Table of Contents
LDC full form Explained
LDC full form is lower division clerks. The LDC is an important position within government institutions. It falls under the category of Group C (or sometimes Group D, depending on the country and specific organization) in government job classifications.
Keep reading if you wish to know about the LDC full form, the various exams, and the qualifications to join the government with this position. OR If you’re considering an LDC post, here’s a comprehensive guide to equip you with all the essentials.
LDC Full Form in Hindi
LDC ka Full Form in Hindi is “लोअर डिवीजन क्लर्क” (Lower Division Clerk).
What is LDC?
Now you wondering what is LDC job? So a Lower Division Clerk (LDC full form) is an entry-level clerical position commonly found in various administrative setups, government organizations, and even private companies. They are the backbone of many administrative functions, ensuring smooth day-to-day operations.
Role and Responsibilities of LDC
LDCs, also known as clerical staff, play a vital role in keeping an organization running smoothly. Here’s why they matter:
1. Helping with Paperwork
LDCs handle paperwork like forms, records, and files. They make sure everything is organized and easy to find.
2. Being the Communication Hub:
When someone calls the office or sends an email, LDCs are the ones who connect them to the right person. They help keep everyone informed.
3. Keeping Records Straight
LDCs update employee records, track attendance, and manage databases. Accurate data helps the organization function well.
4. Supporting Office Coordination
Need to schedule a meeting or set up an event? LDCs help with that. They make sure things happen on time.
5. Following Rules
LDCs help the organization follow its rules and policies. They keep track of deadlines and make sure everyone is doing things the right way.
LDCs are like the behind-the-scenes heroes who make sure everything runs smoothly in an organization!
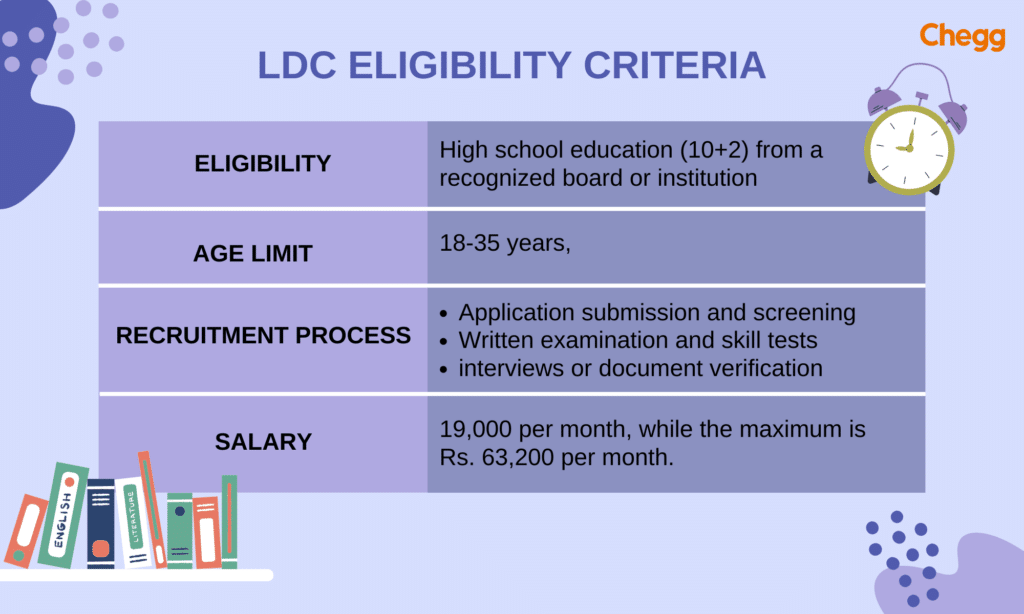
Eligibility Criteria for LDC
Here are the following criteria you need to fulfill if you wish to apply for the LDC post:
1. Educational Qualifications
To become an LDC, the candidate must meet specific requirements. If you wish to apply for the position of an LDC, then you must have completed your high school education (10+2) from a recognized board or institution.
2. Age limit and relaxation criteria
- Age Limit: Applicants must be between 18 and 35 years old, with variations for different categories.
- Relaxation Criteria: Relaxation in age limits is provided for certain categories, such as 10 years for women, 5 years for men, and 10 years for people with disabilities, as per government norms.
3. Typing Proficiency
For aspiring Lower Division Clerks (LDCs), meeting the minimum typing speed criteria of 35 WPM in English and 30 WPM in Hindi (or other regional languages as applicable) is essential.
Recruitment Process of LDC
Landing an LDC (Lower Division Clerk) job often involves a multi-stage recruitment process. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Application: Apply online through the official portal of the recruiting organization.
- Eligibility Screening: Your application is screened to ensure you meet the minimum qualifications.
- Written Exam: If shortlisted, you’ll appear for a computer-based test with objective-type questions (refer to our guide on LDC Exam Pattern for details).
- Skill Test (Optional): Some exams may include a skill test to assess typing speed and accuracy.
- Document Verification: Submit and verify your educational certificates, caste certificates (if applicable), and other required documents.
- Selection/Appointment: Based on your performance, you may be selected for the LDC position and receive an appointment letter.
This is a general framework. Specific timelines, stages, and selection criteria can vary depending on the recruiting body
Click her to get the: LDC Form
Examination Pattern for LDC
The examination pattern for Lower Division Clerks (LDC full form) varies depending on the recruiting organization. Let’s explore the patterns for a few notable LDC exams:
Written Examination:
- Subjects: It usually includes sections on General Intelligence, English Language, Numerical Aptitude, and General Awareness.
- Type of Questions: Questions are multiple-choice, with four options to choose from.
- Duration: The exam lasts for 2 to 3 hours.
- Total Marks: The written exam is usually out of 100 or 200 marks.
Typing Test:
- Candidates must pass a typing test to check their typing speed and accuracy.
- Speed: You’ll need to type around 30 to 40 words per minute (wpm).
- Duration: The typing test usually takes about 10 minutes.
- Language: You may have to type in English or the regional language required for the job.
Understanding this pattern and practicing regularly can help you prepare well for the LDC exam.
Skills and Qualities for LDC
1. Proficiency in computer applications
Proficiency in computer applications is crucial for the position of an LDC. As we know, the LDC full form is lower division clerk. They work with office software for data entry and record keeping.
2. Typing speed and accuracy
A good typing speed with accuracy is essential for efficient data entry. This will also help reduce the time taken while working; thus, the LDC can complete more work.
3. Organizational and time management skills
Strong organizational and time management skills help them handle multiple tasks and maintain orderly records.
4. Attention to detail and multitasking abilities
Attention to detail is vital to ensure accuracy in maintaining files and documents. LDCs must possess multitasking abilities to handle various administrative tasks. Effective communication and interpersonal skills enable them to interact with colleagues and visitors professionally.
Popular Entrance Exams for LDC
Here are some of the popular entrance exams for the position of Lower Division Clerk (LDC) in various organizations:
| Exam Name | Conducting Body | Eligibility Criteria | Selection Process | Exam Pattern |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSC CHSL (Combined Higher Secondary Level) | Staff Selection Commission (SSC) | 12th Pass or equivalent | Tier-I: Computer-Based Exam Tier-II: Descriptive Paper Tier-III: Typing Test | Tier-I: Objective Type (General Intelligence, English, Quantitative Aptitude, General Awareness). Tier-II: Descriptive Paper (Essay/Letter Writing). Tier-III: Skill Test/Typing Test. |
| IBPS Clerk | Institute of Banking Personnel Selection | Graduate in any discipline | Prelims Exam Main Exam Language Proficiency Test | Prelims: English Language, Numerical Ability, Reasoning Ability. Mains: General/Financial Awareness, General English, Reasoning Ability & Computer Aptitude, Quantitative Aptitude. |
| RRB LDC | Railway Recruitment Board | 12th Pass with a minimum of 50% marks | Computer-Based Test (CBT) Document Verification Medical Examination | CBT: General Awareness, Mathematics, General Intelligence and Reasoning. |
| ESIC UDC (Upper Division Clerk) | Employees’ State Insurance Corporation | Graduate in any discipline | Prelims Exam Mains Exam Computer Skill Test | Prelims: General Intelligence and Reasoning, General Awareness, Quantitative Aptitude, English Comprehension. Mains: General Intelligence and Reasoning, General Awareness, Quantitative Aptitude, English Comprehension. Computer Skill Test. |
| DSSSB LDC | Delhi Subordinate Services Selection Board | 12th Pass or equivalent | One-Tier Exam Typing Test | One-Tier Exam: General Awareness, General Intelligence & Reasoning Ability, Arithmetical & Numerical Ability, Hindi Language & Comprehension, English Language & Comprehension |
| High Court Clerk Exams | Various State High Courts | 12th Pass or Graduate, depending on the specific court’s requirements | Written Exam Typing Test | Varies by court, typically includes General Knowledge, English. Typing Test. |
These exams share common eligibility criteria and selection processes but differ in specific patterns and conducting bodies. It’s important for candidates to check the specific requirements and patterns for the exams they are interested in, as they can vary slightly by organization and year.
Salary Structure of LDC
The salary structure of a Lower Division Clerk (LDC full form) can vary depending on factors such as the employer (government or private sector), location, experience, and qualifications. However, here’s a general overview of the salary structure of LDCs in government organizations in India:
Government Sector (India)
- Pay Scale: LDCs are usually placed in Pay Band 1 (PB-1) or Pay Level 2.
- Basic Pay: LDCs typically earn between ₹19,900 to ₹63,200 per month, depending on their level and where they work.
- Grade Pay: Some LDCs may also get extra pay called grade pay.
- Allowances: LDCs get various allowances like
- Dearness Allowance (DA),
- House Rent Allowance (HRA), and
- Transport Allowance (TA).
- Growth Opportunities: LDCs can move up to higher positions like Upper Division Clerk (UDC) with experience and by passing departmental exams.
Private Sector (Varies)
- In private companies, LDC salaries differ a lot based on the
- company,
- industry,
- location, and
- negotiation.
- Generally, private LDCs may earn similar to or slightly more than government LDCs, along with extra benefits depending on company rules.
Career Growth in LDC
Lower Division Clerk (LDC full form) are vital for government tasks, and knowing their career path is crucial for those interested. Here’s how their career typically progresses:
1. Initial Appointment:
- LDC Position: After qualifying through competitive exams, candidates are appointed as LDCs.
- Pay Scale: The initial pay scale varies based on the organization and location.
2. Promotions and Upgrades:
- Promotion to Upper Division Clerk (UDC):
- LDCs can be promoted to UDCs based on their performance, seniority, and vacancies.
- UDCs handle more complex tasks and have higher responsibilities.
- Pay Scale: UDCs receive a salary starting around ₹25,500 per month better than LDCs.
- Departmental Exams and Merit-Based Promotions:
- Some government departments conduct departmental exams for LDCs.
- Clearing these exams can lead to promotions to higher positions.
- Time-Bound Promotions:
- LDCs may receive time-bound promotions based on their years of service.
- These promotions occur automatically without the need for additional exams.
3. Further Progression:
- Assistant Section Officer (ASO):
- ASOs are part of the Central Secretariat Services (CSS) or other central government departments.
- They handle more significant responsibilities and have better pay.
- Section Officer (SO):
- SOs supervise ASOs and manage administrative tasks.
- They play a crucial role in decision-making.
- Under Secretary and Beyond:
- With experience and performance, LDCs can progress to Under Secretary, Deputy Secretary, and even higher positions.
- These roles involve policy formulation, coordination, and management.
LDCs have a clear career path with chances to grow. Hard work, learning, and adaptability are key to moving up. Whether aiming for ASO, SO, or higher roles, focus on improving skills and contributing to your organization’s success.
Benefits and Challenges of LDC
Lower Division Clerks (LDC full form) have important roles in government offices. Like any job, there are both benefits and challenges. Knowing these can help you decide if this job is right for you.
Benefits of LDC:
- Job Security:
- LDC jobs in government are very stable. There is less risk of losing your job suddenly compared to private jobs.
- LDC jobs in government are very stable. There is less risk of losing your job suddenly compared to private jobs.
- Steady Income:
- LDCs get a regular and steady paycheck. While the pay might vary, it ensures a consistent income.
- LDCs get a regular and steady paycheck. While the pay might vary, it ensures a consistent income.
- Allowances and Perks:
- Besides the salary, LDCs get various allowances like Dearness Allowance (DA), House Rent Allowance (HRA), and Transport Allowance (TA). These add to the overall pay.
- Besides the salary, LDCs get various allowances like Dearness Allowance (DA), House Rent Allowance (HRA), and Transport Allowance (TA). These add to the overall pay.
- Promotion and Career Growth:
- There are clear paths for moving up. LDCs can get promoted to Upper Division Clerks (UDC) and other higher positions based on their work and exams.
- There are clear paths for moving up. LDCs can get promoted to Upper Division Clerks (UDC) and other higher positions based on their work and exams.
- Work-Life Balance:
- Government jobs, including LDC roles, often have better work-life balance compared to many private jobs. There are fixed working hours and holidays.
- Government jobs, including LDC roles, often have better work-life balance compared to many private jobs. There are fixed working hours and holidays.
- Pension and Retirement Benefits:
- Government employees, including LDCs, often get pensions and other benefits after retirement, ensuring financial security.
- Government employees, including LDCs, often get pensions and other benefits after retirement, ensuring financial security.
- Additional Benefits:
- LDCs might also get other benefits like medical facilities, housing loans, and education allowances for their children.
Challenges of LDC:
- Workload and Deadlines:
- LDCs handle a lot of paperwork and data entry, leading to a heavy workload, especially during busy times. Meeting strict deadlines can be stressful.
- LDCs handle a lot of paperwork and data entry, leading to a heavy workload, especially during busy times. Meeting strict deadlines can be stressful.
- Monotony of Tasks:
- The work can be repetitive, such as filing, data entry, and managing records. This can get boring over time.
- The work can be repetitive, such as filing, data entry, and managing records. This can get boring over time.
- Technological Adaptation:
- With the rise of technology, LDCs need to keep updating their computer skills and learn new software.
- With the rise of technology, LDCs need to keep updating their computer skills and learn new software.
- Accuracy and Attention to Detail:
- The job requires high accuracy and attention to detail to avoid mistakes, which can be mentally tiring.
- The job requires high accuracy and attention to detail to avoid mistakes, which can be mentally tiring.
- Limited Decision-Making Authority:
- LDCs usually have to follow instructions from higher officials and have little decision-making power, which can be frustrating for those wanting more control.
- LDCs usually have to follow instructions from higher officials and have little decision-making power, which can be frustrating for those wanting more control.
- Work-Life Balance:
- Depending on the department and workload, it can be hard to maintain a good work-life balance, especially when extra hours are needed to meet deadlines.
- Depending on the department and workload, it can be hard to maintain a good work-life balance, especially when extra hours are needed to meet deadlines.
- Limited Career Mobility:
- While there are promotion opportunities, the process can be slow and competitive, sometimes leading to frustration.
Being an LDC has both good and bad points. Knowing these aspects can help you prepare for and succeed in an LDC career.
LDC Full Form in Different Context
LDC has multiple full forms, depending on the context. Here are some common interpretations:
LDC Full Form in Salary
- In the context of salary, LDC stands for “Lower Division Clerk.” Lower Division Clerks are administrative personnel responsible for clerical tasks such as record-keeping, data entry, and administrative support functions. The salary of an LDC varies depending on factors such as experience, organization, and location.
LDC Full Form in Economics
- In economics, LDC can refer to “Less Developed Country.” Less Developed Countries are nations characterized by lower levels of industrialization, income per capita, and standards of living compared to more developed counterparts.
LDC Full Form in Government Job
- In the context of government jobs, LDC typically refers to “Lower Division Clerk,” as mentioned earlier. Government organizations often recruit LDCs for various administrative roles that require clerical support and record maintenance.
LDC Full Form in School
- In the educational context, LDC may stand for “Learning and Development Centre” or “Learning Disability Coordinator,” depending on the institution’s focus and requirements.
LDC Full Form in Medical
- In medical contexts, LDC could represent various terms such as “Lymphocyte Depletion Condition” or “Low-Dose Chemotherapy,” depending on the specific medical condition or treatment being discussed.
LDC Full Form PSC
- LDC Full Form in the context of PSC (Public Service Commission) could indicate the designation of Lower Division Clerk within the commission itself or its affiliated departments.
UDC Full Form:
- UDC stands for “Upper Division Clerk.” Similar to Lower Division Clerks, Upper Division Clerks are administrative personnel responsible for higher-level clerical tasks, documentation, and administrative support functions within government organizations or private institutions.
Summing Up
Lower Division Clerks (LDC full form) play an important role in helping government offices run smoothly. LDCs can have good careers in government and organizations. They need to deal with workload, confidentiality, and stakeholders. They can learn new things and use technology to be successful. LDCs are important assets for organizations.
LDC Full Form: Key Takeaways
- LDCs are important in government offices and offer steady jobs with chances to grow.
- LDCs face problems like too much work, doing the same thing all the time, learning new technology, being very careful with details, not making big decisions, and finding a balance between work and personal life.
- To be an LDC, you need certain qualifications, like finishing high school, being a certain age, and typing fast.
- Common exams for LDC jobs include SSC CHSL, IBPS Clerk, RRB LDC, ESIC UDC, DSSSB LDC, and High Court Clerk Exams.
- LDCs start with a salary of about Rupees. 19,000 a month and can make up to Rupees. 63,200 a month later on, plus benefits and chances to move up.
- Having experience helps LDCs earn more money and get better jobs.
- Even with challenges, LDCs are really helpful in offices and are valued by their bosses.
Learn about some other full form:
| PWD Full Form | CDPO Full Form |
| UIDAI Full Form | FSSAI Full Form |
| FBI Full Form | DGP Full Form |
| PMJJBY Full Form | MLA Full Form |
| ESI Full Form | TRAI Full Form |
Click on the below button to get the whole list of Full Forms
LDC Full Forms: FAQs
What is the LDC exam qualification? Or What is an LDC qualification?
To apply for the position of an LDC, you must pass 10+2 from a reputable board.
Are there age limits for LDC recruitment?
Yes, candidates applying for LDC positions must usually fall within 18-42 years.
What skills are essential for an LDC?
Essential skills for LDCs include proficiency in computer applications, typing speed and accuracy, organizational abilities, attention to detail, and multitasking capabilities.
Can LDCs progress to higher positions?
Yes, LDCs have opportunities for career growth through promotions to higher-level positions based on performance and experience.
How can LDCs prepare for career advancement?
LDCs can participate in training programs offered by the organization.
What is the LDC salary?
Lower Division Clerks earn an average monthly income of ₹22,538 in India. Lower Division Clerks in India receive an average additional pay compensation of ₹538, ranging from ₹333 to ₹742.
What is the job of LDC? Or What is the duty of LDC?
LDCs assist with data entry, recordkeeping, file management, and document organization. On a daily basis, clerks are responsible for composing letters, managing correspondence, and providing administrative support.
What is the full form of LDC area?
The United Nations defines least developed countries (LDCs) as developing countries with the lowest socioeconomic development indicators.
Is LDC a good job?
Based on 18 company reviews on Glassdoor, LDC has an employee rating of 3.7 out of 5 stars, indicating that most employees have a positive working experience there.
Got a question on this topic?