Home » Full Forms » GSM Full Form: Global System for Mobile Communications
GSM Full Form: Global System for Mobile Communications

Table of Contents
GSM Full Form
While everyone has heard of GSM, many still don’t know the GSM’s full form. For those wondering what the GSM full form is, it stands for Global System for Mobile Communications. It is a digital cellular technology used for mobile communication systems. GSM is a second-generation mobile network technology that replaced analog mobile systems. It introduced several key advancements, including digital voice transmission, improved call quality, and data services.
Understanding GSM
GSM revolutionized mobile communication in several ways. It laid the foundation for subsequent generations of mobile communication technologies and further expanded the capabilities of mobile networks. Here is how GSM changed the way we communicate:
1. Standardization
Enabling interoperability between different networks and devices.
2. Digital Voice Transmission
Improved call quality, reduced background noise, and increased clarity.
3. Data Services
Enabling users to make voice calls and send and receive text messages.
4. Global Roaming
Allowing users to use mobile phones to make and receive calls and messages and access data services even in different countries.
5. SIM Cards
Made it easy for users to change phones while keeping their phone numbers and personal information intact.
GSM: The Global Standard
GSM’s success and widespread adoption established a clear evolutionary path for mobile networks. As technology advanced, subsequent generations, such as 3G, 4G, and 5G, built upon the foundation laid by GSM. Subsequent generations of mobile technologies have built upon the principles and advancements introduced by a global system for mobile communications, leading to highly connected and advanced mobile networks.
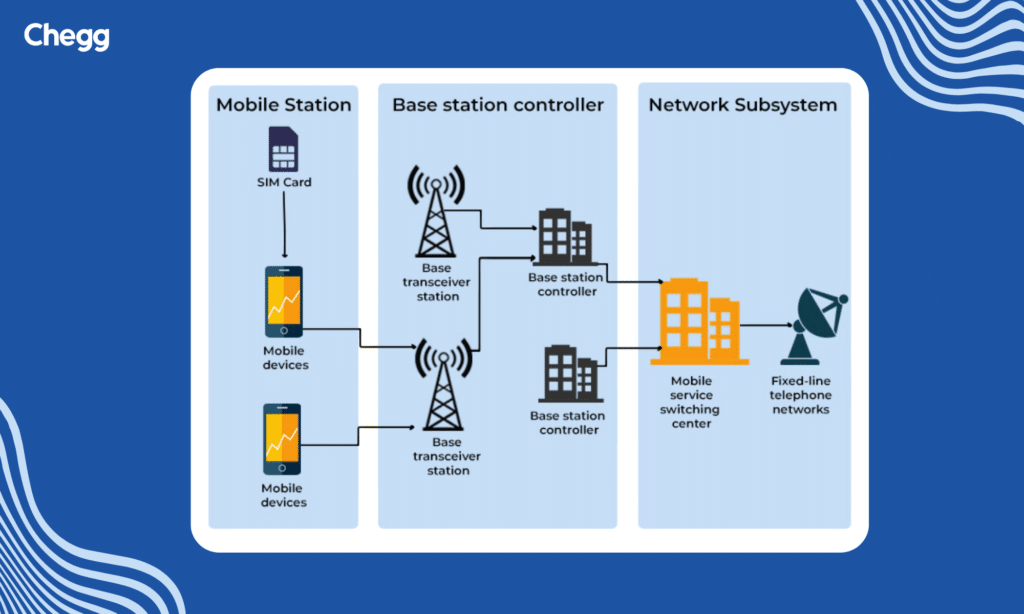
Components of GSM
The essential components of a GSM system are:
1. Base Station Subsystem
- Base Transceiver Station
- Base Station Controller
2. Network Switching Subsystem
- Mobile Switching Center
- Home Location Register
- Visitor Location Register
3. Operation and Support Subsystem
- Authentication Center
- Equipment Identity Register
Advantages of GSM Technology
- Enhanced Security: GSM boasts robust security features. Data, including user identification and network authentication, is stored on a Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) card. This makes it difficult for unauthorized users to duplicate services or access sensitive information.
- Universal Compatibility: A hallmark of GSM is its exceptional compatibility. GSM phones can operate seamlessly on networks worldwide that utilize the GSM standard. This allows for effortless communication when traveling internationally, eliminating the need for region-specific devices.
- Seamless Voice and Data Integration: Unlike some older technologies like CDMA, GSM allows simultaneous use of voice calls and data services. This means you can browse the internet or send text messages while also being available for phone calls – a significant advantage in today’s fast-paced world.
- Crystal-Clear Voice Quality: GSM prioritizes clear and reliable communication. The technology delivers crisp voice quality for calls, ensuring smooth and enjoyable conversations. This clarity is crucial for effective communication, both personal and professional.
Drawbacks of GSM Technology
- Network Congestion and Interference: GSM networks rely on shared bandwidth. During peak usage times or in densely populated areas, this can lead to congestion and decreased signal quality. Multiple users sharing the same bandwidth can create interference, impacting transmission speeds and call clarity. The rise of newer cellular networks like 3G and 4G, which often utilize CDMA technology, addresses this limitation by offering increased capacity and reduced congestion.
- Potential for Electronic Interference: GSM technology uses pulse transmission, which can, in some instances, interfere with sensitive electronic equipment. This is why airlines and hospitals advise passengers to switch their phones to airplane mode – to minimize potential disruption to medical devices or airplane navigation systems.
- Complexity of the System: Compared to newer technologies, GSM can be considered a more complex system. This complexity can impact network maintenance and troubleshooting.
Exploring GSM Frequency Bands
GSM operates on various frequency bands, depending on the region and the specific deployment.
- GSM 900
Range- 890 MHz to 915 MHz (uplink) and 935 MHz to 960 MHz (downlink)
Used in Europe, Africa, Asia, and Oceania.
- GSM 1800
Range- 1710 MHz to 1785 MHz (uplink) and 1805 MHz to 1880 MHz (downlink)
Used in Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Middle East.
- GSM 1900
Range- 1850 MHz to 1910 MHz (uplink) and 1930 MHz to 1990 MHz (downlink)
Used in North America, South America, and some parts of Asia.
Services enabled by GSM
Here is the list of services provided by GSM:
1. Voice Calls
GSM initially focused on providing reliable, high-quality voice communication. It introduced digital voice transmission, which significantly improved call quality, reduced noise, and increased clarity of systems.
2. Short Message Service
GSM introduced SMS, which allows users to send and receive short text-based messages via mobile devices. As SMS offered a quick and cost-effective way to exchange information, it became a popular means of communication.
3. MMS messages
They are typically sent over the data network of a GSM network, such as GPRS or EDGE, and provide the necessary bandwidth to transmit multimedia content.
4. Mobile Internet and Data Applications
With the advancement of GSM and the introduction of GPRS and EDGE, mobile data services expanded to support internet access, email, instant messaging, and basic web browsing.
The Role of SIM Cards in GSM
Subscriber Identity Module or SIM card plays a crucial role in GSM. The SIM card in GSM networks is the portable and secure element that identifies subscribers, enables secure communication, stores personalized subscriber information, supports mobility, and allows access to various network services and value-added features.
Ensuring Security in GSM
Security is an important aspect of GSM networks, and several measures are taken to ensure communication confidentiality, integrity, and authentication. Some security features and mechanisms in GSM are:
- Authentication and Encryption
- Subscriber Identity Protection
- Mutual Authentication
- Ciphering and Encryption
- SIM Card Security
- Network Security
GSM Network Infrastructure
The GSM network infrastructure comprises various elements that provide mobile communication services.
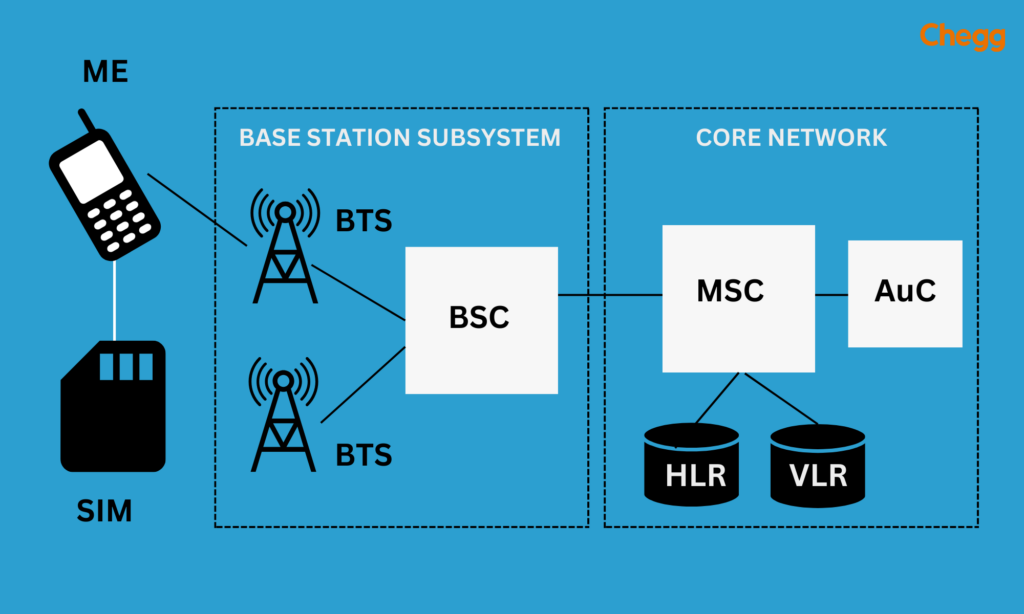
1. Base Transceiver Station
Responsible for transmitting and receiving radio signals to and from mobile devices. It houses the antennas and transceivers communicating with the mobile stations within its coverage area.
2. Base Station Controller
Responsible for managing one or more BTSs. Handles call setup and teardown, traffic management, and coordination between the BTSs under its control.
3. Mobile Switching Center
It handles call routing, mobility management, and other call control functions. It manages subscriber databases, performs call switching, and supports value-added services.
4. Home Location Register
A central database stores subscriber-related information. It includes data such as the mobile number, subscriber profile, authentication credentials, and current location of the mobile device.
5. Visitor Location Register
A temporary database stores subscriber information for visitors roaming in a particular area. It assists in call routing and provides faster access to subscriber data for mobile devices within its coverage area.
Advancement in GSM Technology
GSM technology has undergone several advancements since its inception to meet the evolving demands of mobile communication. GSM was transformed from a basic voice communication system to a versatile platform for mobile data services, multimedia communication, and a wide range of value-added applications. To name a few advancements:
- General Packet Radio Service
- Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution
- Enhanced Voice Services
- Multimedia Messaging Service
- SIM Toolkit
- Security Enhancements
- Evolved GSM Networks
GSM in Everyday Life
GSM has become an integral part of everyday life for millions worldwide. It has permeated various aspects of everyday life, transforming how people communicate, access information, conduct financial transactions, navigate, entertain themselves, and work. Some ways in which GSM technology impacts daily life are mobile communication, internet access, instant messaging, mobile banking and payments, location-based services, mobile entertainment, remote work, productivity, etc.
GSM, CDMA, and LTE: Understanding Their Differences
The world of cellular technology can be a complex one, but understanding the differences between GSM, CDMA, and LTE is crucial for navigating mobile network options. Here’s a breakdown of these key technologies:
GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication):
- The OG: GSM is the granddaddy of the bunch, developed and adopted as a standard in Europe. It utilizes the processor technology of its era for data encoding and decoding.
- Global Reach (with Exceptions): GSM became the dominant cellular technology worldwide, except in the US and parts of South America due to compatibility issues with existing analog systems.
- Focus on Efficiency: GSM offered economies of scale for network operators, making it an attractive option.
CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access):
- Addressing Limitations: As cellular services grew rapidly, TDMA protocols used in GSM networks struggled to keep up. CDMA emerged as a solution, offering increased spectrum efficiency.
- The Power of Codes: CDMA utilizes complex coding schemes for data transmission, requiring powerful processors. This initially led to higher phone costs compared to GSM models.
- Finding a Niche: CDMA gained popularity in countries with older analog AMPS systems due to its compatibility.
LTE (Long-Term Evolution):
- The Data Speed Revolution: LTE represents a significant leap forward from 3G, offering vastly improved data transfer speeds. It’s a GSM technology specifically designed for data, not traditional voice calls.
- VoLTE to the Rescue: For voice calls on LTE networks, a technology called Voice over LTE (VoLTE) is employed, essentially making voice calls over an internet protocol.
- Convergence and the Future: CDMA and GSM eventually converged through a shared encoding protocol called Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA), also used in WiMAX and Wi-Fi networks. As 5G technology unfolds, we can expect further advancements and potential revolutions in mobile communication.
Wrapping up
GSM has revolutionized mobile communication and has become an essential part of everyday life. GSM has had a profound impact on society, enabling seamless communication, connectivity, and access to information, while also transforming industries, enhancing productivity, and improving the quality of life for millions of people worldwide.
Learn About Some Other Full Form:
| RFID Full Form | CGI Full Form |
| XML Full Form | LASER Full Form |
| AI Full Form | PCB Full Form |
| DBMS Full Form | IoT Full Form |
| WWW Full Form | RAM Full Form |
GSM Full Form: FAQs
GSM’s full form is Global System for Mobile Communications. It is a digital cellular network technology that enables mobile communication. It provides the infrastructure for voice calls, text messaging, and data transmission over mobile devices.
Yes. Although newer generations of mobile networks have been introduced, GSM is still used today.
Yes. One of the primary advantages of GSM is its ability to support international roaming. GSM devices can connect to compatible networks in different countries, allowing users to make and receive calls and access data while travelling abroad.
GSM was introduced in the early 1980s, whereas the first GSM network was deployed in 1991.
Technologies like CDMA or WCDMA are not directly compatible with GSM devices. However, many devices currently support multiple network technologies, allowing them to work on different types of networks.
Got a question on this topic?