Quick Summary
Table of Contents
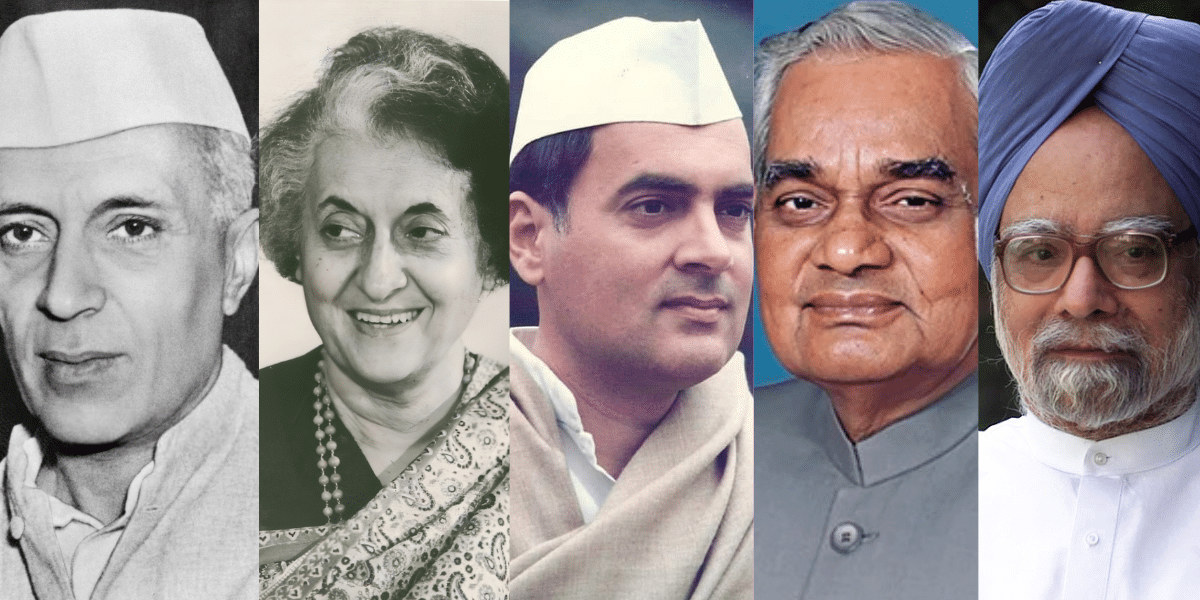
The List of Prime Minister of India features leaders who were visionaries, supporters of impactful initiatives, and key figures in the country’s history. The Prime Minister of India holds one of the most important positions in the nation, with responsibilities of prime minister including governance, policy-making, and shaping the country’s future. They also represent India in international delegations and organizations, acting as the political head of the government.
Many leaders in the all prime ministers list in India have achieved remarkable milestones, helping shape India’s domestic and global presence. The first Prime Minister, Jawaharlal Nehru, played a pivotal role in India’s independence and modernization, while the current Prime Minister, Narendra Modi, has strengthened foreign relations and implemented major domestic reforms.
| S.No | Name of Prime Minister | Tenure Period | Political Party |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Jawaharlal Nehru | 15 Aug 1947 – 27 May 1964 | Indian National Congress |
| 2. | Gulzarilal Nanda (Acting) | 27 May 1964 – 9 June 1964 | Indian National Congress |
| 3. | Lal Bahadur Shastri | 9 June 1964 – 11 Jan 1966 | Indian National Congress |
| 4. | Gulzarilal Nanda (Acting) | 11 Jan 1966 – 24 Jan 1966 | Indian National Congress |
| 5. | Indira Gandhi | 24 Jan 1966 – 24 Mar 1977 | Indian National Congress |
| 6. | Morarji Desai | 24 Mar 1977 – 28 July 1979 | Janata Party |
| 7. | Charan Singh | 28 July 1979 – 14 Jan 1980 | Janata Party (Secular) |
| 8. | Indira Gandhi | 14 Jan 1980 – 31 Oct 1984 | Indian National Congress |
| 9. | Rajiv Gandhi | 31 Oct 1984 – 2 Dec 1989 | Indian National Congress |
| 10. | Vishwanath Pratap Singh | 2 Dec 1989 – 10 Nov 1990 | Janata Dal |
| 11. | Chandra Shekhar | 10 Nov 1990 – 21 June 1991 | Samajwadi Janata Party (R) |
| 12. | P. V. Narasimha Rao | 21 June 1991 – 16 May 1996 | Indian National Congress |
| 13. | Atal Bihari Vajpayee (1st Term) | 16 May 1996 – 1 June 1996 | Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) |
| 14. | H. D. Deve Gowda | 1 June 1996 – 21 April 1997 | Janata Dal |
| 15. | I. K. Gujral | 21 April 1997 – 19 Mar 1998 | Janata Dal |
| 16. | Atal Bihari Vajpayee (2nd Term) | 19 Mar 1998 – 22 May 2004 | Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) |
| 17. | Dr. Manmohan Singh | 22 May 2004 – 26 May 2014 | Indian National Congress |
| 18. | Narendra Modi (1st Term) | 26 May 2014 – 30 May 2019 | Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) |
| 19. | Narendra Modi (2nd Term) | 30 May 2019 – 9 June 2024 | Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) |
| 20. | Narendra Modi (3rd Term) | 9 June 2024 – Present (as of 2025) | Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) |
India’s democratic journey has been shaped by the vision, leadership, and strategic decisions of its Prime Ministers. From laying the foundations of modern India to leading global diplomacy and economic reforms, each leader in the PM of India list from 1947 to 2025 has left a significant mark.
Jawaharlal Nehru, the first Prime Minister in the PM list of India, returned from England after studying at the Inner Temple Bar and immediately entered politics. He became Secretary of the Home Rule League in 1919 and actively participated in India’s independence movement.
Nehru organized the first Kisan March, was imprisoned during the Non-Cooperation Movement (1920-1922), and signed the Nehru Report in 1928, advocating constitutional reforms. His responsibilities of prime minister included guiding India’s modernization through scientific progress and infrastructure development via the Five-Year Plans. His vision earned him recognition on the Prime Minister of India list from 1947 to 2025.
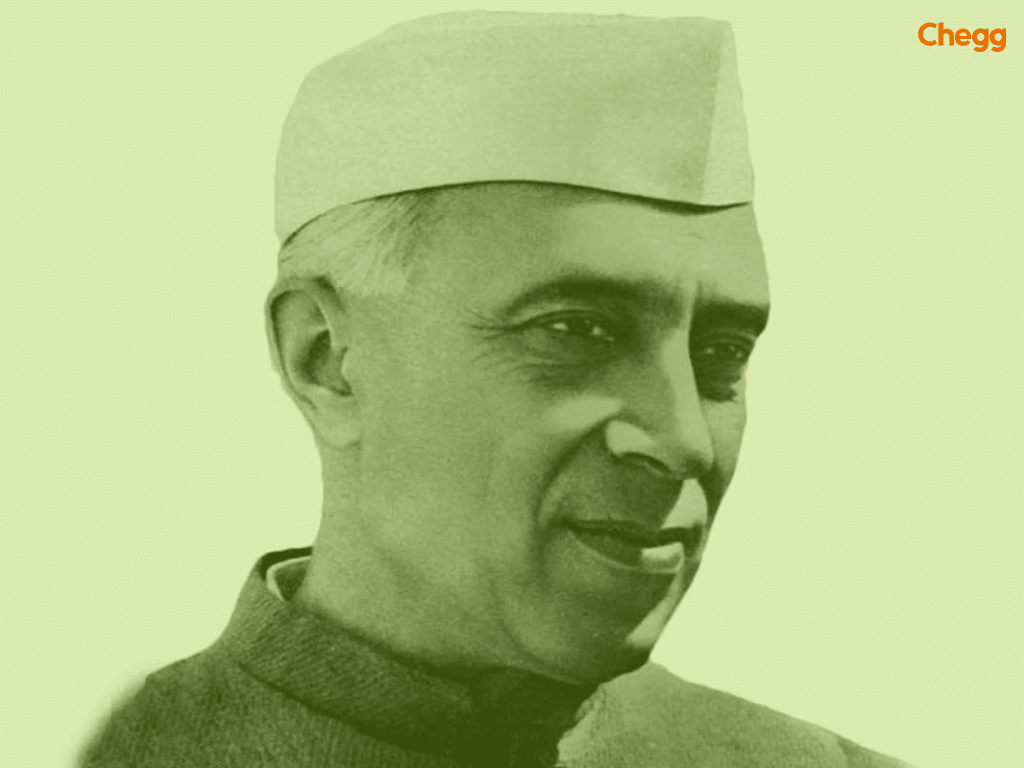

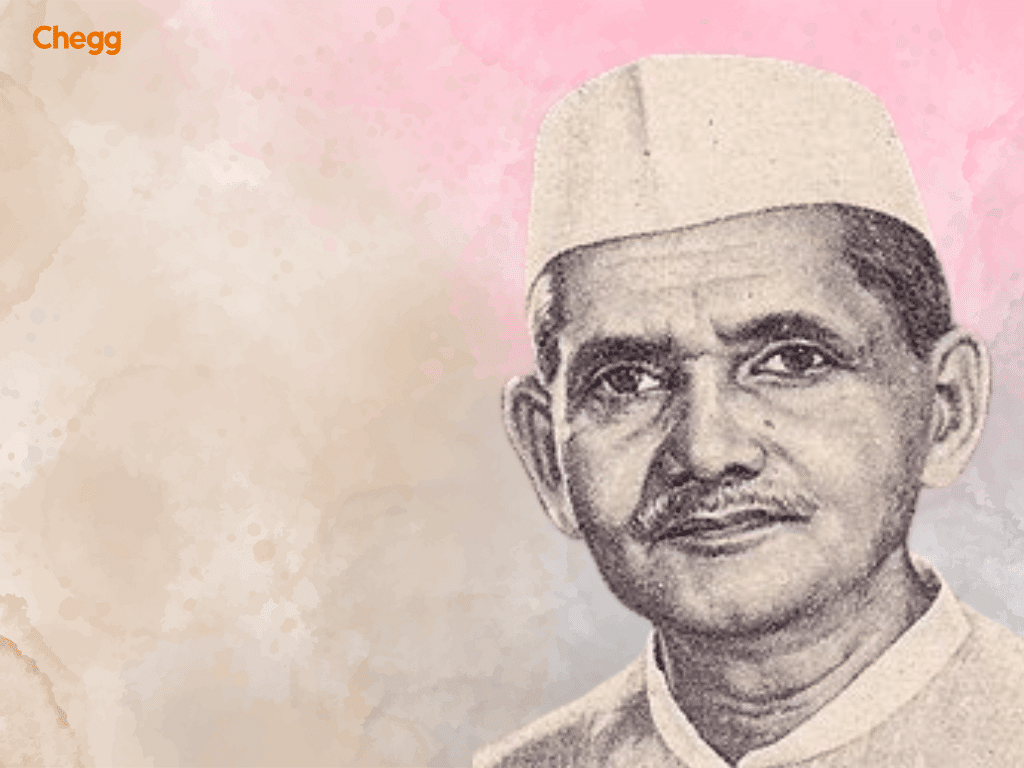
Lal Bahadur Shastri, the second prime minister of India in the List of Prime Minister of India, led India during the 1965 war with Pakistan and promoted national self-sufficiency. His slogan “Jai Jawan, Jai Kisan” encouraged soldiers and farmers alike. Shastri also supported the Green Revolution and agricultural reforms, making him a notable figure in the all prime ministers list in India.
Indira Gandhi, India’s first female Prime Minister, handled internal and international challenges with skill. Her government implemented the Green Revolution’s second phase and ensured food security through hybrid seeds and farmer support. Her decisive leadership during the 1971 war and the 21-month Emergency period cemented her place on the prime minister of India list.
Indira Gandhi’s government played an important role in the Green Revolution. They introduced new hybrid seeds, subsidized farmers, and provided them with water, electricity, and fertilizer. Between 1968 and 1973, the amount of institutional financing available for the agriculture industry was also increased. This was done to ensure food security in India. She also helped with the second phase of Indian Foreign policy from 1966 to 1989. She was known as the “Iron Lady of India” because of her great leadership during the 1971 war and her tough decisions, earning her a place on the list of Prime Minister of India for her remarkable contributions to the nation’s progress.

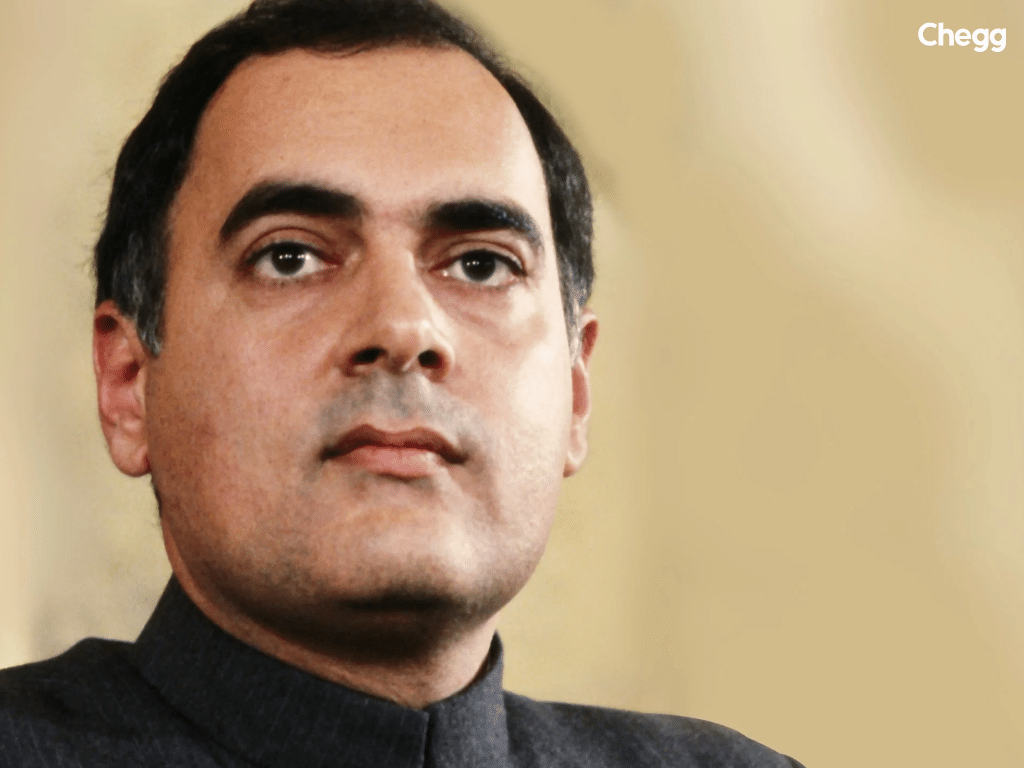
Rajiv Gandhi, at the age of 40, became the youngest Prime Minister in India. He also became the president of the Congress. He was familiar with politics since childhood because he was the son of Indira Gandhi. During his early years, he lived with his grandparents at her official Teen Murti House residence. When he was young, he had no interest in politics. However, he got into politics after his brother passed away, and his leadership later earned him a prominent place on the list of Prime Minister of India.
After the tragic assassination of his mother, he rose to power as the new prime minister. His main goal as list of prime minister of India was to help India advance technologically. His initiatives contributed to India’s global positioning and are highlighted in the Prime Minister of India list from 1947 to 2025. Unfortunately, he was assassinated on May 21, 1991, by a suicide bombing.

Morarji Desai holds the distinction of being the oldest leader in the List of Prime Minister of India, serving from 1977 to 1979. Born on February 29, 1896, in Gujarat, Desai’s journey in Indian politics began with his active participation in the freedom struggle against British rule. He later served as Chief Minister of Bombay State and as Deputy Prime Minister under Indira Gandhi.
During his tenure as part of the prime minister of India list, Desai was renowned for his commitment to transparency, simplicity, and integrity in governance. He implemented key reforms aimed at accountability and reducing government corruption. Despite his age, he demonstrated tireless dedication to public service, earning respect as one of the most disciplined leaders in the all prime ministers list in India.
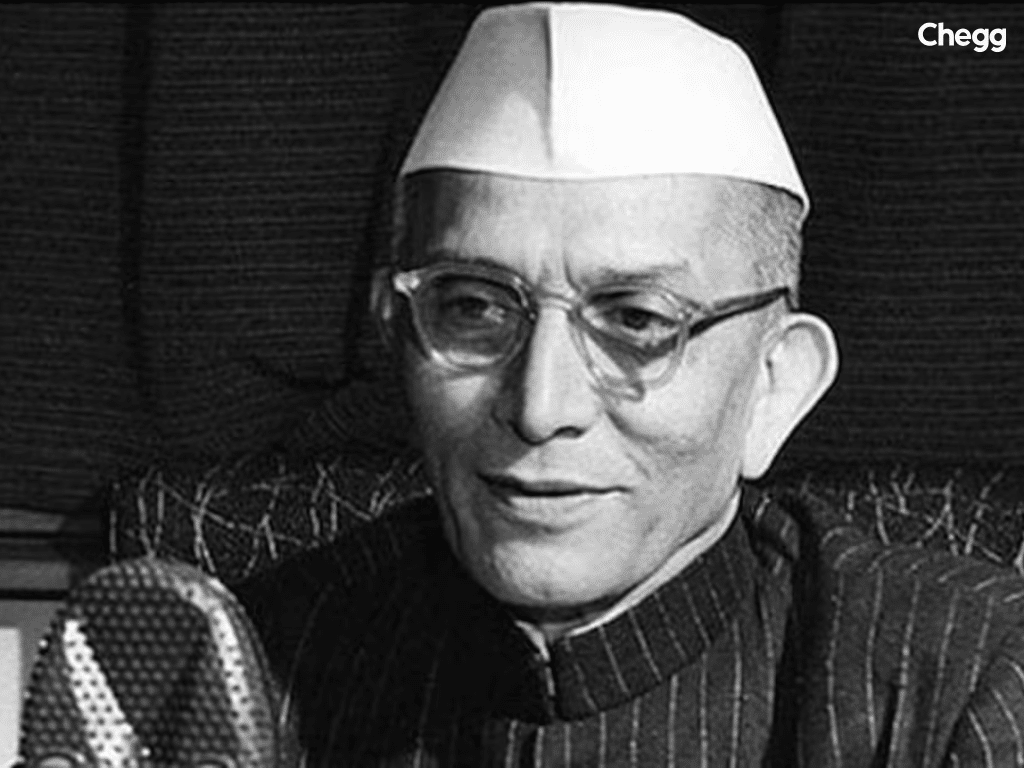

Atal Bihari Vajpayee was the 10th in the list of prime minister of India. He was called a statesman because of his efforts to improve our country’s economy. His leadership style was aimed at avoiding conflict. He preferred finding common ground rather than confrontation.
In May 1998, the Indian nuclear tests held in Pokhran succeeded. During Vajpayee’s government, APJ Abdul Kalam oversaw the nuclear tests. Vajpayee had announced that India had conducted 3 underground nuclear tests at Pokhran. However, he also stated that they would follow the “No First Use” policy. He made it clear that nuclear weapons will never be deployed against a non-nuclear state. He also oversaw the Kargil war and the pursuit of peace with Pakistan, securing his place on the list of Prime Ministers of India for his strong leadership and pivotal decisions during a critical time.

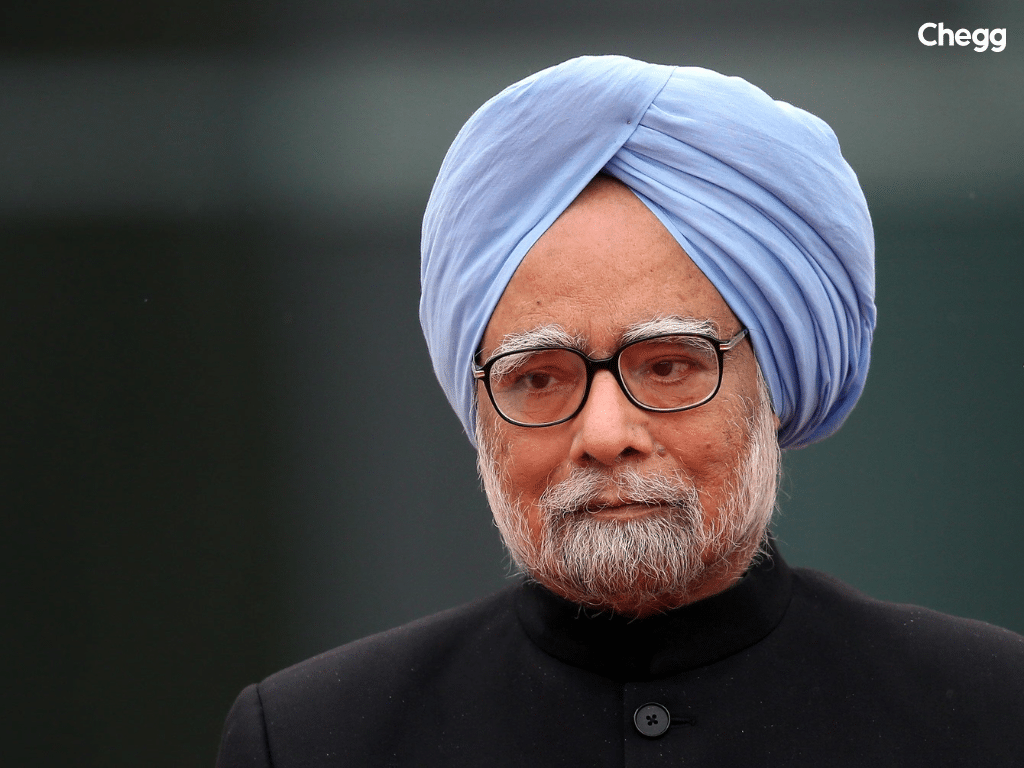
Dr. Manmohan Singh, the 13th leader on the prime minister of India list, served from 2004 to 2014 and recently passed away on December 26, 2024, at the age of 92 while receiving treatment at AIIMS, New Delhi. His tenure was the third-longest in India’s history. Singh continued Vajpayee’s foreign policy approach, focusing on strengthening international relations with the USA, China, and Pakistan.
Under his leadership, India and the United States signed the civil nuclear deal, marking a milestone in bilateral relations. Singh also engaged with three different Pakistani governments, making multiple gestures toward peace. His efforts in economic reforms and diplomacy earned him a prominent place in the all prime ministers list in India.

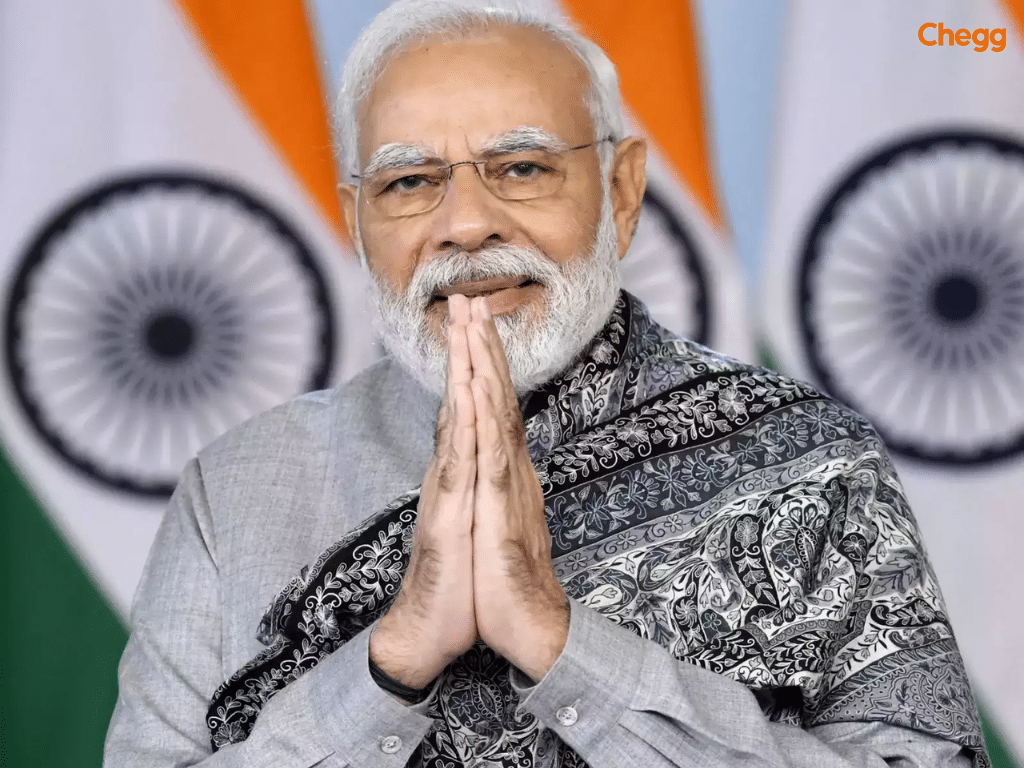
Narendra Modi has been the Prime Minister of India since 2014, bringing a dynamic vision for development, governance, and transformation. His political journey began with the RSS in Gujarat in 1971, and he later joined the BJP in 1985. Rising through party ranks, Modi became Chief Minister of Gujarat, where his Gujarat Model of development gained national attention, establishing him as the BJP’s frontrunner for the 2014 general elections.
Modi’s tenure in the prime minister of India list from 1947 to 2025 is marked by ambitious initiatives in infrastructure, foreign policy, and digital governance. He continues to play a central role in shaping India’s domestic growth and global standing, making him a key figure in the prime minister of India list.

Since becoming Prime Minister of India, Narendra Modi has launched ambitious programs aimed at addressing India’s core challenges and boosting national development. Initiatives like the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan, the world’s largest cleanliness drive, and Digital India have engaged millions, moving India toward becoming cleaner, smarter, and digitally connected. His government has also prioritized infrastructure development through the Smart City Mission, Skill India, and AMRUT Strategy, cementing his position in the List of Prime Minister of India for transformative governance.
Under Modi’s leadership, programs like Make in India and Startup India have strengthened entrepreneurship and created job opportunities, reflecting the responsibilities of a Prime Minister in promoting economic growth and social welfare. These initiatives illustrate how a Prime Minister of India can combine visionary leadership with practical strategies for national progress.
Modi has significantly strengthened India’s international presence, especially with ASEAN, East Asian countries, and key global powers. His foreign policy aligns with India’s Look East and Neighborhood First strategies, emphasizing trade, defense cooperation, and cultural diplomacy. These efforts demonstrate the responsibilities of a Prime Minister in representing India on global platforms, fostering strategic partnerships, and maintaining India’s diplomatic stature.
While Modi’s tenure in the prime minister of India list from 1947 to 2025 is marked by decisive leadership, public engagement, and reforms, his government continues to face challenges. Issues like unemployment, inflation, rural development, and domestic social concerns remain focal points. Despite these, Modi’s administration emphasizes building a self-reliant India, also known as Atmanirbhar Bharat, reflecting the ongoing responsibilities of a Prime Minister in ensuring economic stability and inclusive growth.
Narendra Modi’s tenure has added a unique chapter to the prime minister of India list, blending modernization, foreign diplomacy, and development-focused governance. His efforts in digital transformation, urban infrastructure, and social welfare programs demonstrate how contemporary leaders adapt the responsibilities of a Prime Minister to meet 21st-century challenges.
Every leader in the List of Prime Minister of India has contributed to shaping India socially, politically, and economically. From Jawaharlal Nehru’s vision of modernization to Narendra Modi’s transformative programs, these leaders have collectively created a legacy of excellence in governance. By learning from their achievements and policies, one can understand the prime minister of India list from 1947 to 2025, the responsibilities of a Prime Minister, and the evolving role of India’s top political office in global and domestic affairs.
This comprehensive guide provides insights into the all prime ministers list in India, their contributions, and how each Prime Minister has influenced the country’s journey toward growth and development.
Read More:-
List of Prime Minister of Pakistan
Narendra Modi is the 14th and current Prime Minister on the List of prime minister of India since 26 May 2014. He is the first Indian leader to win three consecutive general elections in 2014, 2019, and 2024, securing a third straight term in office.
Jawaharlal Nehru was the country’s first prime minister of India. He led the Dominion of India from August 15, 1947, to January 26, 1950, and the Republic of India from that date until his death in May 1964.
There have been fifteen prime ministers of India since the country’s independence. The first was Indian National Congressman Jawaharlal Nehru. Since 2014, Narendra Modi of the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) has been as prime minister.
Narendra Modi is currently serving his second term as the Prime Minister of India
As of 2025, Prime Minister Narendra Modi receives a monthly salary of approximately ₹1.66 lakh.
Gulzarilal Nanda was the shortest-serving Prime Minister of India, serving twice as acting PM for 13 days each in 1964 and 1966 after the deaths of Nehru and Shastri.
Several Prime Ministers have received the Bharat Ratna, including Jawaharlal Nehru, Lal Bahadur Shastri, and Atal Bihari Vajpayee.
Rajiv Gandhi, her son, was sworn in as Prime Minister on 31 October 1984, just hours after her assassination.

Authored by, Muskan Gupta
Content Curator
Muskan believes learning should feel like an adventure, not a chore. With years of experience in content creation and strategy, she specializes in educational topics, online earning opportunities, and general knowledge. She enjoys sharing her insights through blogs and articles that inform and inspire her readers. When she’s not writing, you’ll likely find her hopping between bookstores and bakeries, always in search of her next favorite read or treat.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.