History
History isn’t just about dates; it’s about people, their dreams, and their struggles. It helps us appreciate the diversity of human experiences, beliefs, and traditions, fostering empathy and understanding. Learning from past mistakes and successes helps us make informed decisions in the present and navigate future challenges.
History GK invites us to explore the remarkable achievements and enduring struggles of humanity.
From the earliest cave paintings to the grand empires, every era holds stories of courage, innovation, and resilience. Whether it’s the construction of the Great Wall of China, the Renaissance in Europe, or the Indian freedom movement, each chapter reveals the indomitable spirit of individuals and communities.
Diving into History and Different Historical Events:
India’s history stretches back millennia, rich with diverse civilizations, empires, and cultural influences. The Indus Valley Civilization flourished around 3300 BC, followed by the Vedic Period, laying the foundation for Hinduism and societal structure.
To make your learning journey smoother we have combined important dates and famous historical events in a table format.
Event | Date (Approximate) | Location |
India | ||
Indus Valley Civilization | 3300-1300 BC | Indus Valley (Present-day Pakistan & North-West India) |
Mauryan Empire | 322-185 BC | Present-day India, Pakistan, Afghanistan, parts of Iran and Nepal |
Gupta Empire | 320-550 AD | Northern India, Bangladesh, parts of Pakistan, Nepal and Afghanistan |
Delhi Sultanate | 1206-1526 AD | India |
Mughal Empire | 1526-1857 AD | Indian subcontinent & Afghanistan |
Sepoy Mutiny | 1857-1858 AD | British India |
Indian Independence Movement | 1857 – 1947 AD | British India |
Indian Independence | 15 August 1947 | India |
International | ||
Fall of Troy | 1200 BC (Approximate) | Greece |
Founding of Rome | 753 BC (Approximate) | Italy |
Life of Buddha | 563-483 BC | India & Southeast Asia |
Life of Confucius | 551-479 BC | China |
Alexander the Great’s Conquests | 336-323 BC | Greece, Middle East, parts of Asia & Africa |
Rise of the Roman Empire | 27 BC – 476 AD | Mediterranean region |
Life of Jesus Christ | 4 BC – 30 AD (Estimated) | Judea (Present-day Israel & Palestine) |
Fall of the Roman Empire | 476 AD | Europe |
The Middle Ages | 5th – 15th Centuries | Europe |
The Renaissance | 14th – 17th Centuries | Europe |
The Printing Press Invented | 1440 | Europe |
Christopher Columbus Sails the Atlantic | 1492 | Europe & Americas |
Martin Luther’s 95 Theses | 1517 | Germany |
The Protestant Reformation | 1517 – 1648 | Europe |
The Scientific Revolution | 16th – 18th Centuries | World (primarily Europe) |
The Age of Exploration | 15th – 17th Centuries | Europe & world |
The Thirty Years’ War | 1618 – 1648 | Europe |
The Enlightenment | 17th – 18th Centuries | Europe |
The American Revolution | 1775 – 1783 | North America |
The French Revolution | 1789 – 1799 | France |
Mauryan and Gupta empires saw political and cultural zeniths, while empires like the Cholas and Mughals left lasting legacies.
Let’s learn more about the most important historical events:
1. Muhammad Ghori:
A 12th-century Afghan ruler who invaded India several times, eventually defeating Prithviraj Chauhan at the Second Battle of Tarain in 1192, marking the beginning of Delhi Sultanate rule in India. He was known for his military prowess and expansionist policies. He established the Ghurid dynasty, which laid the foundation for the Delhi Sultanate.
2. Bloody Sunday:
It refers to multiple historical events where violence occurred on a Sunday, particularly:
- 1920 Bloody Sunday in Ireland: British troops opened fire on unarmed Irish civilians during a protest, leading to widespread outrage and fueling the Irish War of Independence.
- 1972 Bloody Sunday in Northern Ireland: British soldiers shot and killed 14 unarmed civilians during a civil rights march in Derry, Northern Ireland, further intensifying the conflict.
3. Battle of Buxar:
Battle of Buxar was fought in 1764 between the forces of the Mughal Empire and the British East India Company. A decisive victory for the British, marking a turning point in their expansion in India. Weakened the Mughal Empire significantly and paved the way for British dominance in the region.
4. Humayun:
Humayun was the second Mughal emperor of India, son of Babur and father of Akbar. Ruled from 1530 to 1540 and again from 1555 to 1556. He briefly lost his throne to Sher Shah Suri but regained it with Safavid Persian aid. Known for his patronage of arts and architecture, including the construction of Humayun’s Tomb in Delhi.
5. The Second Battle of Panipat
The second battle of Panipat was fought in 1556 between the Mughal forces led by Akbar and the Afghan forces under Hemu Vikramaditya. It was a decisive victory for Akbar, consolidating his power and marking the beginning of the Mughal Empire’s golden age. It established Akbar as a powerful ruler and paved the way for Mughal expansion in North India. It also marked the end of Afghan resistance to Mughal rule. Batte had a lasting impact on Indian history, shaping the political and cultural landscape of the subcontinent.
6. Exploring Key Periods of History
This broad topic encompasses various historical periods, each with its own unique characteristics and events. Some examples include:
- Indus Valley Civilization (3300-1300 BCE)
- Mauryan Empire (322-185 BCE)
- Gupta Empire (320-550 CE)
- Delhi Sultanate (1206-1526)
- Mughal Empire (1526-1857)
British Raj (1858-1947)
7. Medieval Period of India (6th-16th centuries CE)
This period witnessed diverse political, social, and cultural developments:
Political landscape:
Rise and fall of various regional kingdoms, such as the Chalukyas, Pallavas, Cholas, and Rajputs. Emergence and expansion of the Delhi Sultanate and the Mughal Empire. Foreign invasions and their impact, including those by Mahmud of Ghazni and Genghis Khan.
Social changes:
Rise of the caste system and its impact on the social hierarchy. Spread of Islam and its influence on society and culture. Development of the Bhakti movement and its emphasis on devotional worship.
Cultural advancements:
The flourishing of literature, art, and architecture, including masterpieces like the Khajuraho temples and the Taj Mahal. Development of scientific knowledge and mathematics, with contributions from scholars like Aryabhata.
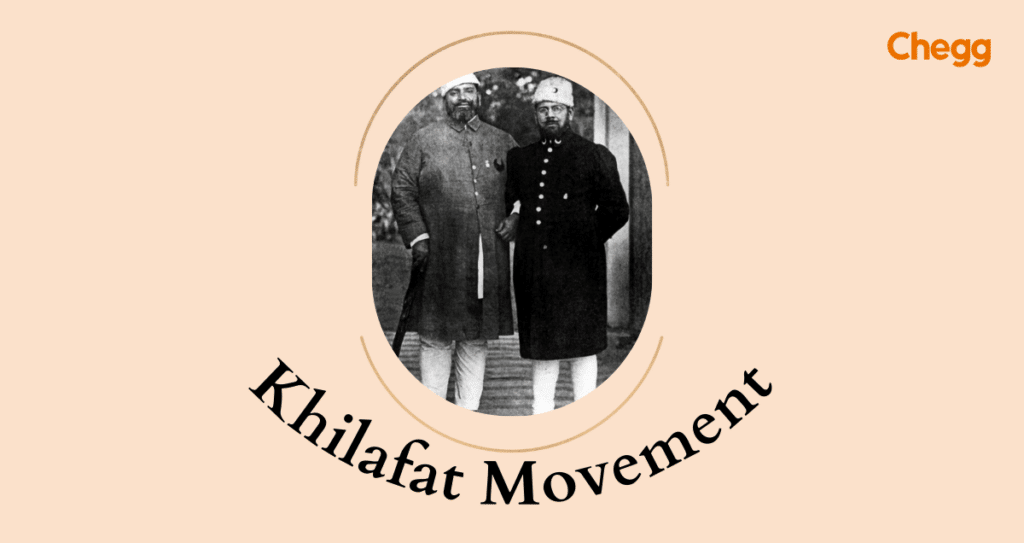
8. Khilafat Movement
The Khilafat Movement (1919-1924) was a mass mobilization of Indian Muslims seeking to preserve the Ottoman caliphate after World War I. Fearing the caliphate’s demise and the weakening of Islamic unity, Muslims across India participated in non-violent protests, hartals (strikes), and Khilafat committees. Led by Maulana Azad and Muhammad Ali Jinnah, the movement initially united Hindus and Muslims under a common cause.
However, its later association with emerging Muslim nationalism and violent incidents led to a decline in Hindu support and contributed to the rise of communal tensions. Despite its failure to achieve its primary objective, the Khilafat Movement played a significant role in shaping Indian politics, mobilizing the Muslim masses, and influencing the growth of the Indian National Congress and the Muslim League.
9. Indus Valley Town Planning
Dating back to 3300-1300 BCE, the Indus Valley Civilization (Harappan Civilization) boasted remarkable urban planning and engineering feats. This sophisticated urban planning demonstrates the advanced social organization and technological prowess of the Indus Valley people. Their legacy provides valuable insights into early urban development and offers a glimpse into one of the earliest and most influential civilizations in human history.