Table of Contents
LED Full Form
LED full form stands for Light Emitting Diode. It is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current passes through it. LEDs are widely used in various applications such as indicator lights, display screens, and lighting fixtures due to their energy efficiency, durability, and compact size. They have largely replaced traditional incandescent and fluorescent lights in many applications due to their longer lifespan and lower energy consumption.
LED Full Form in Hindi
Full Form of LED in Hindi is “प्रकाश उत्सर्जक डायोड” (Prakash Utsarjak Diode).
LED Symbol

History and Development of LEDs

Origins of LEDs
Light Emitting Diode (LED full form) technology started developing in the early 1900s when scientists discovered a way to make certain materials glow with light when electricity passed through them.
- Early Discoveries: In 1907, H.J. Round noticed that certain materials would emit light when an electric current passed through them. This was the first observation of what would later become LEDs. However, limitations in practical uses existed at that time due to the materials available.
- First Practical LED: In 1962, a researcher named Nick Holonyak Jr. created the first usable LED that emitted red light. This was a big step forward because it showed LEDs could work effectively.
Evolution of LED Technology
- 1970s-1980s: Over the next decades, scientists improved LEDs to make them brighter and more reliable. They developed LEDs that emitted green, yellow, and amber light, expanding the range of colors available.
- 1990s: A major breakthrough came in the 1990s when scientists figured out how to make blue LEDs. This completed the color spectrum needed to create white light. These advancements were so important that the inventors received a Nobel Prize for their work in 2014.
- 2000s-Present: Since the 2000s, LEDs have continued to get better and more powerful. Nowadays, people use them in everyday lighting, TVs, and even in agriculture and medicine for special lighting needs.
Key Milestones in LED Technology Development
- 1962: Nick Holonyak Jr. invents the first practical LED that emits red light, showing that LEDs can be useful for lighting.
- 1970s: Researchers developed more colors like green, yellow, and amber, making LEDs more versatile.
- 1990s: Scientists invented blue LEDs, completing the color mix needed to create white light. This achievement was a big breakthrough.
- Early 2000s: LEDs become powerful enough to replace traditional light bulbs, leading to their widespread use in homes and businesses.
- Recent Advances: Today, LEDs are still improving, making them even more efficient and useful for new technologies like smart lighting and advanced displays.
LEDs have come a long way from a scientific curiosity to an essential part of our daily lives. Their development continues to make lighting more efficient and environmentally friendly.
How LEDs Function
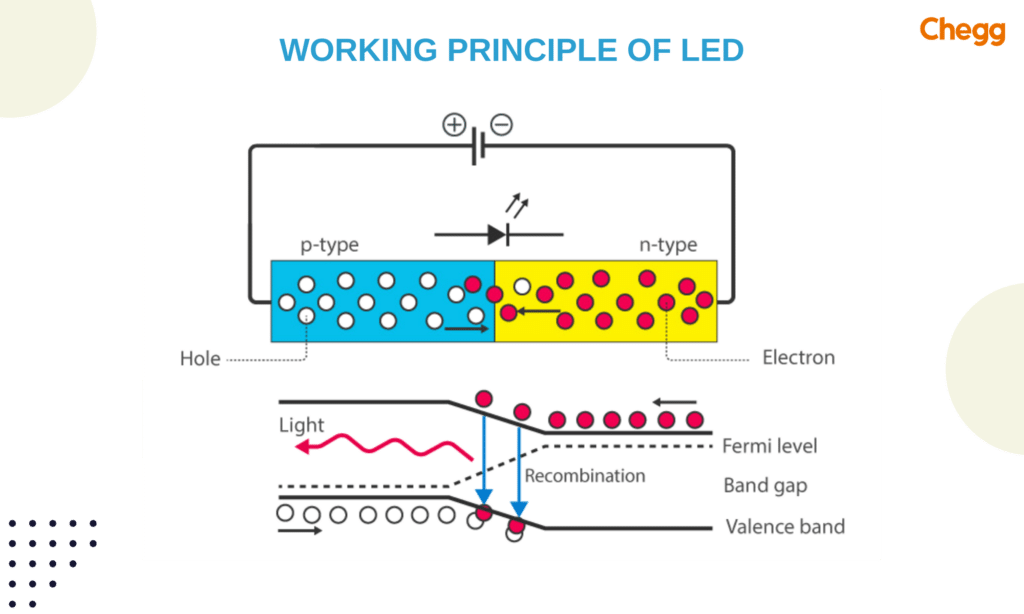
Light Emitting Diode (LED full form), create light through a process called electroluminescence. Here’s how it happens:
- Semiconductor Material: Inside an LED is a special material called a semiconductor. It conducts electricity when a voltage is applied. Common semiconductors used include materials like gallium nitride and silicon carbide.
- Doping: Scientists treat the semiconductor with small amounts of other materials, called doping. This creates two parts in the material: one with more positive charges (p-type) and one with more negative charges (n-type).
- PN Junction: Where the p-type and n-type parts meet is crucial. This junction is where light is produced.
- Applying Voltage: When you connect the LED to a power source with the correct polarity (positive to p-type, negative to n-type), electrons start moving from the n-type to the p-type, and holes (positive spaces) move the other way.
- Light Creation: When electrons and holes meet at the junction, they release energy in the form of light particles called photons. The color of the light depends on the materials used in the LED.
- Light Color Control: Engineers can control the color of the light by choosing specific semiconductor materials and doping them in different ways.
- Transparent Casing: A clear plastic encloses the LED, allowing the light to escape and enabling us to see it.
Additional Points:
- LEDs use electricity very efficiently, turning most of it into light and producing little heat.
- Unlike old-fashioned bulbs that have fragile filaments, LEDs are durable and can last for tens of thousands of hours.
- LEDs come in various sizes and colors, making them useful for different purposes like lighting, displays, and electronics.
LEDs are small devices that use special materials to produce light when electricity passes through them. They are efficient, long-lasting, and come in many colors, making them ideal for many modern uses.
Advantages of LEDs
Why LEDs Are Better Than Traditional Lights
Light Emitting Diode (LED full form) have several benefits over old-fashioned light bulbs like incandescent and fluorescent ones. Here’s why they’re a smarter choice:
- Save Energy
- LEDs use much less electricity than old bulbs to give off the same amount of light.
- This means lower electricity bills and less energy wasted, which is good for your wallet and the environment.
- Last Longer
- LEDs can keep working for up to 25 times longer than regular bulbs. They also outlast fluorescent lights by a big margin.
- This means fewer trips to the store and less waste.
- Strong and Durable
- LEDs are tough because manufacturers make them without fragile parts like filaments or tubes.
- They can handle bumps, vibrations, and changes in temperature better than other lights.
- Good for the Environment
- LEDs promote eco-friendliness by using less energy and avoiding harmful chemicals like mercury, found in fluorescent lights.
- Using LEDs helps cut down on pollution from making electricity and lowers your carbon footprint.
Examples in Everyday Life
- Saving Money: Switching to LEDs can lower your electric bill each month because they use less power.
- Less Maintenance: Since LEDs last so long, you won’t need to replace them as often, saving time and money.
- Safe and Reliable: LEDs don’t get hot like incandescent bulbs, so they’re safer to use and less likely to cause accidents.
LEDs are not only a smart choice for saving money and energy but also for keeping our environment cleaner and providing dependable lighting solutions for homes and businesses.
Applications of LEDs
People use Light Emitting Diodes (LED full form) in many different ways because they are versatile and efficient. Here are some places where you can find them:
1. General Lighting
- Homes: People use LEDs for regular lighting in houses because they save energy and last a long time.
- Offices and Stores: Many businesses use LEDs for lighting because they’re bright and save money on electricity bills.
- Factories and Warehouses: LEDs are tough and durable, making them ideal for industrial lighting.
2. Automotive Lighting
- Headlights: Cars use LEDs for headlights because they are bright and use less energy than older types of lights.
- Taillights: Automakers also use LEDs for tail lights because they can manufacture them in different colors and they last a long time.
- Interior Lighting: Inside cars, manufacturers use LEDs for dashboard lights and interior lighting because they are reliable.
3. Electronic Displays
- TVs and Monitors: TVs and computer monitors use LEDs to show clear and bright pictures.
- Smartphones: Many smartphones use LEDs for their screens to display colors vividly and use less battery power.
4. Signage and Advertising
- Billboards: Large outdoor ads use LEDs because they can show bright colors and be seen from far away.
- Digital Displays: Cities and businesses use LEDs in signs to show messages and information clearly.
5. Specialized Lighting
- Horticulture: LEDs help plants grow indoors because they can provide the specific light plants need to grow well.
- Medical Use: Hospitals use LEDs for surgical lights and medical equipment because LEDs produce bright, focused light.
- UV Applications: LEDs can emit ultraviolet (UV) light, which people use to disinfect water and surfaces by killing germs.
Types of LEDs
Different Kinds of LEDs
Light Emitting Diode (LED full form) come in different types based on their color, size, and specific uses. Here are the main ones:
- RGB LEDs
- Colorful Lights: RGB LEDs can make red, green, and blue light. Mixing these colors creates many different colors, useful for displays and mood lighting.
- White LEDs
- General Lighting: White LEDs give off white light like traditional bulbs but use less energy. They’re common in homes, offices, and streetlights.
- High-Power LEDs
- Bright and Strong: These LEDs make very bright light, good for places needing lots of light, like stadiums or outdoor lights.
- SMD LEDs
- Small and Efficient: SMD LEDs are tiny and fit on circuit boards. They’re in small gadgets like smartphones, TVs, and computers.
Examples in Everyday Use
- At Home: People use white LEDs for energy-saving lights that last a long time.
- On TV Screens: RGB LEDs make bright, colorful pictures on TVs.
- At Events: High-power LEDs light up concerts and stadiums so everyone can see well.
LEDs have different types for different jobs, from lighting rooms to making colorful displays. Knowing these types helps use LEDs well in many ways.
How LEDs are Made
Making LED Chips
Manufacturers produce Light Emitting Diodes (LED full form) through a process that begins with special materials and involves several steps:
- Materials: Manufacturers use materials such as gallium arsenide or gallium nitride, which emit light when electricity passes through them, to make LEDs.
- Growing Crystals: Initially, researchers grow crystals of these materials under controlled conditions to render them suitable for LEDs.
- Adding Layers: Manufacturers add different layers to the crystal to determine the LED’s color—red, green, blue, or other colors.
- Making the LED: These layers arrange to form a junction through which electricity can flow, thereby generating light.
Assembling LED Products
After making the LED chips, manufacturers put them into products like light bulbs or displays:
- Mounting: Manufacturers place LED chips on a small board to keep them cool and working well.
- Protection: They cover the chips with a lens or resin to protect them and help direct the light they produce.
- Testing: Manufacturers test every LED product to ensure it works correctly and emits the right amount and color of light.
Manufacturers make LEDs by growing crystals, adding layers, and assembling them into products that save energy and provide efficient lighting and displays.
Environmental Impact of LEDs
Benefits for the Environment
Light Emitting Diode (LED full form) help the environment in several important ways compared to older types of light bulbs:
- Lower Carbon Footprint
- LEDs use less electricity than traditional bulbs, which reduces the amount of fossil fuels burned to make electricity.
- This lowers greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to climate change.
- Reduced Waste
- LEDs last much longer than traditional bulbs, so they don’t need to be replaced as often.
- This reduces the amount of waste going into landfills from discarded bulbs.
- No Harmful Substances
- LEDs do not contain harmful substances like mercury, which is found in fluorescent bulbs.
- This makes LEDs safer to use and dispose of at the end of their life.
Examples of Environmental Benefits
- Energy Savings: Using LEDs in homes and businesses reduces electricity use, saving money and lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
- Long Lifespan: LEDs can last up to 25 times longer than traditional bulbs, reducing the number of bulbs thrown away.
- Safer Disposal: Since LEDs don’t have mercury, they are safer for the environment when disposed of.
LEDs help protect the environment by using less energy, lasting longer, and being safer to use and dispose of compared to older types of bulbs.
Comparing LEDs to Other Lighting Technologies
Light Emitting Diode (LED full form) are different from other types of lights. Let’s compare them with a few common ones.
| Feature | LED | Incandescent | CFL (Compact Fluorescent Lamp) | Fluorescent |
| Light Source | Light Emitting Diode | Heated Filament | Mercury Vapor & Phosphor Coating | Mercury Vapor & Phosphor Coating |
| Energy Efficiency | Most Efficient | Least Efficient | More Efficient than Incandescent | More Efficient than Incandescent |
| Lifespan | Longest (25,000-50,000+ hours) | Shortest (1,000-2,000 hours) | Moderate (8,000-15,000 hours) | Moderate (10,000-20,000 hours) |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost | Lower upfront cost | Moderate upfront cost | Moderate upfront cost |
| Warm-up Time | Instantaneous | Gradual | Takes some time | Takes some time |
| Dimming | Most Options Available | Limited Dimming Options | Most Options Available | Most Options Available |
| Color Quality | Excellent | Good | Good | Good |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal Mercury, Recyclable Materials | Contains Mercury, Requires Special Disposal | Contains Mercury, Requires Special Disposal | Contains Mercury, Requires Special Disposal |
Conclusion
Light Emitting Diode (LED full form) have changed lighting with their energy savings, durability, and usefulness. They save money on electricity bills and are better for the environment compared to older lights. As technology gets better, LEDs are becoming even more efficient and useful for all kinds of lighting needs at home, work, and beyond.
LED Full Form: Key Takeaways
- LED stands for Light Emitting Diode, a type of light that glows when electricity passes through it.
- LEDs use less energy, saving electricity and money.
- They last significantly longer than traditional bulbs, reducing replacement frequency.
- LEDs are sturdy and resilient to shocks and vibrations.
- They have a lower carbon footprint and contain no harmful substances like mercury.
- Used widely from general lighting to specialized applications like displays and horticulture.
- Despite higher initial costs, LEDs offer long-term savings.
- Continuous improvements in brightness and efficiency enhance their utility across various industries.
Learn more about some other full forms:
| RAM Full Form | ROM Full Form |
| HDD Full Form | USB Full Form |
| SSD Full Form | SIM Full Form |
| PCD Full Form | MCB Full Form |
| CRT Full Form | LCD Full Form |
Ready to learn more? Click on below button to get the complete list of Full Forms!
LED Full Form: FAQs
What is LED full form and LCD full form?
LED: Light Emitting Diode (tiny, light-emitting chips).
LCD: Liquid Crystal Display (uses liquid crystals and backlighting for screens).
Where are LEDs used?
LED is a special diode that emits light when electricity passes through it.
How can an LED be safe in an environment?
Unlike incandescent bulbs which use mercury and other harmful things that can impact your family. However, no such threats are associated with LED and are eco-friendly
What is the average lifespan for the working of LED bulbs?
The average working lifespan for LED bulbs is 50,000 hours.
What is MCB and CFL?
MCB: Miniature Circuit Breaker (safety switch for electrical circuits).
CFL: Compact Fluorescent Lamp (energy-efficient bulb).
Why is LED called LED?
The term “LED” succinctly captures both the nature (a diode) and the function (light emitting) of the device, making it a straightforward and descriptive name.
Got a question on this topic?
