

Quick Summary
Crafting the perfect email is an important skill in today’s professional world. First impressions often happen in the inbox. Whether you’re applying for a job, reaching out to a client, or communicating with colleagues, using the right email format can make a big difference in how your message is received. A well-structured email shows your professionalism and improves your chances of getting a quick and positive response.
In this guide, you’ll find email format samples, practical writing tips, and real-world examples to help you communicate effectively in any situation. Based on industry best practices and years of experience, we’ll show you how to structure your emails for clarity, impact, and trustworthiness. Whether you’re a student, job seeker, or working professional, this article will give you the tools you need to make every email count in 2025 and beyond.
A formal email is a type of email used for professional communication or official purposes. It is typically employed in communication between colleagues, clients, or superiors within a business or professional setting. Formal emails are characterized by their professional tone, language, and format, which are designed to convey respect, courtesy, and expertise.
Step 1: Use a Professional Email Address
Step 2: Craft a Clear and Concise Subject Line
Step 3: Begin with an Appropriate Salutation
Step 4: Write a Brief Introduction
Step 5: Develop the Main Body Content
Step 6: Conclude with a Polite Closing
Step 7: Add a Professional Signature
An email subject line informs the recipient about the specific contents of an email. It is the single, most important thing in email writing because someone opens a mail or not, depending on it. Moreover, a good, crisp, clear, and to-the-point subject line is a priority email component. Hence, it will compel and coerce the recipient to read it. A subject line depends on the content and purpose of the sender.
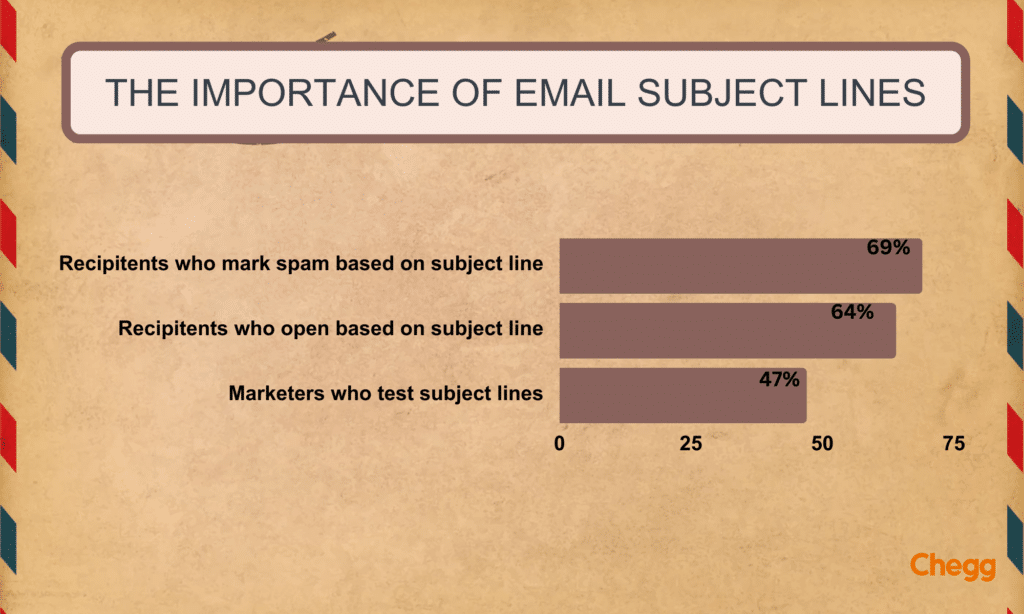
Some examples of perfectly written subject lines –

Salutation in an email format is a means to greet someone before starting to talk about the main subject. Besides, it varies from person to person, depending on the relationship one has with the recipient. Various options are available depending on the individual’s level of formality with the receiver. Therefore, it may begin with a simple ‘Hi’ preceding the name, or a more formal one like ‘Dear Madam/Sir’, ‘Dr. XYZ’ or ‘Professor XYZ.’
The body states what the email is talking about. Here, the sender crafts all the points or information they want to present to the recipient. Hence, it is a vital part of an email format. When writing an email to a stranger, a brief introduction must be provided in the body to get to the main topic immediately. The body in a format states the purpose of the sender. Moreover, the body should be short and simple without extra, ambiguous information. An email is not the place to have lengthy, continuous conversations.
Structuring the email body like a cover letter can be beneficial when applying for jobs. This includes using formal language, personalizing the salutation, and showcasing relevant qualifications to stand out to hiring managers.
The tone of your email can determine how the recipient will interpret your message. A negative or aggressive tone can create a hostile environment and make the recipient defensive, whereas a positive and friendly tone can make the recipient feel valued and appreciated. Your tone can also help to establish a professional relationship with the recipient, especially if you’re communicating with them for the first time.
In contrast, informal email writing is more relaxed and used for personal correspondence, lacking the strict rules of formal email writing.
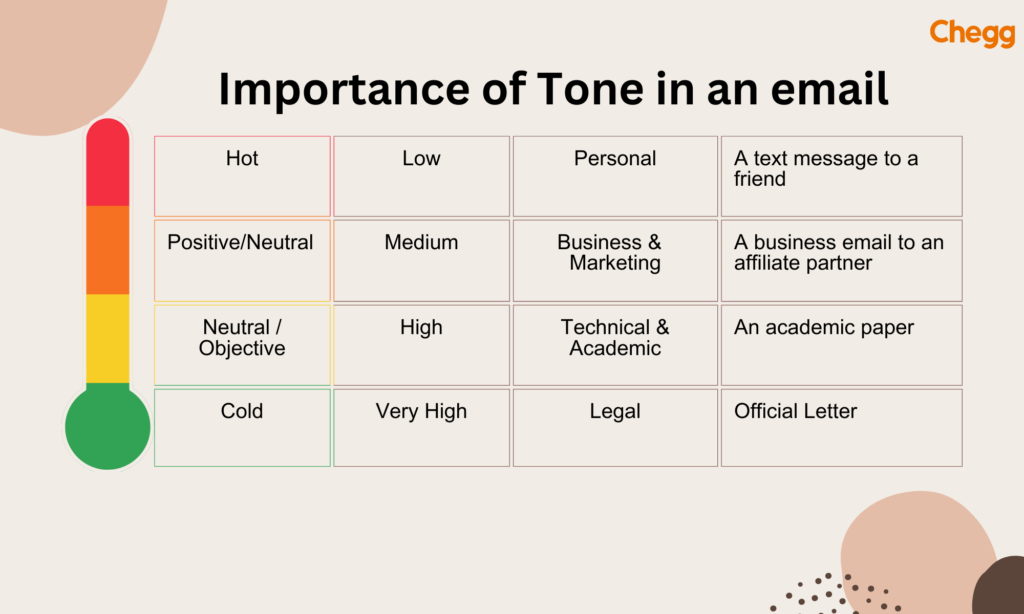
Email closing is a crucial component of the email format. Here, the sender has to end his email respectfully after stating the matter earlier in the body. Also, the email closing tells the recipient what’s next. It includes a final call to action, wishing them luck and success or wanting a favor regarding something. Any of these have to be stated respectfully and formally. Similarly, the best way is to get cordial at the end and provide a brief salutation to finish. Another way to form an email closing can be to end on a friendly note, showing one wants to keep in touch with the recipient.
Font Selection:
Alignment and Spacing:
Use of Lists:
It’s important to show gratitude in your emails, especially when someone has done something for you or has provided you with information. Adding a simple “thank you” to your message can make the recipient feel appreciated and valued, helping to build a positive relationship between you and the recipient. Incorporating a thank you message in your email signature is also a good practice to show appreciation.
Attachments:
Follow-Up Emails:
A call-to-action (CTA) is a statement encouraging the recipient to take a specific action, such as replying to your email or clicking a link. Including a clear CTA in your email can help ensure that the recipient understands what you want them to do and prevent any confusion or misunderstandings. Make sure your CTA is clear and concise, and it’s always good to follow up after sending an email with a CTA.
An email format ends with the last component called a signature. These are the final words to denote the recipient, along with your name and credentials. A well-formed signature is sure to leave an impression on the reader.
Signatures should be simple words conveying respect toward the recipient. Some individuals design their signatures to make them look attractive and practical. The email signature should look visually appealing and well organized. Hence, if the signature is memorable and aesthetic, it will earn extra credit points from the recipient.
A conventional email format typically includes a subject line, greeting, body (containing the introduction, details, and conclusion), closing, and signature. Likewise, professional emails include an effective subject line that is both informative and clear, a formal greeting (e.g., “Dear Mr./Ms [Last Name]), and a closing (e.g., ” Sincerely, [your name]).
Here is an enlarged version:
Other Tips:
You can also read our Blog on how to write a bona fide certificate.
Choosing the right tone and format in your email depends mainly on your relationship with the recipient and the purpose of your communication. While formal emails are rooted in professionalism and structure, informal emails offer a relaxed and personal touch. Here’s a detailed comparison to help you decide which approach is appropriate for different scenarios:
| Aspect | Formal Email | Informal Email |
|---|---|---|
| Recipient | Professionals, clients, professors, officials, or unknown contacts | Friends, family, close colleagues, and personal acquaintances |
| Tone | Polite, respectful, and professional | Casual, friendly, and conversational |
| Structure | Introduction → Body → Conclusion | Flexible; may or may not follow a structured format |
| Formatting | Standard font, proper alignment, clear paragraphing | Varies based on personal preference |
| Grammar & Language | Correct grammar, formal language, no slang or abbreviations | Conversational, includes slang, emojis, and abbreviations |
| Purpose | Sharing information, making requests, giving updates, or professional networking | Sharing personal news, social conversations, and friendly check-ins |
| Length | Concise and to the point (1–2 paragraphs usually) | Can vary—short or long depending on the relationship and content |
| Use of Sign-off | Required; includes full name, job title, and contact details | Optional; may end with first name or a casual phrase |
| Attachments | Used with a clear mention in the body and properly named files | Rarely used or casually referenced |
| Follow-Up | Often followed by a reminder or polite check-in if no response is received | Informal or optional; usually only if there’s a close connection |
Avoiding Informal Language:
Proofreading:
Clarity:
Understanding Cultural Norms:
Language Sensitivity:
Some functional format samples used for different purposes are discussed –
Subject: Formal Leave Application Request
Dear [Recipient’s Name],
I am writing to formally request a period of leave from [start date] to [end date] due to [reason for leave]. I believe it is essential for me to take this time to [explain reason]. I will ensure all pending tasks are completed before my departure and arrange coverage during my absence.
Thank you for your understanding and support.
Warm regards,
Subject: Request for Assistance with Recent Order (Order #12345)
Dear Customer Care Team,
I hope you are doing well. I am reaching out regarding my recent order, Order #12345, which was delivered on February 20th. Unfortunately, upon receiving the package, I noticed that one of the items, the Bluetooth Headphones, was missing from the shipment.
Could you kindly assist me in resolving this issue? I would appreciate it if you could provide guidance on how we can proceed, whether it be a replacement or a refund for the missing item.
Please let me know if you need further details regarding the order or shipping information. I look forward to your prompt assistance in this matter.
Thank you for your time and support.
Best regards,
John Thompson
[Phone Number]
[Email Address]
Subject: Request for a Meeting to Discuss Project Progress
Dear Ms. Johnson,
I hope you’re doing well. I want to request a meeting to discuss the progress of the ongoing project. It would be great to align on the next steps and ensure we are on track to meet our deadlines.
Could you please let me know your availability next week? I am flexible and can adjust my schedule to suit your convenience.
Thank you for your attention to this matter. I look forward to your response.
Best regards,
Name and designation
Bonus Tip – A formal complaint should be professional in tone but strongly worded and criticized adequately. The content should not be dramatic and undignified. Improving your email writing skills can help you craft clearer and more effective complaints or queries.
Bonus Tip – It’s vital to be clear with the request asap. Follow it with a legitimate reason to make the request sound stronger. Maintaining professionalism in professional emails is crucial when making such requests.
Subject: Invitation to Annual Company Picnic – RSVP by March 5th
Dear Team,
I hope you’re all doing well. We are excited to announce our Annual Company Picnic, which will take place on Saturday, March 12th, at Greenwood Park starting at 11:00 AM. This is an excellent opportunity to relax, enjoy some fun activities, and connect with colleagues outside the office.
We have planned various activities, including team games, a barbecue lunch, and plenty of outdoor games. There will also be a raffle with some fantastic prizes!
Please RSVP by March 5th if you plan to attend so we can ensure we have enough food and seating for everyone. You can RSVP by replying to this email or filling out the form linked here: [RSVP Form Link].
We hope to see you there for a day of fun and relaxation!
Best regards,
[Your Name]
[Your Job Title]
[Company Name]
Subject: Request for One-on-One Meeting
Dear [Boss’s Name],
I hope you’re doing well. I want to request a one-on-one meeting with you to discuss my current projects and some of the goals I’m working towards in the coming months. I believe getting your feedback and guidance on a few key areas would be helpful.
Could you please let me know your availability for next week? I am flexible and can adjust to your schedule at your convenience.
Thank you for considering my request, and I look forward to meeting with you.
Best regards,
[Your Name]
[Your Job Title]
| Aspect | Formal Email | Informal Email |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Used for professional, academic, or official communication. | Used for casual, personal, or friendly communication. |
| Recipient | Boss, client, professor, or official authority. | Friends, family, or close colleagues. |
| Tone | Polite, respectful, and professional. | Friendly, relaxed, and conversational. |
| Salutation | Uses casual greetings like “Hi [Name]” or “Hey [Name].” | Uses casual greetings like “Hi [Name]” or “Hey [Name]”. |
| Structure | Uses formal greetings like “Dear [Name]” or “Respected [Name].” | Less structured, may be brief and direct. |
| Grammar & Spelling | It is well-organized with an introduction, body, and conclusion. | It ends with casual closings like “Best,” “Take care,” and “See you soon.” |
| Signature | It uses complete sentences with proper grammar and punctuation. | It ends with formal closings like “Best regards” and “Sincerely,” followed by name and designation. |
| Attachments | Used for official documents, resumes, or reports. | Used for personal files, photos, or informal attachments. |
A bullet-point list summarizing key elements to review before sending an email, such as:
Mastering the skill of professional email writing is crucial for building strong relationships and reaching your goals in today’s fast-paced digital world. By following effective formats, applying helpful tips, and focusing on clarity and tone, you can make sure your messages create a positive and lasting impression.
Every email you send reflects your professionalism and attention to detail. Keep improving your skills, stay informed about the latest communication trends, and don’t hesitate to learn from industry experts. With the right approach, you will be ready to tackle any email situation confidently and credibly, helping you stand out in any academic or professional environment.

The format of an email includes: subject line, greeting, body, closing, and signature.
Subject: [Your Subject Here]
Dear [Recipient’s Name],
[Your message content here.]
Best regards,
[Your Name]
[Your Position]
[Your Company]
[Your Contact Information]
[Your Address]
To write a formal email, start with a clear subject line. Use a polite greeting. Write a concise and professional body. End with a formal closing. Include your name and contact information.
An email address is formatted as username@domain.com. The username comes before the @ symbol, and the domain (like example.com) follows after it. To maintain a professional appearance, there should be no spaces or special characters.
To write an email, use this format. Start with a clear subject line. Add a polite greeting. Write a concise and professional body. End with a formal closing. Include your name and contact information.
Subject: Request for Meeting
Dear [Recipient’s Name],
I hope this message finds you well. I am writing to request a meeting to discuss [briefly state the purpose of the meeting]. It would be beneficial to [mention any specific outcomes or topics of interest].
Could you please let me know your availability for next week? I am flexible and can adjust to a time that suits you best.
Thank you for considering my request. I look forward to your reply.
Best regards,
[Your Name]
[Your Position]
[Your Company]
[Your Phone Number]
[Your Email Address]
Start a formal email with a polite greeting like “Dear [Name],” or “Hello [Name],” followed by a comma. Then, begin the email body.
Read More

Authored by, Mansi Rawat
Career Guidance Expert
Mansi crafts content that makes learning engaging and accessible. For her, writing is more than just a profession—it’s a way to transform complex ideas into meaningful, relatable stories. She has written extensively on topics such as education, online teaching tools, and productivity. Whether she’s reading, observing, or striking up a conversation while waiting in line, she’s constantly discovering new narratives hidden in everyday moments.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.