valued skill in almost every profession.
Based on the job role and industry, the computer skills that hiring managers seek can differ. However, many computer skills are useful across all industries. Knowing these skills can help you secure a job more quickly. Here are some computer skills you should learn and master before your next interview:
Understanding office suites like G-suite and Microsoft Office is important for many daily activities, no matter your role. Word processors such as Google Docs and Microsoft Word allow you to create digital documents at work. Employers often expect applicants to be familiar with word processors, as this is a basic job requirement. You will rarely see these office suites mentioned in a job description.
If you are applying for a job in analytics, accounting, or any position that involves numbers, be skilled in spreadsheets like Google Sheets and Microsoft Excel. In addition, employers prefer candidates who are familiar with Outlook and other Microsoft Office tools.
For marketing, branding, and advertising, knowing how to use social media is an important skill. It helps grow an organization’s online presence. To stand out, you should demonstrate how you use your social media skills. For example, if you are a branding specialist, you might have increased your organization’s followers through a successful branding campaign. It’s also helpful to show your expertise with various social media tools.
Creating visually appealing designs for documents, presentations, and posters is crucial in many roles. From editing videos to modifying photos for international marketing campaigns, graphic design is one of the most in-demand computer skills. Familiarity with different graphic design software makes you a strong candidate for the job.
Knowing how to create presentations is an important skill that helps you share ideas internally and externally. Whether you are a financial analyst or a writer, mastering presentation software is key to thriving in your job. Microsoft PowerPoint is one of the most commonly used presentation tools across different industries.
Creating and maintaining software requires computer programming skills. These skills are vital for roles such as programmer, software developer, software tester, and software architect. Programming knowledge is also beneficial for technical writer positions because being able to code improves communication with the development and research teams. Some commonly used programming languages include HTML, Java, PHP, C++, C#, Automation software, XML, and Unix.
As many companies transition to remote work, communication and collaboration tools have become essential. These tools include video calls, chatting, and document sharing with teammates. If these skills are relevant to the job you’re applying for, list all the communication and collaboration tools you can use. Make sure to check the job description to see if you should include or leave out this computer skill.
Professionals in data entry roles must have speed, precision, and familiarity with structured systems. Key skills include:
Bonus Skill: Experience with AI-enhanced data entry tools that reduce manual repetition.
Graphic design requires a creative flair supported by technical tool mastery. The top computer efficiency skills include:
Bonus Skill: Familiarity with AI design generators (e.g., MidJourney, DALL·E).
Civil, mechanical, or software engineers need a firm grip on specialized software and systems.
Bonus Skill: Using version control tools like Git for collaboration on technical projects.
Digital marketing is tech-driven and data-heavy. The most important computer skills are:
Bonus Skill: AI content generation and automation (e.g., ChatGPT, Jasper, Zapier).
Educators in 2025 must be digitally literate to enhance virtual and hybrid learning environments.
Bonus Skill: Familiarity with AI teaching assistants or lesson planners.
This field demands analytical tools, precision, and data management capabilities.
Bonus Skill: Using AI-based forecasting or financial analysis tools.
You can showcase computer skills in any of the following areas:
Template Example:
Computer Skills
Example:
Professional Summary:
Tech-savvy marketing professional with 5+ years of experience in digital content creation and campaign execution. Proficient in Google Analytics, WordPress, Canva, and AI tools like ChatGPT. Strong command of Excel for data tracking and automation.
This shows how you’ve applied computer skills on the job.
Example:
Digital Marketing Executive – XYZ Pvt. Ltd.
Jan 2021 – Present
- Managed social media campaigns using Meta Business Suite and Hootsuite
- Analyzed weekly performance reports via Google Analytics and Excel
- Designed creatives on Canva and Adobe Illustrator
- Automated content planning with Notion and AI writing tools (Jasper, ChatGPT)
Support your resume with relevant training or credentials.
Example:
Certifications
Scan the job posting and match your skills with the tools mentioned. Use exact phrases where applicable, like:
Read More:
Here’s a list of common computer skills interview questions along with sample answers to help candidates prepare confidently:
Answer:
“I’m most comfortable using Microsoft Office Suite—especially Excel and PowerPoint. I also use Google Workspace daily for collaboration and Canva for quick design tasks.”
Answer:
“I’d say I’m at an intermediate to advanced level. I regularly use formulas, pivot tables, data sorting/filtering, and conditional formatting. I’ve also automated reports using simple macros.”
Answer:
“At my previous job, our monthly reports took hours to compile. I used Excel to automate calculations and created templates, reducing task time by over 60%.”
Answer:
“I’m very comfortable. I recently self-learned Notion for project management and adapted quickly by exploring tutorials and applying it in real tasks within a week.”
Answer:
“Yes, I regularly use Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Google Meet for virtual meetings. I’m familiar with features like screen sharing, chat, breakout rooms, and recordings.”
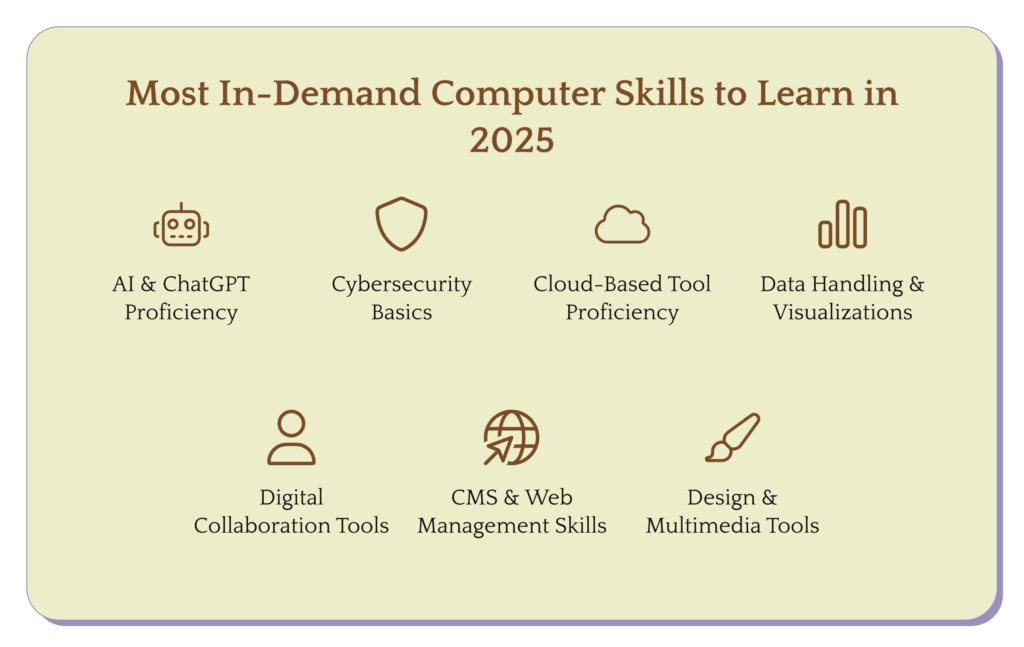
As technology evolves rapidly, employers in 2025 will prioritize candidates who can adapt to digital transformation, AI automation, cloud ecosystems, and data-centric operations. Here’s a breakdown of the most in-demand computer skills this year:
With AI now integrated into everyday workflows, familiarity with tools like ChatGPT, Jasper, Copy.ai, and other AI assistants is becoming essential.
In-Demand Roles: Content creators, marketers, virtual assistants, analysts, educators
With increasing data breaches and remote work vulnerabilities, basic cybersecurity awareness is necessary for all professionals—not just IT staff.
In-Demand Roles: All office-based roles, especially those handling sensitive data
Cloud ecosystems have become the backbone of hybrid and remote work culture.
In-Demand Roles: HR, marketing, operations, virtual assistants, freelancers
As data-driven decision-making becomes standard, even non-technical professionals are expected to work with data.
In-Demand Roles: Analysts, finance, HR, operations, sales
Companies want employees who can collaborate effectively in distributed teams.
In-Demand Roles: Team leads, remote professionals, consultants, educators
With online presence crucial, employers value basic knowledge of websites and content systems.
In-Demand Roles: Content writers, marketers, small business owners, bloggers
Visual communication is key in 2025—especially on social media and digital platforms.
In-Demand Roles: Designers, marketers, content creators, educators
Whether you need job-specific computer skills or just want to improve, there’s always more to learn. Explore university programs or try online platforms like Coursera, where you can find beginner courses like Introduction to Computers or Office Productivity Software.
Don’t just learn use what you learn. Try new tools like different word processors or manage your budget with Excel or Google Sheets. The more you practice, the faster you’ll improve.
Learning takes time. Some skills may be tough at first, but stay consistent. Every bit of effort adds up and will pay off in the long run.
Including your computer skills in your resume is important, but how you list them can make a difference. A great way to do this is by dividing your skills based on your proficiency level. Here’s how you can describe them effectively:
Beginner-level computer skills refer to basic knowledge of using a computer and common software programs. If you can use tools like Microsoft Word or Excel and manage emails, you fall under this category.
Examples of beginner-level computer skills:
Intermediate skills show that you are comfortable using more advanced tools and software. This may include working with design tools, presentations, or managing online content.
Examples of intermediate-level computer skills:
Advanced computer skills involve a high level of expertise. These may include programming, using advanced Excel functions, or developing applications.
Examples of advanced-level computer skills:
With the ever-evolving landscape of technology, keeping pace with the skills employers demand can be challenging. However, specific computer skills remain consistently valuable across industries. Among the most sought-after are data analysis, web development, software design, graphic design, and project management. Web development skills—such as creating and maintaining websites—are always in demand due to the growing digital presence of businesses.
Graphic design plays a key role in visual communication, while project management ensures effective team coordination and timely delivery. Data analysis is equally crucial in helping businesses make informed decisions. Employers specifically look for candidates skilled in tools like Microsoft Excel, SQL, and Tableau. Building expertise in these areas can significantly improve career prospects in today’s competitive job market.
Typing and Keyboard Use
Mouse or Touchpad Use
Operating System Basics
Internet and Web Browsing
Using Common Software
Example: Writing a document in Microsoft Word.
Tip: Use templates to save time and improve formatting.
Basic: Typing, email, file management
Office software: Word, Excel, PowerPoint
Communication: Zoom, Teams, Slack
Technical: Data analysis, basic troubleshooting
Design (if relevant): Photoshop, Canva
Tip: Customize your skills to match the job you want!
Basic Skills
Using a keyboard, mouse, email, and web browsing.
Software Skills
Using programs like Word, Excel, PowerPoint.
Technical Skills
Coding, troubleshooting, hardware knowledge.
Digital Communication Skills
Using tools like Zoom, Teams, and email platforms.
Creative Skills
Graphic design, video editing, and multimedia tools.
The best computer skill depends on your goals, but generally, proficiency in Microsoft Excel is highly valuable. It’s widely used in many jobs for data analysis, budgeting, and reporting.
If you’re aiming for tech roles, coding/programming skills (like Python) are top-tier.
Yes, basic computer skills are definitely considered a skill! They’re the essential abilities needed to use a computer effectively, like typing, using a mouse, navigating files, and browsing the internet.

Authored by, Mansi Rawat
Career Guidance Expert
Mansi crafts content that makes learning engaging and accessible. For her, writing is more than just a profession—it’s a way to transform complex ideas into meaningful, relatable stories. She has written extensively on topics such as education, online teaching tools, and productivity. Whether she’s reading, observing, or striking up a conversation while waiting in line, she’s constantly discovering new narratives hidden in everyday moments.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.