Table of Contents
PWD’s full form is Public Works Department. It’s a part of the Government of India and takes care of public infrastructure like roads, bridges, and water systems. PWD also makes sure towns have safe drinking water and fixes broken pipelines in government projects. It works closely with CPWD, a major organization. Good roads help people travel easily and boost the economy. Construction work is important for transportation and other needs. PWD aims to design and maintain public services effectively.
PWD full form in Hindi
In Hindi PWD full form can mean two things, depending on where it is being used:
1. लोक निर्माण विभाग (पीडब्ल्यूडी) (Lok Nirman Vibhag) .
2. अपंग व्यक्ति (पर्सन विद डिसएबिलिटी) (Person With Disability).
Core Functions of PWD
The Public Works Department (PWD) is made up of four branches:
- Construction and Maintenance,
- Water Supply and Sanitation,
- Public Transportation, and
- Disaster Management and Emergency Response.
PWD’s Work Main Categories in Detail
PWD’s work can be divided into four main categories let’s see them in detail:
- Construction and Maintenance: PWD oversees the construction and maintenance of public infrastructure such as roads, bridges, highways, and government buildings. This involves planning, designing, and executing construction projects, as well as regular upkeep and repairs to ensure safety and functionality.
- Water Supply and Sanitation: PWD is responsible for ensuring access to clean water and proper sanitation facilities in communities. This includes managing water treatment plants, distribution networks, sewage systems, and implementing measures for water conservation and pollution control.
- Public Transportation: PWD plays a role in developing and maintaining public transportation systems such as buses, trains, and tramways. This involves planning routes, managing schedules, maintaining vehicles and infrastructure, and ensuring accessibility for all passengers, including those with disabilities.
- Disaster Management and Emergency Response: PWD is involved in disaster preparedness, response, and recovery efforts. This includes developing evacuation plans, setting up emergency shelters, providing relief supplies, and repairing infrastructure damaged by natural disasters such as floods, earthquakes, and cyclones.
History of PWD
The Public Works Department (PWD full form) has a long history of building and maintaining infrastructure like roads, bridges, and buildings. Here’s a simple overview of how PWDs have evolved over time:
Ancient and Medieval Times
1. Ancient Civilizations:
- Early Examples: Long ago, ancient societies like those in Mesopotamia, Egypt, Greece, and Rome built large public projects.
- Roman Empire: The Romans were especially good at this, constructing roads, aqueducts (water channels), and public buildings that were very advanced for their time.
2. Medieval Period:
- Local Management: During the Middle Ages, local lords or religious groups often managed public works.
- Common Projects: They built castles, cathedrals, and systems for irrigation to help water crops.
Colonial Era
3. British Rule in India:
- Start of PWD: In the mid-1800s, the British established formal Public Works Departments in their colonies, including India. They needed good infrastructure for administration, trade, and resource extraction.
- Military Board’s Works Department: In the 1850s, the East India Company set up a department to manage engineering projects, which was reorganized in 1854 by Lord Dalhousie to create the PWD.
- Expansion in the 1860s: After the British Crown took control from the East India Company, the PWD’s responsibilities grew to include all sorts of civil engineering projects like building roads and canals.
Post-Colonial Period
4. After Independence in India (1947):
- Growth of PWD: India kept and expanded its PWD after gaining independence. The department became very important in planning and building public infrastructure across the country.
Modern Era
5. Global Presence:
- Other Countries: Similar departments exist worldwide. For example, in the United States, local and state governments manage public works. In the UK, local councils and agencies handle these tasks.
6. Today’s PWDs:
- Expanded Roles: Modern PWDs don’t just build and maintain roads and bridges. They also focus on urban development, environmental care, disaster response, and using new technology.
- Advanced Practices: They use advanced project management, sustainable practices, and work closely with communities to make sure infrastructure projects meet current needs.
Responsibilities of PWD
The responsibilities of the Public Works Department (PWD full form) encompass a wide range of crucial tasks aimed at ensuring the development, maintenance, and sustainability of public infrastructure. Here’s an overview of some key responsibilities typically undertaken by PWDs:
- Developing and maintaining infrastructure like roads and bridges.
- Ensuring the upkeep of government buildings and public facilities.
- Managing water resources and environmental conservation efforts.
- Responding to disasters and coordinating relief operations.
- Enhancing public safety and accessibility.
- Managing traffic flow and congestion in urban areas.
- Budgeting, procurement, and financial management for projects.
Organizational Structure of PWD
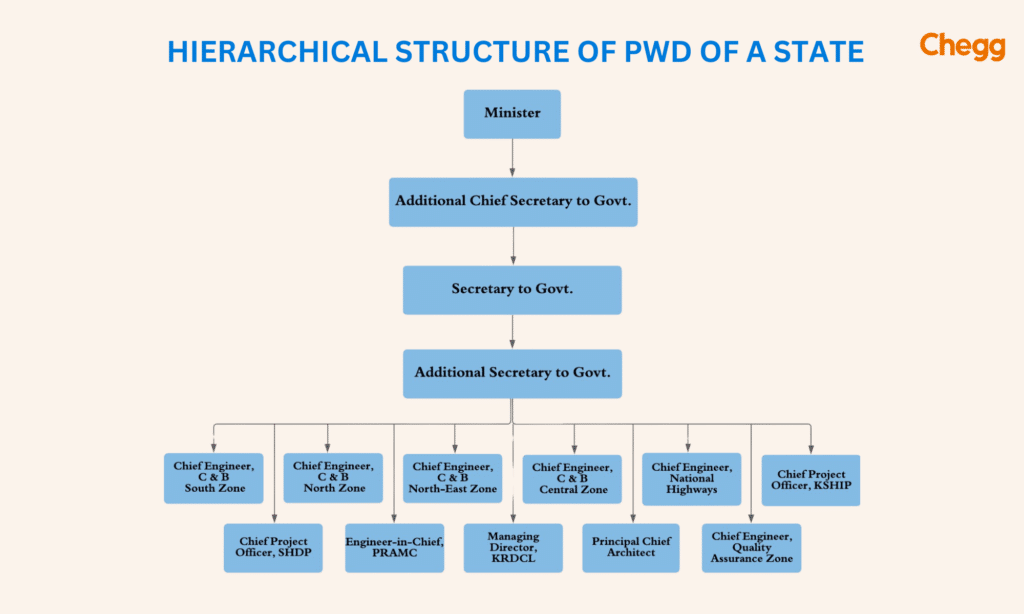
The Public Works Department (PWD full form) plays a crucial role in building and maintaining public infrastructure like roads, bridges, and buildings. While the structure of PWDs can vary slightly depending on the state or region, here’s a general look at how they are organized:
1. Ministerial Head:
- Role: The PWD is usually headed by a government minister or cabinet member.
- Duties: This person is in charge of setting policies and deciding the budget for the PWD.
2. Administrative Head:
- Role: An administrative head, often called the Principal Secretary or Chief Secretary, manages the PWD’s daily operations.
- Duties: They ensure that the department follows government rules and policies.
3. Engineering Wing:
- Role: This is the technical core of the PWD, responsible for designing, building, and maintaining public infrastructure.
- Leadership:
- Chief Engineer: The top engineer who oversees all technical work.
- Superintending Engineers: They manage large areas called circles or zones within the state.
- Executive Engineers: They handle smaller divisions within these circles.
- Assistant Engineers: They work on specific projects and supervise construction activities.
4. Other Departments:
- Accounts Department: Handles the PWD’s money, including budgeting and spending.
- Stores and Purchase Department: Buys materials and equipment needed for construction.
- Town Planning Department: Focuses on planning urban areas and managing land use.
- Estates Department: Takes care of government buildings and properties.
5. Field Staff:
- Roles: These are the people who do the actual work on the ground.
- Examples: Surveyors, draftsmen, mechanics, inspectors, and laborers.
Importance of Organizational Structure:
- Clear Responsibilities: Each level knows what they are responsible for, making the work more efficient.
- Better Coordination: Different departments can work together smoothly.
- Effective Communication: Information flows easily up and down the hierarchy.
This simplified structure helps everyone understand their role in building and maintaining essential infrastructure in their community.
Infrastructure Planning and Development of PWD
The Public Works Department (PWD full form) plays a vital role in building and maintaining public infrastructure in India. Let’s break down how they plan and develop these important projects:
Planning Process
1. Identifying Needs:
PWD works with local authorities to understand what infrastructure is needed. They look at things like population growth, economic activities, and existing infrastructure. This could mean identifying the need for new roads, better water supply, or improved sanitation facilities.
2. Feasibility Studies:
PWD conducts studies to see if the proposed projects are possible and practical. Key Factors Considered:
- Costs: How much will the project cost, and where will the money come from?
- Land: Is there enough land, and how will it be acquired?
- Environment: What impact will the project have on the environment?
- Community: How will the project affect local people, and will it disrupt their lives?
- Sustainability: Can the project use eco-friendly materials and designs?
3. Project Design and Budgeting:
PWD creates detailed plans and budgets for how the project will be built. It includes Technical details, materials needed, construction methods, timelines, and costs.
4. Stakeholder Consultation:
PWD talks to people who will be affected by the project, including community members and local businesses. This ensures the project meets community needs and reduces disruption.
5. Approval and Procurement:
PWD submits the project plans and budgets for approval by government authorities. Once approved, they invite bids from contractors to build the project, ensuring a fair and open selection process.
Development and Construction
1. Contract Award and Mobilization:
PWD awards the contract to the best bidder. The contractor then gathers all resources and prepares to start construction.
2. Project Monitoring and Quality Control:
PWD engineers and inspectors regularly check on the construction progress. They make sure everything is built according to the plans, maintaining high quality and safety standards.
3. Environmental and Social Safeguards:
PWD implements measures to protect the environment and minimize disruptions during construction. This could include controlling dust, managing waste, and ensuring fair treatment of workers.
4. Project Completion and Handover:
PWD conducts final inspections to confirm the project is complete and meets all standards. Once everything is in order, the project is handed over to the authorities who will operate and maintain it.
PWD is essential in planning and developing infrastructure, ensuring that projects are well-designed, well-built, and beneficial to the community.
Project Management in PWD
The Public Works Department (PWD full form) shoulders a crucial responsibility: managing India’s infrastructure. This encompasses a vast array of technical and operational aspects, including buildings, machinery, regulations, data, and software.
The Importance of Infrastructure:
Sound infrastructure is the backbone of essential services like clean water delivery, sanitation, and waste disposal. Efficient PWD management directly translates to better public services. Improved efficiency, enhanced safety, reduced environmental impact, and ultimately, more effective delivery of public goods are just some of the immediate benefits.
Challenges of PWD Project Management:
Navigating public works projects requires the PWD to address several key issues:
- Cost Control: Keeping projects within budget is paramount.
- Scheduling: Meeting deadlines ensures timely completion of vital infrastructure.
- Procurement: Obtaining the necessary materials and services efficiently is crucial.
- Risk Assessment: Identifying and mitigating potential problems protects project success.
Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation:
The PWD doesn’t stop at project completion. Continuous monitoring and evaluation play a vital role in ensuring:
- Desired Outcomes: Are the completed projects meeting the intended goals?
- Execution Efficiency: Are there areas for improvement in project execution?
- Unexpected Outcomes: Are there any unforeseen consequences that need to be addressed?
By implementing these practices, the PWD can ensure the safety and functionality of public infrastructure, ultimately serving the community better.
PWD Jobs in India
The Public Works Department (PWD full form) is a key government agency in India. They are responsible for building and maintaining important infrastructure like roads, bridges, and buildings. Working in PWD offers a chance to be part of projects that help develop the country. Here are some of the main job roles in PWD:
1. Civil Engineers
- What They Do: Civil engineers design and oversee construction projects such as roads, bridges, and buildings.
- Key Tasks:
- Drawing up plans and designs for infrastructure projects.
- Preparing cost estimates and project schedules.
- Supervising construction work to ensure it meets quality standards.
- Conducting site inspections to ensure safety and compliance.
2. Architects
- What They Do: Architects design buildings and public spaces, focusing on both aesthetics and functionality.
- Key Tasks:
- Creating detailed drawings and blueprints for new buildings.
- Selecting materials and specifying construction methods.
- Working with engineers to make sure designs are practical and safe.
- Overseeing the architectural aspects of construction projects.
3. Quantity Surveyors
- What They Do: Quantity surveyors estimate costs and manage the budget for construction projects.
- Key Tasks:
- Preparing lists of materials needed for projects.
- Estimating the total cost of projects, including materials and labor.
- Keeping track of spending and making sure projects stay within budget.
4. Town Planners
- What They Do: Town planners develop plans for the growth and development of urban areas.
- Key Tasks:
- Creating master plans for cities and towns.
- Zoning land for different uses like housing, businesses, and parks.
- Designing transportation systems and public spaces.
- Ensuring that town planning rules are followed.
5. Project Management Professionals
- What They Do: Project managers oversee all aspects of infrastructure projects from start to finish.
- Key Tasks:
- Planning project timelines and tasks.
- Managing resources like money, materials, and workers.
- Monitoring project progress and solving any problems that come up.
- Ensuring projects are completed on time and meet quality standards.
Other PWD Job Roles
PWDs also offer roles like:
- Surveyors: Measure and map land areas for construction.
- Geo-technical Engineers: Analyze soil and rock for construction suitability.
- Electrical Engineers: Design and maintain electrical systems in buildings and infrastructure.
- Mechanical Engineers: Work on systems involving machines and equipment.
- Public Works Inspectors: Ensure that construction work complies with regulations.
- Draftsmen: Create detailed technical drawings and plans.
- Data Entry Operators: Handle data management and record-keeping.
- Stenographers: Assist with administrative tasks and note-taking.
- Accounts Assistants: Manage financial records and budgeting.
How to Find PWD Jobs in India
- Government Websites: Check the official websites of Central and State PWDs for job announcements.
- Employment Portals: Visit job sites like Naukri.com, Indeed, and Monster India for PWD job listings.
- Newspapers: Look for job advertisements in local newspapers.
- Recruitment Agencies: Some agencies specialize in government job placements, including PWD positions.
PWD jobs provide a stable and rewarding career, contributing to the nation’s infrastructure. Each role has specific requirements, so make sure to read job descriptions carefully before applying.
Salary in PWD
If you’re thinking about working in the Public Works Department (PWD), here’s what you can expect in terms of salary:
1. Starting Salary:
- First Job: When you start your job at PWD, your salary might be around ₹56,100 per month. This is based on the central government’s 7th Pay Commission.
- Comparison: Think of this as a very generous allowance or pocket money you get for your hard work!
2. Total Earnings:
- Extra Bonuses: Besides the basic salary, PWD employees get extra money called “allowances.” These are like bonuses and can include:
- Housing Allowance: Money to help pay for your home.
- Travel Allowance: Money for travel expenses.
- Medical Allowance: Sometimes, money for healthcare costs.
- Combined Income: These allowances make your total monthly earnings higher than just your base pay.
Also read: How to Calculate HRA in Salary: Simplified Calculation
3. Overall Salary Range:
- Starting Out: When you add up the basic salary and allowances, a new PWD employee might earn between ₹60,000 to ₹85,000 per month.
- Variation: The exact amount can change depending on the specific state, your position, and the pay structure of the PWD.
So, working in PWD not only gives you a stable income but also additional benefits that boost your overall earnings!
Advantages & Disadvantages of PWD
Advantages of PWD (Public Works Department)
- Stronger Infrastructure: PWD builds and maintains roads, bridges, buildings, and other things we use every day. This makes our communities stronger and more connected.
- Improved Transportation: Good roads and bridges mean it’s easier and faster to get around. This helps businesses operate smoothly and helps people get where they need to go.
- Creates Jobs: PWD projects require a lot of workers for construction and maintenance. This creates jobs for people in the community.
- Boosts Safety: PWD works on road safety by adding signs, signals, and flyovers. This helps keep people safe on the roads.
Disadvantages of PWD (Public Works Department)
- Can Be Slow: Sometimes, PWD projects can take a long time to get finished. This can be frustrating for people who are waiting for new roads or buildings.
- Budget Issues: There might not always be enough money to build everything that’s needed. This can lead to delays or projects being put on hold.
- Environmental Impact: Building new roads and infrastructure can sometimes have a negative impact on the environment. PWD needs to consider these effects and try to minimize them.
- Political interference: Politicians keep getting involved in these projects. Their involvement leads to delays in starting the project. Sometimes, the project even gets stopped by them.
- Corruption Risk: Like any big organization, there’s a chance of corruption in PWD projects. This can lead to wasted money and poor-quality construction.
Overall, PWD plays a vital role in building and maintaining our communities. However, it’s important to be aware of both the benefits and drawbacks of their work.
PWD Full Form in Different Contexts
PWD Full Form in Medical / PWD Full Form in Exam / PWD Full Form in Reservation
In the medical/academic/competitive exams/reservation policies context, PWD stands for “Persons With Disabilities.”
PWD Full Form in Government / PWD Full Form in Civil Engineering
In governmental settings / civil engineering, PWD stands for “Public Works Department.”
PWD Full Form in Salary
In certain contexts, particularly in military or defence sectors, PWD could stand for “Pay While Deployed.”
PWD Full Form: Key Takeaways
- PWD stands for Public Works Department, managing vital infrastructure projects.
- PWD follows a hierarchical model for efficient coordination.
- Technical wings handle specific areas like roads, buildings, and irrigation.
- Development Process:
- Identification and feasibility studies
- Planning, design, and approvals
- Tendering, execution, and quality control
- Completion, handover, and maintenance
- PWD works with government agencies, contractors, and communities.
- PWD’s work boosts economic growth and enhances citizens’ quality of life.
Learn about some other full form:
| FBI Full Form | CDPO Full Form |
| UIDAI Full Form | FSSAI Full Form |
| LDC Full Form | DGP Full Form |
| PMJJBY Full Form | MLA Full Form |
| ESI Full Form | TRAI Full Form |
Ready to learn more? Click on the below button to get the complete list of Full Forms!
PWD Full Form: FAQs
What is PWD full form?
PWD Full Form: Public Works Department.
Who is the founder of Indian PWD?
Lord Dalhousie founded the Public Health Department in India.
Does the Public work department work under the Central government?
Every state has its own department of public works. The CPWD, which stands for Central Public Work Department, works under the central government.
What is the highest post in a PWD office?
The Director General, also the Chief Technical Advisor of the Indian government, has the highest post in the public work department in India.
What is the full form of PWD salary?
The full form of PWD salary is Pay While Deployed, it is usually used in the military or defence sectors.
What is meant by PWD in civil engineering?
Public Works Department is referred to as PWD. Infrastructure plays a crucial role in the public and government domains. Building roads and bridges, like all other civil projects, needs to be organized and meticulous. The Public Works Department (PWD) is in charge of numerous government initiatives as a result.
What is the full form of PWD in road?
“Public Works Department.” Manages road construction and maintenance.
What is the full form of PDW in government?
State Public Works Department (PWD) by Ministry of Road Transport & Highways, Government of India.
What is the full form of PWD in exam eligibility?
“PWD” in exam eligibility stands for “Person with Disability” on government tests. Those who struggle to perform daily tasks due to a physical or mental health issue are referred to by this phrase.
Got a question on this topic?
