Home » Full Forms » IC Full Form: Integrated Circuit
IC Full Form: Integrated Circuit

Table of Contents
IC Full Form
The IC full form is the Integrated Circuit. It is a tiny electronic device made from a semiconductor material that includes numerous microscopic elements, such as Diodes and Transistors, Resistors & Capacitors. Integrated Circuit (IC full form) stands for a small electronic device made of semiconductor materials that combines tiny components such as diodes, transistors, resistors, and capacitors into a single unit. These silicon-based circuits have become crucial in our modern society, running a broad range of electrical devices ranging from consumer items to industrial systems.
IC full form in Computer
IC full form in computer stands for “Integrated Circuit”. It’s a tiny electronic device consisting of multiple transistors, resistors, and capacitors integrated into a single chip. A lot of electronic devices, such as computers, cell phones, and other gadgets, are built using integrated circuits. For these devices to work, they process, store, handle electrical signals, and carry out other duties. Devices today have greater power, efficiency, and compactness than in the past because of integrated circuits (IC).
History of IC
Regarding the origins of Integrated Circuits (IC full form), many theories exist. But one of the theories put forth by German engineer Werner Jacobi in 1949 is noteworthy. He submitted a patent application for an integrated circuit-like semiconductor that, when combined with a three-stage amplifier configuration and five transistors on a common substrate, can be used as an amplifier.
Integrated circuits were first created in 1947 when William B. Shockley and his colleagues at Bell Laboratories of the American Telephone and Telegraph Company invented the transistor. Under the correct circumstances, electrons would form a barrier at the surface of some crystals, as discovered by Shockley’s team (which included Walter H. Brattain and John Bardeen). By adjusting this barrier, one can regulate the flow of electricity through the crystal.
The group was able to develop a gadget that could carry out electrical tasks that vacuum tubes were previously able to do, like signal amplification, through managing the flow of electrons via a crystal. Transistor, a compound word made up of the terms transfer and resistor, was the name given to this device.
Types of ICs
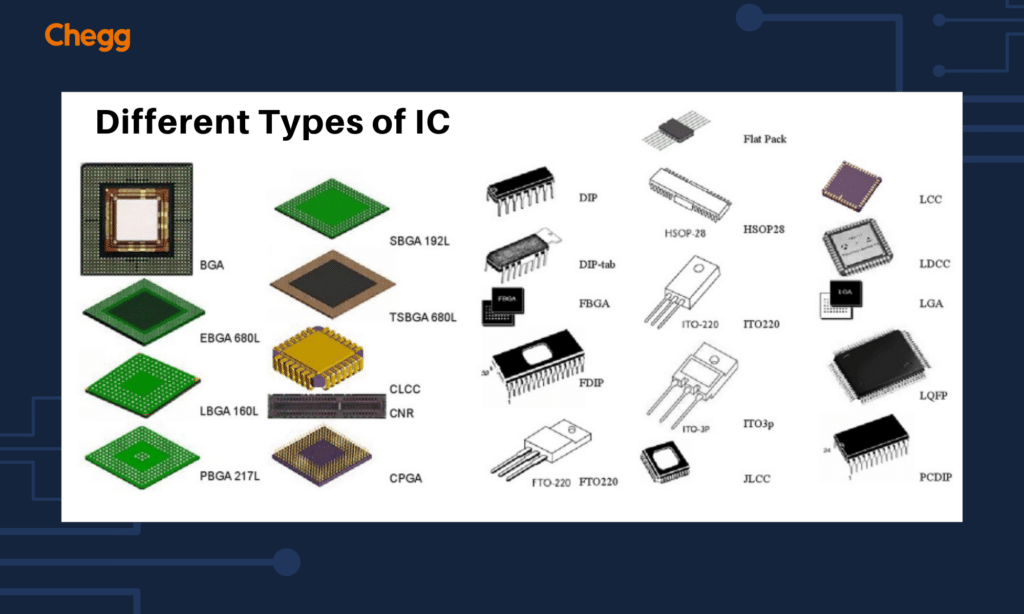
What is the full form of IC? The IC full form is the Integrated Circuit, is an electronic system in which all components are made on a single semiconductor plate or chip.
ICs are divided into two main categories: traditional integrated circuits and digital integrated circuits.
Analog ICs are meant to process ongoing inputs, such as sound or light, whereas digital ICs are used for handling discrete data represented by binary code (0s and 1s). Within these categories, ICs can further be divided into groups such as operational amplifiers (op-amps), microcontrollers, memory chips, and more.
Integrated Circuits, or ICs for short, have gone through many development processes before being categorized as follows:
- Small Scale Integration (SSI): Each chip in this variety has 100 transistors. Small Scale Integration Circuits were used in early aerospace projects.
- Medium Scale Integration (MSI): There are more than hundreds of transistors in this. The total could reach one thousand. After many changes, the chip had hundreds of MOSFETs by the end of the 1960s.
- Large-Scale Integration (LSI): Hundreds of thousands or even more transistors could be found on a single chip thanks to large-scale integration (LSI), which emerged in the middle of 1970.
- Very Large-Scale Integration (LSI): Around 1980, the Very Large Scale Integration circuit was developed, with up to a million or even a hundred thousand transistors per IC.
- Ultra Large-Scale Integration (LSI): These integrated circuits have millions or even billions of transistors.
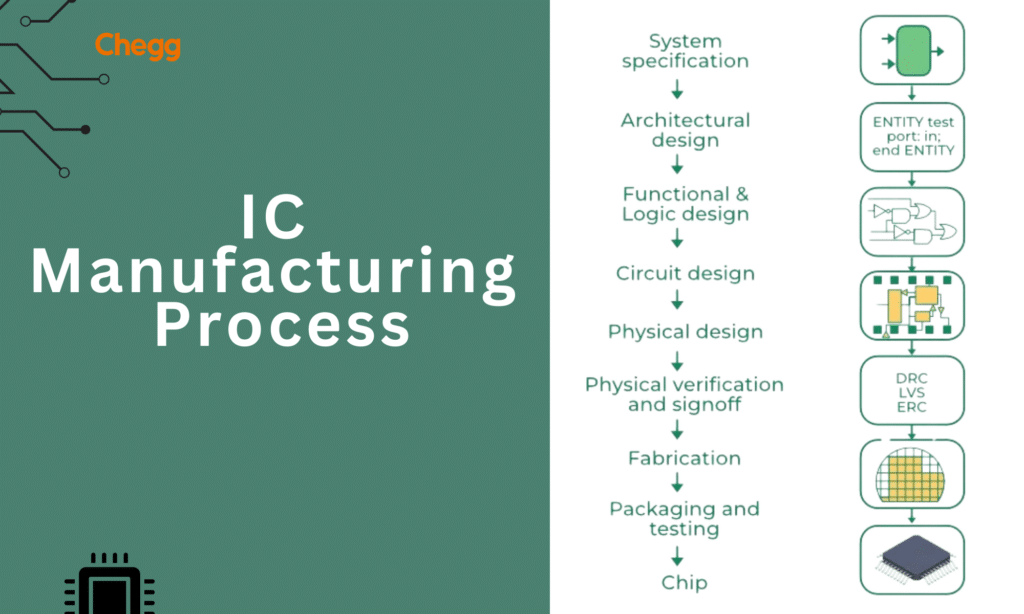
IC Design and Manufacturing Process
The design of an Integrated Circuit (IC full form) comprises an organized process that spans various stages, from idea to final make.
Several tasks are performed throughout the IC-making process:
- Manufacturing of wafers
- Wafer rating
- Wafer chopping
- Packaging
- Final test
- The following steps are involved in the chip-making process:
- Layers are placed one after the other.
- Photolithography
- Etching
- Doping to build circuit components
- The wafers are checked once they have been made.
- Individual chips are made from the testing plates.
- The chips are placed in safety cases.
- The final checking ensures the quality and proper operation of the packed ICs.
- The integrated circuits are later given to customers.
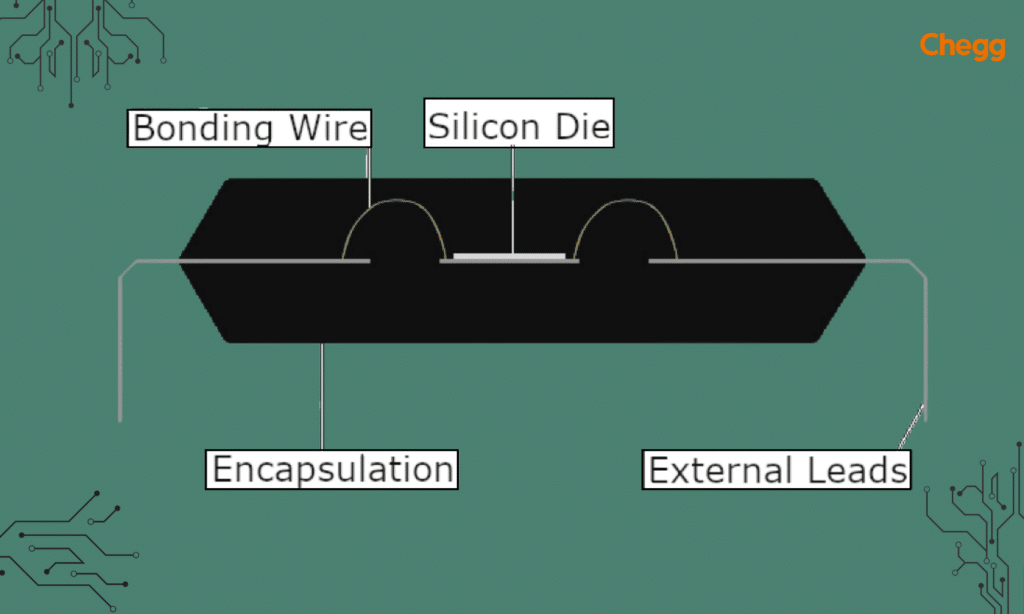
IC Packaging and Integration
Packaging Techniques and Types
IC packing includes wrapping the chip in a protected shell and giving electrical links and mechanical support. There are different packing methods, including leaded packages, surface-mount packages, and chip-scale packages.
System-on-Chip (SoC) and Multi-Chip Modules (MCM)
System-on-Chip (SoC) and Multi-Chip Modules (MCM) are complex packing and assembly methods. SoC unites all or most of the electrical components of a system into a single chip, lowering size, power usage, and cost. MCM combines many IC chips into a single module, combining different functions while keeping flexibility.
Chip Stacking and 3D Integration
Chip stacking and 3D integration methods allow the vertical Integration of many IC chips. This approach boosts the usefulness and performance of electronic systems by reducing link lengths and improving data transfer speeds. Through chip stacking and 3D Integration, the overall size of electronic systems may be reduced, leading to more small and efficient devices.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ICs
Advantages of ICs
Integrated circuits (IC full form) provide major improvements over separate computer components. These include:
- Compactness: ICs compact several components onto a single chip, lowering the size and weight of electrical equipment.
- Reliability: Integrating parts into a single chip reduces the number of links, lowering the danger of failure.
- Power economy: ICs take less power than separate components, improving the energy economy.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Mass production of ICs lowers manufacturing costs, making them cheaper.
- High Performance: ICs offer high-speed data processing and complicated functions.
Disadvantages and Limitations of ICs
Despite their benefits, ICs nevertheless have major limitations:
- Complexity: Designing and producing ICs need specific knowledge and equipment, making the process difficult and costly.
- Heat Dissipation: High-density ICs make heat, and efficient heat dissipation is important to protect their performance and stability.
- Rapid Obsolescence: Rapid technological improvements can make ICs old quickly, requiring regular updates and replacements.
Emerging Trends in IC Technology
Moore’s Law and Scaling Challenges
Moore’s Law, which predicts the doubling of chip density every two years, has driven the growth of IC technology for decades. However, scaling problems appear when transistors hit atomic sizes, making it increasingly difficult to continue the shrinking rate and efficiency improvements. However, Alternative technologies, such as quantum computing and nanoelectronics, are being studied to handle these problems.
Internet of Things (IoT) and ICs
The Internet of Things (IoT) movement has created a demand for ICs to connect and interact with many gadgets. Hence, ICs with low power usage, wireless links, and integrated sensors are important for IoT apps, allowing smart houses, industrial automation, and automated systems.
Applications of IC in Various Industries
The IC in full form is the Integrated Circuit, ICs find broad uses across different industries:
- Electronics for the Home: ICs provide complex functions and high-speed networking to smartphones, tablets, TVs, game systems, and gadgets.
- Telecommunications: Integrated circuits (ICs) provide fast data transfer and network control in mobile networks, satellite communication, and optical communication systems.
- Automotive: Controlling engine operations, entertainment systems, and driving help features, ICs add to car safety, pleasure, and performance.
- Healthcare: In medical equipment, ICs help in tracking, data processing, and correct treatment delivery, which improves patient care and results.
- Defense and aerospace: ICs allow mission-critical activities and national security by ensuring the reliability of communication systems, radar, navigation tools, and electronics.
- Automation in the Industrial Sector: Integrated circuits improve efficiency and safety in industrial automation. Because it gives control and tracks capabilities for production processes and machines.
Future Prospects and Challenges of IC Technology
- IC technology is going to progress, driven by study and development in materials science, nanotechnology, and chip design.
- Materials study, nanotechnology, and chip design are driving ongoing breakthroughs and advances in IC technology.
- Integration of integrated circuits with new technologies such as 5G, AI, quantum computing, and virtual reality for smooth integration and increased power.
- For successful IC development, handle design and manufacturing problems such as power loss, dependability, and yield optimization.
- Focus on sustainability through using energy-efficient integrated circuits, recycling activities to lessen electrical trash, and environmentally friendly materials and production practices.
Conclusion
The IC full form is the Integrated Circuit. ICs have changed the world of electronics and are the backbone of modern technology. Their size, sturdiness, and flexibility have built strong electrical gadgets and systems across different sectors. IC technology continues to improve. Therefore, we may expect more fantastic improvements, Integration with future technologies, and fascinating prospects. However, design, production, and environmental problems need proper solutions to ensure the continued growth and success of IC technology in the future.
Learn more about some other full forms:
| RAM Full Form | CPU Full Form | SSD Full Form |
| HDD Full Form | USB Full Form | ALU Full Form |
| PCD Full Form | MCB Full Form | SIM Full Form |
IC Full Form: FAQs
An integrated circuit (IC) can work as an amplifier, timer, clock, counter, computer memory, logic gate, microcontroller, or microprocessor.
These integrated circuits process analog signals like sound and light. In comparison to digital ICs, they contain fewer transistors but are more difficult to design. Analog integrated circuits can be used in a variety of applications, such as amplifiers, filters, oscillators, voltage regulators, and power management circuits.
Third-generation computers adopted integrated circuit chips. Third-generation computers came to light because of the integrated circuit (IC) development.
Monolithic integrated circuits (ICs) are the most common form of ICs nowadays.
The importance of IC in mobile device circuits to provide data storage to apps. You may lose access to your info if you have a broken flash or memory IC.
IC maker numbers are identification codes that electronics manufacturers place on integrated circuits.
The 555 timer chip, invented in 1971, is still one of the most widely used integrated circuits today. According to some estimates, more than a billion of them are produced and sold each year. The 555 circuit is, as the name implies, a timer.
Got a question on this topic?