Quick Summary
Table of Contents
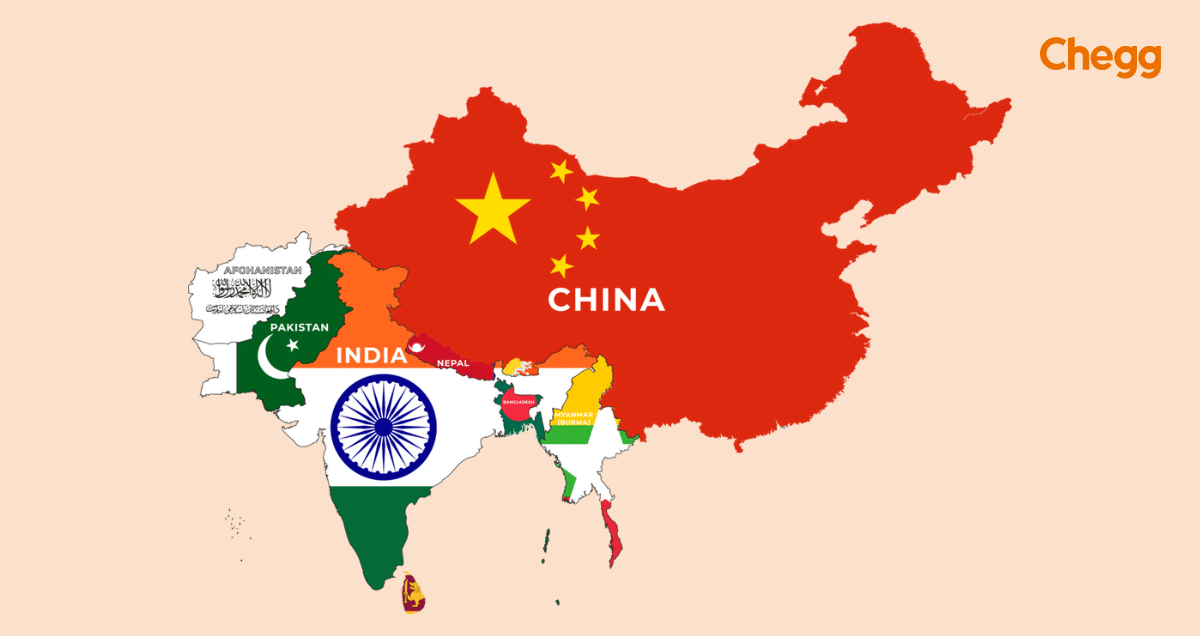
India is the seventh-largest country in the world and shares its borders with seven neighboring countries. Knowing these neighboring countries for geography and understanding India’s history, culture, trade, and international relations is essential. India’s neighbors play a key role in shaping the region, from the Himalayas in the north to coastal borders in the south.
Understanding the neighboring countries of India helps us see how India connects with the rest of Asia. These countries include powerful economies, strategic allies, and culturally rich nations. They also share borders with different Indian states, which makes them essential for local and national interactions.

India shares its borders with 7 neighboring countries, each unique in geography, culture, and bilateral relations.
India has a land border that stretches 15,200 km. India’s coastline, including the mainland, Lakshadweep Islands, and Andaman and Nicobar Islands, is 7,516.6 km. India shares its borders with seven countries:
India also has water borders with two countries:
Understanding the historical and geopolitical context of neighbor countries of India is key to appreciating the region’s complexities. Each neighbor has its unique history and relationship with India, shaped by centuries of interaction, conflict, and cooperation. Here, we provide a concise overview of these relationships.
India and Pakistan were created after British India’s partition in 1947, leading to significant violence and displacement. Major conflicts include the wars of 1947-48, 1965, and 1971, and the Kargil conflict in 1999, primarily over the Kashmir region.
India and China share a long history of cultural and economic exchanges. Border disputes complicate modern relations, notably the 1962 Sino-Indian War over Aksai Chin and Arunachal Pradesh.
Nepal and India share deep cultural and religious ties with an open border. The 1950 Indo-Nepal Treaty of Peace and Friendship is foundational to their relationship.
Bhutan and India enjoy a friendly relationship, strengthened by the 1949 Treaty of Friendship, updated in 2007. India supported Bhutan’s transition to a democratic monarchy.
Bangladesh gained independence from Pakistan in 1971 with India’s support. This historical connection has fostered strong bilateral relations.
India and Myanmar have historical links dating back to ancient trade routes. Modern relations emphasize economic and strategic ties through policies like “Act East.”
India and Afghanistan share ancient trade and cultural connections. Post-2001, India has focused on supporting Afghanistan’s reconstruction.
Neighboring India countries’ historical and geopolitical context highlights South Asia’s intricate dynamics. Each neighbor has a distinct relationship with India, shaped by history and contemporary geopolitical strategies.
The cultural and economic ties between India and its neighbor countries are rich and multifaceted, contributing significantly to regional cohesion and development. Historical connections, shared traditions, and economic collaborations strengthen these relationships.
India and its neighbors share many cultural similarities that bind the region together. These shared aspects foster stronger people-to-people connections and enhance mutual understanding.
Festivals and traditions play a pivotal role in promoting cultural unity and diversity among neighboring countries of India.
Economic ties between India and its neighbor countries are crucial for regional prosperity. These collaborations include trade routes, investment opportunities, and joint ventures that drive economic growth.
Economic corridors and trade agreements facilitate the flow of goods, services, and capital, promoting economic development in the region.
Foreign investments and joint ventures stimulate economic growth and infrastructure development, benefiting all parties involved.
Cultural and economic ties between India and its neighbor countries are vital in fostering regional harmony and development. Shared cultural practices, festivals, and traditions enhance mutual understanding, while economic collaborations drive growth and prosperity.
India’s diplomatic relations and international influence are pivotal in shaping regional and global dynamics. India works towards peace, cooperation, and global impact through various diplomatic initiatives and its role in international organizations.
India is a leader in the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC), a regional forum that promotes economic and regional integration.
India engages in bilateral agreements with neighboring countries to foster peace, cooperation, and mutual development.
India’s participation in international organizations highlights its diplomatic stature and global influence.
India leverages cultural diplomacy and international collaborations to showcase its soft power and global relevance.
Its geographic location and relationships with neighboring countries shape India’s strategic importance and security concerns. Ensuring border security and managing disputes are critical for maintaining national and regional stability.
India’s geographical location and extensive borders with multiple countries give it a strategic position in South Asia.
Maintaining secure and peaceful borders is essential for India’s national security and sovereignty. The country employs various measures to address border security challenges and manage disputes.
India manages border disputes with neighboring countries through dialogue and diplomatic channels to ensure peaceful resolutions.
India’s border security measures protect its territorial integrity and sovereignty.
India faces several security concerns related to its borders, which require vigilant management and strategic planning.
The strategic importance and security concerns of neighboring countries of India play a crucial role in shaping its foreign policy and defense strategies. Effective management of border disputes, robust security measures, and diplomatic initiatives are essential for maintaining regional stability and national security.
Here is the list of neighboring countries of India and their capitals along with other key facts:
| Country | Capital | Border Length with India (Approx.) | Indian States Sharing Border | Type of Border | Key Facts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan | Kabul | 106 km (via PoK) | Jammu & Kashmir (Pakistan-occupied region) | Land (Disputed) | Shares border only through PoK; no direct access from India |
| Bangladesh | Dhaka | 4,096 km | West Bengal, Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram | Land | India’s longest land border; strong trade and cultural ties |
| Bhutan | Thimphu | 699 km | Sikkim, West Bengal, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh | Land | Friendly ties; important buffer between India and China |
| China | Beijing | 3,488 km | Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh | Land | Ongoing border disputes; site of 1962 war and recent standoffs |
| Myanmar (Burma) | Naypyidaw | 1,643 km | Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram | Land | Gateway to Southeast Asia; cross-border ethnic and trade connections |
| Nepal | Kathmandu | 1,751 km | Sikkim, West Bengal, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand | Land | Open borders; deep cultural, religious, and economic links |
| Pakistan | Islamabad | 3,323 km | Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan, Gujarat | Land | Long-standing conflict over Kashmir; fought several wars |
| Sri Lanka | Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte | Maritime only | Tamil Nadu (via Palk Strait / Adam’s Bridge) | Maritime | Strong cultural links; located ~30 km from India by sea |
Key Takeaways:
Travel and tourism between neighboring countries of India play a significant role in fostering cultural exchange and economic growth. India’s rich cultural heritage, historical landmarks, and religious sites attract tourists from across its borders, contributing to the tourism industry.
India’s historical landmarks and cultural heritage sites are major attractions for tourists from neighboring countries.
Religious sites in India are significant pilgrimage destinations for people from neighboring countries, promoting spiritual and cultural ties.
India’s visa policies promote tourism and facilitate cultural exchanges with neighboring countries.
India has initiated various programs to promote itself as a tourist-friendly destination with diverse attractions.
Travel and tourism between India and its neighboring countries are vital for cultural exchange and economic development. India’s diverse tourist attractions, including historical landmarks, cultural heritage sites, and pilgrimage destinations, draw visitors across its borders.
To gеt a bеttеr undеrstanding of neighboring countries of India on the map and thеir gеographical proximity, lеt’s takе a look at a map:
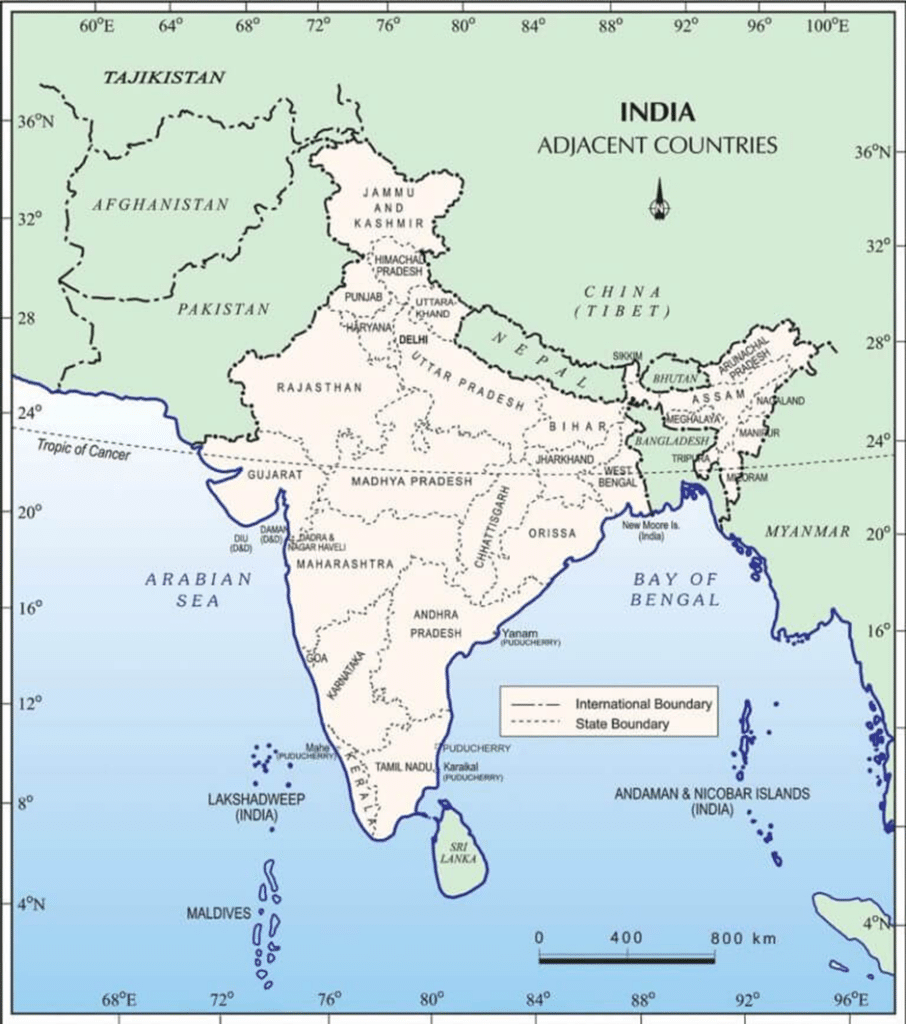
If you’re preparing for a one-day exam, having a solid grasp of India’s neighboring countries on the map is a game-changer! Here are the crucial details you must know:
Here, we present all the important details of Sri Lanka necessary for every government job aspirant for state and central jobs.
| Some Important Facts About Sri Lanka | |
| President | Gotabaya Rajapaksa |
| Prime Minister | Mahindra Rajapaksa |
| Chief Justice | Jayantha Jayasuriya |
| Official languages | Sinhala, Tamil |
| State/ Provinces | 9 states |
| Capital and largest city | Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte |
| Currency | Sri Lankan Rupee (LKR) |
Here, we present all the important details of China that are necessary for every government job aspirant, both state and central.
| Some Important Facts About China | |
| President | Xi Jinping |
| Official languages | Standard Mandarin (Putonghua) |
| State/ Provinces | 23 provinces (excluding autonomous regions, municipalities, and SARs) |
| Capital | Beijing |
| Currency | Renminbi |

Here, we present all the important details of Myanmar necessary for every government job aspirant for state and central jobs.
| Some Important Facts About Myanmar | |
| President | Min Aung Hlaing |
| Prime Minister | Nyo Saw |
| Official Language | Burmese |
| Capital and Largest City | Capital: Naypyidaw Largest City: Yangon |
| Currency | Myanmar Kyat |
Here, we present all the important details of Afghanistan necessary to know every government job aspirant for state and central jobs.
| Some Important Facts About Afghanistan | |
| Head of State | Hibatullah Akhundzada |
| Parliament | Wolesi Jirga |
| Official languages | Dari and Pashto |
| State/ Provinces | 34 Provinces |
| Capital and largest city | Kabul |
| Currency | Afghan Afghani |
Check the important details of our neighbor, Bhutan, which are necessary for every government job aspirant for state and central jobs.
| Some Important Facts About Bhutan | |
| Name of the King | Druk Gyalpo (Dragon King) |
| Monarch | Jigme Khesar Namgyel Wangchuck |
| Prime Minister | Tshering Tobgay |
| Upper House | National Council |
| Official Language | Dzongkha |
| State/Provinces | 20 districts (Dzongkhags) |
| Capital and Largest City | Thimphu |
| Currency | Bhutanese Ngultrum (BTN) |
Check some of the important details of Nepal that are necessary to know every government job aspirant.
| Some Important Facts About Nepal | |
| President | Ram Chandra Poudel |
| Prime Minister | Sushila Karki (Interim) |
| Official Language | Nepali |
| State/Provinces | 7 Provinces |
| Capital and Largest City | Kathmandu |
| Currency | Nepalese Rupee (NPR) |

You can check some of the essential details of Bangladesh, which are necessary to know about every government job aspirant.
| Some Important Facts About Bangladesh | |
| President | Mohammed Shahabuddin |
| Prime Minister | Sheikh Hasina |
| Official Language | Bengali (Bangla) |
| State/Provinces | 8 Divisions |
| Capital | Dhaka |
| Currency | Bangladeshi Taka |
Some crucial facts about our neighbor Pakistan are necessary to know every government job aspirant for state and central jobs.
| Some Important Facts About Pakistan | |
| President | Asif Ali Zardari |
| Prime Minister | Shehbaz Sharif |
| Official Languages | Urdu, English |
| State/Provinces | 4 Provinces (Punjab, Sindh, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Balochistan) |
| Capital | Islamabad |
| Currency | Pakistani Rupee (PKR) |

Here, we present all the important details of the Maldives necessary for every government job aspirant for state and central jobs.
| Some Important Facts About Maldives | |
| President | Mohamed Muizzu |
| Parliament | People’s Majlis (Unicameral, 93 members) |
| Official Language | Dhivehi |
| State/Provinces | 20 Administrative Atolls, 4 Cities |
| Capital and Largest City | Malé |
| Currency | Maldivian Rufiyaa (MVR) |
For India, fostering strong relations with its neighboring countries is a strategic imperative. This diplomacy is crucial for ensuring regional stability and security, which directly enables economic growth through enhanced trade, investment, and cooperation. As a prominent global leader, India’s foreign policy prioritizes these relationships to navigate complex international dynamics. Ultimately, by building mutual understanding and cooperation with its neighbors, India not only secures its own borders but also paves the way for a more integrated, peaceful, and prosperous future for all of South Asia.
Read More:
India shares land borders with 7 countries.
The smallest neighboring country of India in terms of land area is Bhutan.
The 7 neighboring countries of India are:
-Pakistan,
-China
-Nepal
-Bhutan
-Bangladesh
-Myanmar(Burma)
-Afghanistan.
The largest neighboring country of India in terms of land area is China.
Bangladesh shares the longest land border with India, stretching over 4,096 km.
India’s SAARC neighbors include Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.
India has nine neighboring countries Pakistan, Afghanistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, and Maldives linked by land and sea borders.

Authored by, Muskan Gupta
Content Curator
Muskan believes learning should feel like an adventure, not a chore. With years of experience in content creation and strategy, she specializes in educational topics, online earning opportunities, and general knowledge. She enjoys sharing her insights through blogs and articles that inform and inspire her readers. When she’s not writing, you’ll likely find her hopping between bookstores and bakeries, always in search of her next favorite read or treat.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.