Quick Summary
Table of Contents
The Invention of the camera revolutionized how humans capture and preserve memories. Starting with the camera obscura concept, the first successful photographic camera emerged in the early 19th century, thanks to innovators like Joseph Nicéphore Niépce and Louis Daguerre. This blog explores the timeline of camera development, its inventors, and how cameras evolved from bulky boxes to modern digital marvels used worldwide today.

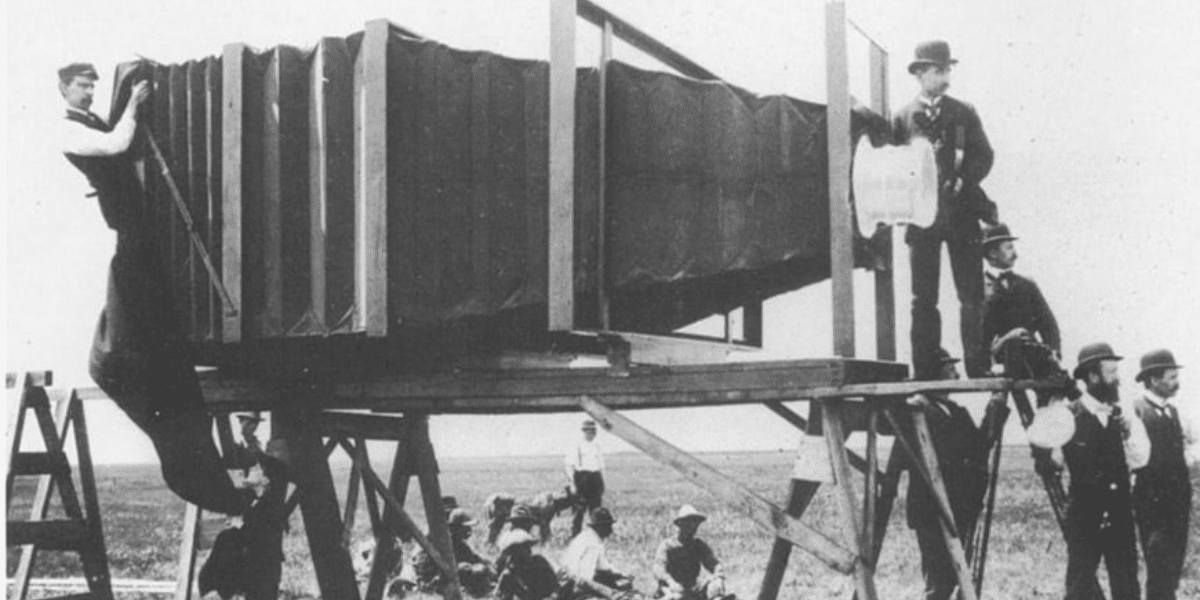
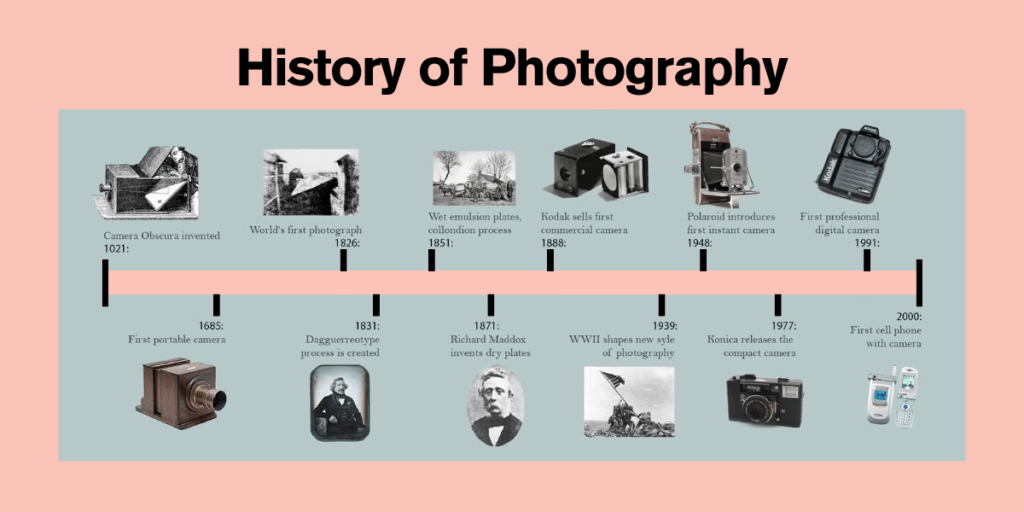
In 1816, Joseph Nicéphore Niépce invented the “Camera Obscura” in France. The word “Obscura” is a Spanish word meaning “Dark”. This camera invention marked a turning point in human history by setting the stage for another era of visual documentation. The history of photography dates back to the early 19th century when the first camera was invented.
Cameras are essential in our daily lives. With the help of a camera or an optical device, images can be stored internally, sent to another place, or used for both. These graphics could still be images from a movie or a simple photo.
A camera is a device that uses light to take still or moving pictures. Light gives everything around us a particular appearance. Without it, we wouldn’t have contrast, highlights, shadows, or colors. To take advantage of this, a camera combines chemistry, mechanics, and optics to cause light to be imprinted on a material that is sensitive to light.
Photographic film serves as the medium for analog cameras. An electronic sensor serves as the medium in digital camera technology. The scene in front of the camera is recreated since the film and sensor respond to light levels differently.
Before answering the question, ” Who invented the camera?”, let us discuss the initial days that led to its invention. Johann Zahn was the first to create a portable camera-like device in 1685. Development did not progress over the next 130 years, and most attempts to develop cameras failed. Joseph Nicephore Niepce took the first picture in 1826 after successfully creating the device in 1816.
Nicephore’s picture did not last long. He took it with a camera he made himself on paper coated in silver chloride. The sections of the paper that did not receive any light turned black. Frenchman Joseph Nicéphore Niépce created the first photographic camera in 1816.
Instead of taking pictures, the camera projected them onto a different surface. By the 17th century, the camera obscura had shrunk down to the point of portability. At this time, they introduced basic light-focusing lenses. Joseph Nicephore Niepce, a French inventor who created the heliograph in 1816, captured the first picture.
While discussing when the camera was invented and its timeline, it’s essential to recognize the many pioneers who contributed to its development. The journey began with the “camera obscura,” a rudimentary device that projected images onto a surface. People knew about this concept in ancient times, but Joseph Nicephore Niepce first practically applied it in the early 19th century.
His work laid the foundation for future inventors like Louis Daguerre, who introduced the Daguerreotype in 1839. This was the first publicly available photographic process, marking a significant leap in camera technology.
Another key figure is George Eastman, who founded Kodak in 1888 and made photography accessible to the public by introducing roll film. This innovation eliminated the need for glass plates, making cameras portable and easy to use. In the 20th century, Edwin Land revolutionized the industry by introducing the Polaroid camera, which produced instant photos.
The evolution of cameras has been remarkable, advancing from simple pinhole devices to the high-tech digital systems we use today. The gradual process of developing the camera has marked significant milestones. Initially, cameras were large, cumbersome devices operated only by professionals.
Over time, they evolved into smaller and more user-friendly gadgets. The transition from film to digital in the late 20th century was another game-changer. It allowed for quicker image processing and storage, paving the way for the digital cameras we use today.
In recent years, smartphone cameras have taken center stage, offering high-quality images with the convenience of portability. The journey from the first Camera to today’s advanced models shows the incredible strides made in technology and design. Each advancement has expanded the Camera’s role, making it an indispensable tool in various aspects of life.
The quest to capture images has been a long-standing human endeavor. Before the camera was invented, people experimented with light and lenses to project images.
The camera obscura, an ancient concept, played a pivotal role in this journey. It was a simple box with a hole on one side that allowed light to pass through. Projecting an inverted image on the opposite side. Artists and scientists used this device to study light and create realistic drawings.
The camera obscura was more than just a tool; it was a stepping stone in the invention process of the Camera. It inspired early inventors like Joseph Nicephore Niepce to think about how images could be captured permanently.
This led to the development of the first Camera and the various photographic processes that followed. The camera obscura, therefore, serves as a landmark in the history of camera invention, bridging the gap between ancient techniques and modern technology.
The first Camera, the “camera obscura,” was a groundbreaking invention. In 1816, Joseph Nicephore Niepce created a simple wooden box with a small aperture to let in light.
The light would then project an image onto a surface inside the box. While the concept was ancient, Niepce’s innovation was in making the image permanent using a plate coated with bitumen.
Early photographic techniques were far from the quick snaps we are accustomed to today. The first process was the Daguerreotype, which Louis Daguerre introduced in 1839.
It involved exposing a silver-plated copper sheet to light, which would then be developed using mercury vapor. The result was a highly detailed albeit fragile image. These early methods were cumbersome and time-consuming, but they laid the groundwork for the rapid advancements in camera technology.
There have been many advancements, from the Daguerreotype to today’s cameras. After the Daguerreotype, other visual techniques were developed, for example, the collodion wet plate and the tintype. These techniques further developed picture quality and diminished openness time, making photography more available.
The Creation of roll film by George Eastman in 1888 was another achievement. It supplanted glass plates, making cameras lighter and more versatile. This prompted the large-scale manufacturing of cameras and permitted photography to become a side interest for the overall population. Headways in film innovation went on throughout the twentieth 100 years with the presentation of various films and upgrades in openness strategies.
In the latter part of the 20th century, digital cameras revolutionized photography. They eliminated the need for film and considered moment review and alteration. As this evolution progressed, cameras have become more versatile and user-friendly, expanding their role in our lives.

George Eastman’s contributions to the world of photography are monumental. He founded Kodak in 1888 and introduced roll film. A technology that made photography accessible to the average person. Before Eastman, photography was a complex and expensive hobby limited to those with technical expertise. Roll film simplified the process, replacing cumbersome glass plates and making cameras portable.
The introduction of the Kodak camera in the late 19th century was a landmark event. The slogan “You press the button, we do the rest” encapsulated the ease of use that Kodak offered. For the first time, photography was not just for professionals or enthusiasts; it was for everyone. The Kodak camera came preloaded with a roll of film for 100 exposures and could be easily sent back to the company for development and printing. This innovation democratized photography, making it a pastime that anyone could enjoy.
Innovative cameras underwent a paradigm shift in the late 19th century. Portable and consumer-friendly cameras were developed during this period, making them distinctive. Because of innovations like roll film and the Kodak camera, it became simpler for the common person to pursue their passion for photography. These devices were lighter, smaller, and simpler than their earlier models.
These inventions significantly influenced the spread of photography. Moments can now be captured by anybody, not only studios or experts. People may bring their cameras along for park walks or even event excursions. Due to its broad acceptance and subsequent democratization, photography has become a universally accepted method of expression and record.
Camera technology made significant strides in the 20th century. A turning point in the century was the debut of instant Polaroid and color film SLR cameras. These developments made photography much more adaptable, enabling creative expression and practical usage in various industries, including journalism and research.
However, the digital revolution of the late 20th century brought the most significant transformation. With instantaneous image viewing and editing capabilities, digital cameras have made film obsolete. This has adjusted how we trade and save photos. Advanced cameras, shrinking or expanding in ability, have finally integrated into cell phones, making photography a fundamental part of our daily existence.
The digital revolution has profoundly impacted photography. It has made it more available and flexible, opening new roads for innovativeness and documentation. The Camera has made some amazing progress from its initial days, and its advancement makes it clear that things are not pulling back.
The camera was not invented in India, but it made its debut during the early 19th century under British rule. The first recorded use of a camera in India dates back to the 1840s, introduced by British photographers and officials. Soon after, Indian pioneers like Raja Deen Dayal embraced photography, laying the foundation for the country’s rich photographic heritage.
Numerous cameras have significantly influenced the history of photography. They altered people’s perceptions of photography and highlighted its various functions, not just because they added amazing new features or technological innovations (e.g., art, documentary, social, cultural, etc.). Here are the most significant ones:
Johannes Gutenberg created the first photograph using a simple wooden box with a lens and light-sensitive material, revolutionizing photography history by enabling the camera obscura.
Wolcott’s photography revolutionized the industry, demonstrating its versatility for recording memories and experimenting with chemicals to enhance the process. His success in portrait studios and lighting laid the foundation for photography.
Richard Leach Maddox invented gelatin dry plates, which Charles Harper Bennett used in his camera to revolutionize instantaneous photography with a 1/25 second exposure time, making it the first “action camera.”
The Kodak Brownie, introduced in 1900, was the first affordable, easy-to-use camera. It transformed photography from professional studios to the streets, and its massive popularity showcased photography’s mesmerizing effect and contributed to early 20th-century social and cultural changes.
The Leica I and II cameras revolutionized photography, introducing 35mm film, interchangeable lenses, and a separate viewfinder, transforming ordinary people into professional photographers. They also influenced landscape, photojournalism, and war photography, influencing the Spanish Civil War and WWII.
Zeiss and Canon pioneered SLR cameras, featuring eye-level pentaprism and a Fresnel lens for accurate image orientation. Modern SLR cameras still use these design features for easy framing.
The world’s first instant camera, released in 1948, revolutionized photography by allowing immediate photo printing without a dedicated studio. Polaroid promoted these cameras among professional photographers like Ansel Adams and Andy Warhol.
In 1999, Nikon released the world’s first purpose-built professional DSLR, the Nikon D1. It features a 2.7MP sensor, 4.5fps continuous shooting, interchangeable lenses, an autofocus system, multiple metering modes, a built-in flash, an optical viewfinder, an LCD screen, and a 1.1kg battery pack.
Leica’s R-D1 was the first mirrorless camera in 2004, featuring a 6.1MP APS-C sensor, manual focus, and Leica M-mount lenses. Despite its small size and 560g weight, it set a precedent for mirrorless cameras, demonstrating their potential.
Leica, a pioneer in 35mm cameras, has influenced famous photographers like Henri Cartier Bresson and Annie Leibovitz. It offers a perfect balance between technical abilities and artistic freedom.
From the camera obscura to today’s AI-powered smartphones, the camera’s evolution is a testament to human innovation, transforming complex chemical processes into instant, professional-quality images. Now deeply woven into our daily lives, cameras are powerful tools for storytelling and preservation, with a future driven by computational photography and AI promising even greater possibilities for capturing and sharing our most meaningful moments.
Read More:-
The term “camera obscura” referred to the first camera. Joseph Nicéphore Niépce created this camera in 1816 in France.
The first photograph was taken in 1826 by Joseph Nicéphore Niépce using a camera obscura. The image, titled View from the Window at Le Gras, required about eight hours of exposure on a pewter plate coated with bitumen, making it the earliest surviving permanent photograph in history.
Most people agree that Louis Daguerre’s daguerreotype Boulevard du Temple, created in 1838, is the first known photograph.
Yes, cameras existed in 1920. By this time, box cameras, folding cameras, and early 35mm film cameras were widely available. Kodak’s Brownie cameras made photography affordable for the public, and professional photographers used large-format cameras with glass plates or roll film. The 1920s marked a key period when photography became more accessible and portable.
George Eastman founded Kodak in 1888 and introduced roll film, making cameras portable and accessible to the general public.
No practical cameras existed in the 1700s, but the concept of camera obscura was known. Photography began developing in the 1800s.
The first camera, known as the camera obscura, evolved into the first photograph-producing camera invented in 1816 by Joseph Nicéphore Niépce.

Authored by, Muskan Gupta
Content Curator
Muskan believes learning should feel like an adventure, not a chore. With years of experience in content creation and strategy, she specializes in educational topics, online earning opportunities, and general knowledge. She enjoys sharing her insights through blogs and articles that inform and inspire her readers. When she’s not writing, you’ll likely find her hopping between bookstores and bakeries, always in search of her next favorite read or treat.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.