Home » General Knowledge » About Black Soil and Types of Soils Its Significance
About Black Soil and Types of Soils Its Significance
Table of Contents
Introduction
The black soils found in the lava-covered regions are the most noticeable among India’s in situ soils. Although they are sometimes referred to as regur, those soils are more commonly referred to as “black cotton soils” since cotton has traditionally been the most widely grown crop in the regions where they are found. On the Deccan lava plateau and the Malwa Plateau, where there is moderate rainfall and underlying basaltic rock, black soils, which are derivatives of trap lava, are mostly found in interior Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Madhya Pradesh. Black soils have a high percentage of clay, which causes large fissures to form during the dry season, yet their iron-rich granular structure prevents wind and water erosion.
Types of Soil in India
The many types of soil in India have produced a rich mosaic of farming techniques, with various crops and cropping systems adapted to various soil and climatic circumstances. For the nation’s food security and agricultural output to be sustained, soil management and conservation practices are essential. India has a wide variety of soils due to its varied geography and climate.
Only two factors—fertile or sterile soil—were used to categorize objects in the ancient era. The categorization was as follows:
- Urvara (fecund)
- Usara (inert)
When mankind became aware of the many attributes of soil in the modern era, they started to categorize soil according to its texture, color, moisture content, etc. Here are the various types of soils found in India.
Alluvial Soil
- Found in the river basins and Indo-Gangetic plains.
- Consists of organic material, sand, clay, and silt.
Black Cotton Soil
- Found mostly in Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, and portions of Gujarat on the Deccan Plateau.
- Clay minerals, notably montmorillonite, are abundant.
- It is well-known for its ability to retain moisture.
Red & Yellow Soil
- Found across India, especially the southern states.
- It thrives in places with abundant rainfall and high temperatures.
- It holds iron oxide, lending it a reddish hue.
Laterite Soil
- The Western Ghats, sections of the Eastern Ghats, and northeastern states are all home to this species.
- Iron-rich soil that has been heavily leached.
Mountainous soil
- Found in hilly and mountainous regions like the Himalayas.
- Varies widely in composition due to local geological conditions.
Arid soil
- Arid parts of northern India, especially Rajasthan, are home to this species.
- Organic matter and moisture-retentive capacity are low.
Saline and Alkaline Soil
- Found along the shore and in locations with poor drainage.
- Alkalinity and high salt content.
Peaty and Marshy Soil
- Found in the swampy areas of Kerala and the Sundarbans delta.
- High organic content and waterlogged.
Diverse soil types have diverse physical and chemical qualities, which influence their appropriateness for various crops. Understanding these features allows farmers to pick the best crops for their location, maximizing production and lowering crop failure risk.
Soil Map of India
Here is a soil map of India
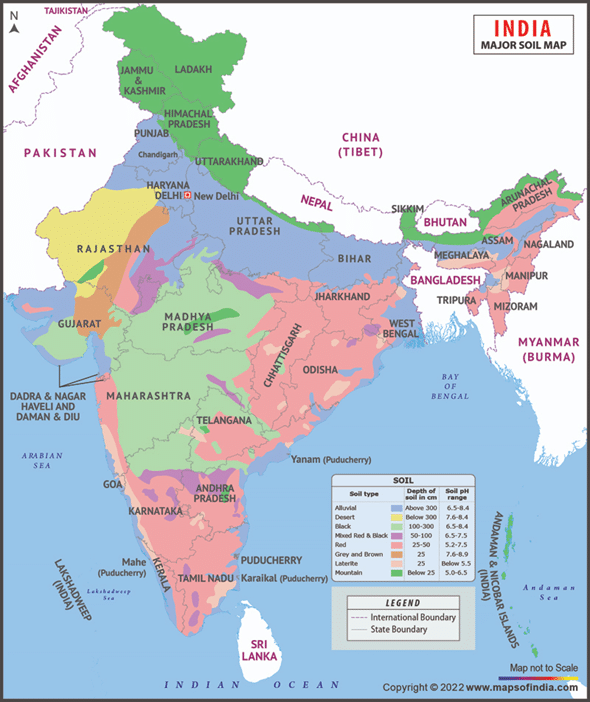
Because of India’s unique geography, temperature, and geological history, the geographical distribution of different soil types can vary greatly. Here is a broad summary of India’s regional distribution of key soil types:
Alluvial
- The Indo-Gangetic plains, comprising sections of Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and West Bengal, are the most common habitat.
Regur Soil (Black Soil):
- Concentrated on the Deccan Plateau, states such as Maharashtra, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and parts of Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh are affected.
Red Soil:
- Southern areas such as Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and parts of Odisha, Jharkhand, and Chhattisgarh have high temperatures and rains.
Arid and Desert
- The plant is found in desert areas of northwestern India, particularly in Rajasthan.
Soil maps show the many types and qualities of soils in a given area. Farmers may use this information to choose the best crops for their individual soil conditions, maximizing production and profitability. The nutrient content and nutrient-holding capacity of different soils vary. Soil maps assist farmers in determining nutrient deficits and excesses, allowing for accurate fertilizer application to maximize crop growth while minimizing environmental consequences.
Black Soil: Characteristics and Formation
Black soil is quite fascinating. It’s a type of soil that has unique qualities, and people often refer to it as “black cotton soil” because it’s excellent for growing cotton.
How It Forms:
The formation of this soil is a gradual and intriguing process. It occurs due to factors like the gradual breakdown of rocks over an extended period. Additionally, the decomposition of plants and animals adds richness to the soil, giving it a distinct dark color.
Special Traits:
This soil is unique for a reason. Most noticeably, it’s really black, making it quite eye-catching. When you touch it, it feels soft and crumbly. Also, when it’s wet, it becomes a bit sticky, like moldable clay.
Significance in Agriculture:
Farmers love this soil because it’s like a superhero for plants. It can hold a lot of water, making sure plants don’t get thirsty. Plus, it gives plants the important stuff they need to grow big and strong. This makes it super important for farming, especially in places like India, where it helps grow all kinds of crops, making sure there’s enough food for everyone.
Black Cotton Soil
Black cotton soil is a fascinating type of earth with distinctive features. Its name comes from its dark color, and it is particularly well-suited for the cultivation of cotton. This soil stands out due to its unique properties and significant role in agriculture.
Properties and Good for Cotton:
The outstanding characteristic of black cotton soil lies in its exceptional water retention capacity. This quality positions it as an excellent choice for cultivating cotton, as the soil retains water for extended periods, ensuring a consistent water supply for cotton plants. Additionally, the soil exhibits a soft and crumbly texture, transforming into a sticky consistency, reminiscent of cotton candy, when wet.
Why it Matters in Indian Farming:
The significance of black cotton soil in Indian agriculture cannot be overstated. Its suitability for cotton cultivation is akin to a natural boon for farmers. The soil’s capacity to retain water and furnish essential nutrients creates an environment conducive to robust crop growth. This factor plays a pivotal role for Indian farmers, significantly contributing to high crop yields and bolstering the overall agricultural productivity of the country. In essence, black cotton soil transcends its earthly nature; it stands as a valuable resource crucial to the prosperity of Indian farming.
Major Soil Types in India Map
Below is a map of the major soil types in India:
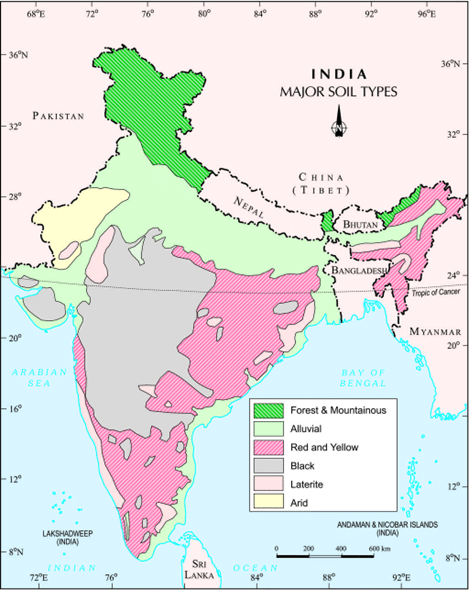
Here are some of the most prevalent states and places where black soil may be found:
- Maharashtra: Much of Maharashtra, particularly in the Vidarbha area, has black dirt. Nagpur and Amravati are well-known for their black cotton soil.
- Gujarat: Gujarat’s Saurashtra region features substantial sections of black soil, notably in districts such as Bhavnagar, Amreli, and Surendranagar.
- Madhya Pradesh: Madhya Pradesh has black soil in areas such as the Malwa region and districts such as Hoshangabad.
- Karnataka: Northern Karnataka has a lot of black soil, especially in areas like Raichur and Bellary.
- Andhra Pradesh: Andhra Pradesh has black soil in several areas, especially the Rayalaseema region.
In India, the different types of soil are super important for farming. They affect which crops to grow, how to water them, and how to use the land. Knowing about these soils is crucial for farming that takes care of the environment and lasts a long time. Soil mapping is a big help. It gives farmers and others important info to make smart choices. This helps grow more crops, keep the environment safe, and make sure farming can keep going for a long time. Soil mapping is like a tool that’s needed for modern and smart farming.
Also Read :-
The Ecological Pyramid: Dеfinition, Biomass,Types.
Father of Green Revolution in India: Discover the Pioneer
National Science Day: Notable Celebrations, Impact.
Agriculture and Black Soil in India
Black soil, or Regur soil, is a boon for certain crops. It acts as a nurturing bed for crops like cotton, soybeans, and sugarcane due to its exceptional fertility.
Role of Black Soil in Indian Agriculture:
Black soil plays a pivotal role in Indian agriculture. Its fertility level is a game-changer, supporting high yields and contributing significantly to the nation’s food production and economic prosperity.
Challenges and Opportunities in Farming on Black Soil:
While farming on black soil presents exciting opportunities, it comes with challenges such as water retention issues. Smart irrigation practices and conservation methods provide opportunities for farmers to overcome these challenges, ensuring sustainable and fruitful farming ventures.
In summary, the partnership between agriculture and black soil is rich and dynamic, supporting the growth of essential crops, driving agricultural success, and offering both challenges and opportunities for India’s farming community.
Conservation and Management and Significance of Black Soil in India
Black Soil in India: Nurturing Prosperity
Importance of Soil Conservation:
Black soil, also known as Regur soil, is a treasure for Indian agriculture. Its conservation is vital to maintaining fertility and ensuring sustained agricultural productivity.
Methods for Preserving Black Soil Fertility:
To preserve its fertility, farmers adopt practices like crop rotation, organic farming, and minimal use of chemical fertilizers. These methods enhance soil structure and nutrient retention.
Sustainable Farming Practices in Black Soil Regions:
Embracing sustainable practices, such as water conservation, agroforestry, and contour plowing, helps safeguard black soil. These methods promote long-term environmental and agricultural sustainability.
Economic Importance of Black Soil:
Black soil contributes significantly to India’s economy. It supports the growth of various crops like cotton, soybeans, and sugarcane, playing a pivotal role in the country’s agricultural and economic prosperity.
The conservation and management of black soil in India are essential for maintaining its fertility, supporting sustainable farming practices, and ensuring continued agricultural prosperity. Recognizing the economic, historical, and cultural significance of black soil underscores the importance of preserving this valuable resource for future generations.
Conclusion
To sum up, looking after India’s black soil is vital for successful farming. Farmers use clever methods, like growing different crops and using natural fertilizers, to keep the soil healthy. This not only ensures abundant food production but also safeguards the land for the future. It’s akin to preserving a valuable treasure that sustains both agriculture and the environment, fostering prosperity for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions ( FAQ’s )
The pH of black soil, which is also called Regur or Black Cotton soil, is usually around 6.5 to 7.5. This pH range is good for growing different crops like cotton, cereals, oilseeds, and some pulses. Black soil is known for its fertility, making it suitable for agriculture. Keep in mind that the pH level can slightly vary based on factors like location and how the soil is managed.
Crops like blueberries, potatoes, and rhubarb grow well in acidic soil. These plants prefer soil with a lower pH, making them suitable for such conditions.
To test soil pH:
1. Collect soil samples.
2. Remove debris, let soil air-dry.
3. Use a pH testing kit or meter, follow instructions.
4. Read results from the color change.
5. Interpret pH: below 7 is acidic, 7 is neutral, above 7 is alkaline. Regular testing helps plant care.
Black soils are generally not recommended for construction due to their moisture-absorbing properties. They can expand when wet and shrink when dry, causing stability issues.
Plants like broccoli, cauliflower, and spinach thrive in alkaline soil. These crops prefer soil with a higher pH, making them well-suited for such conditions.
Got a question on this topic?