
Quick Summary
-
Managerial economics is a stream of management studies that focuses on solving business problems and making decisions by applying the theories & principles of microeconomics & macroeconomics.
-
3 concepts of managerial economics are liberal managerialism, normative managerialism and radical managerial.
Table of Contents
Businesses must make critical decisions every day. Managerial Economics equips managers with the tools and techniques to analyze market demand, assess costs, determine pricing strategies, evaluate risks, and understand competitive dynamics. These decisions can involve investment opportunities, new products, emerging competitors, or the overall direction of the company.
When it comes to such important decisions, businesses rely on experts with a background in managerial economics. When we think about how to define managerial economics. The question also arises how these experts assess the monetary value of various opportunities and advise the company on how to proceed.
What is Managerial Economics?
Managerial economics is a stream of management studies that focuses primarily on solving business problems and making decisions by applying the theories and principles of microeconomics and macroeconomics.
It is a specialized stream dealing with an organization’s internal issues using various economic tools. Economics is an indispensable part of any business. This single concept derives all the business assumptions, forecasting, and investments.
Nature and Scope of Managerial Economics
You need to know about the various characteristics of managerial economics to gain more knowledge about it. Let’s read in detail about the nature of managerial economics.
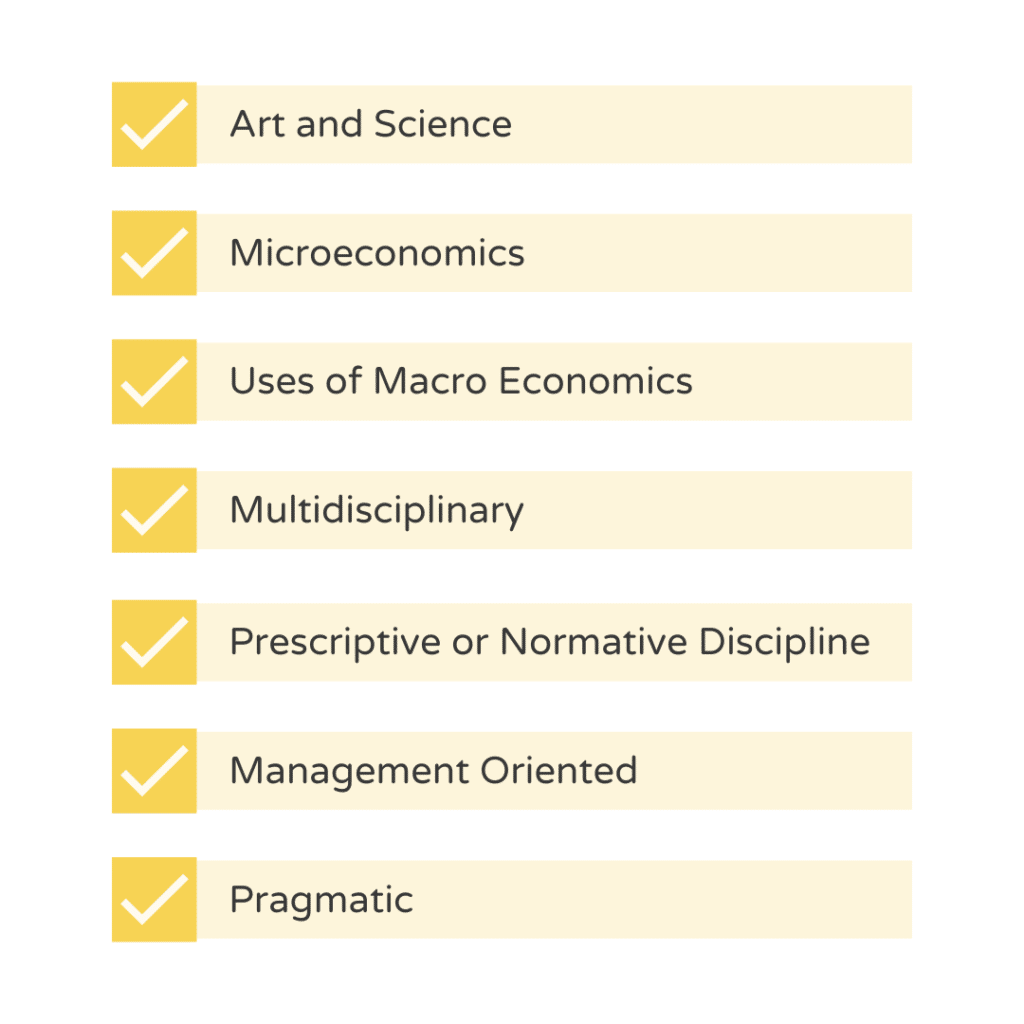
The concept of nature of managerial economics includes the following:
1. Art and Science
Management theory requires a lot of critical and logical thinking and analytical skills to make decisions or solve problems. Many economists also find it a source of research, saying it includes applying different economic concepts, techniques, and methods to solve business problems.
2. Microeconomics
Managers typically deal with problems relevant to a single entity rather than the economy as a whole. It is, therefore, considered an integral part of microeconomics.
3. Uses of Macro Economics
A corporation works in an external world, i.e., serving the consumer, an important part of the economy. For this purpose, managers must evaluate the various macroeconomic factors, such as market dynamics, economic changes, government policies, etc., and their effect on the company.
4. Multidisciplinary
Managerial economics uses many tools and principles that belong to different disciplines, such as accounting, finance, statistics, mathematics, production, operational research, human resources, marketing, etc.
5. Prescriptive or Normative Discipline
By introducing corrective steps, managerial economics aims to achieve its objective and solves specific issues or problems.
6. Management Oriented
This serves as an instrument for managers to deal effectively with business-related problems and uncertainties. This also allows for setting priorities, formulating policies, and making successful decisions.
7. Pragmatic
The solution to day-to-day business challenges is realistic and rational.
Different individuals take different views of the principles of managerial economics. Others may concentrate more on customer service and prioritize efficient production.
Recommended Read: Nature and Scope of Macroeconomics
Scope of Managerial Economics
The definition of managerial economics is commonly used to deal with various business problems within organizations. Both microeconomics and macroeconomics have an equal effect on the organization and its work. The following points illustrate the scope of managerial economics:
1) Micro-Economics applied to Operational Matters
The various theories or principles of microeconomics used to solve the internal problems of the organization arising in the course of business operations are as follows:
- Demand Theory: Demand Theory emphasizes the consumer’s behavior toward a product or service. This considers the customers’ desires, expectations, preferences, and conditions to enhance the manufacturing process.
- Decisions on Production and Production Theory: This theory is primarily concerned with the volume of production, process, capital and labour, costs involved, etc. It aims to optimize the production analysis to meet customer demand.
- Market Structure Pricing Theory and Analysis: It focuses on assessing a product’s price considering the competition, market dynamics, production costs, optimizing sales volume, etc.
- Exam and management of profit: the companies are operating for assets; hence, they aim to maximize profit. It also depends on demand from the market, input costs, level of competition, etc.
- Decisions on capital and investment theory: Capital is the most important business element. This philosophy takes priority over the proper distribution of the resources of the company and investments in productive programs or initiatives to boost operational performance.
2) Macro-Economics Applied to Business Environment
Any organization is greatly affected by the environment in which it operates. The business climate can be defined as follows:
- Economic Environment: A country’s economic conditions, GDP, government policies, etc., have an indirect effect on the company and its operations.
- Social Environment: The society in which the organization works, like employment conditions, trade unions, consumer cooperatives, etc., also affects it.
- Political Environment: A country’s political system, whether authoritarian or democratic, political stability, and attitude towards the private sector, impact the growth and development of the organization.
The Concepts of Managerial Economics
The branch of managerial economics comprises various concepts:

1. Liberal Managerialism
A market is a democratic space where people make their choices and decisions. The organization and its managers must function according to the customers’ demand and market trends; otherwise, this can lead to business failures.
2. Normative Management
Managerial economics’ normative view states that administrative decisions are based on experiences and practices of real life. They systematically study demand, forecasting, cost control, product design and promotion, recruitment, etc.
3. Radical Management
Managers have to have a creative approach to business concerns, i.e., make decisions to improve the current situation or circumstance. We concentrate more on the needs and satisfaction of the consumer rather than just the maximization of income.
4. Managerial Economic Values
The excellent macroeconomist N. Gregory Mankiw has given ten principles to explain the significance of managerial economics in business operations.
Principles of Managerial Economics
Managerial economics follows several principles. These principles help in assessing its application in diverse areas. Both conceptual and metrical aspects are dealt with in this field. Problems often arise due to a disequilibrium in the economic theory and managerial theory of business organizations. Various analytical tools enable firms to identify the nature and measure of problems.
The principles of managerial economics are as follows:
1. Principles of How People Decide
Let us go through the following principles to understand how decision-making takes place in real life:
- Humans face trade-offs: To make decisions, people have to determine whether to choose from the different options available or not.
- Price of Opportunity: Each decision involves a cost of opportunity, which is the cost of those options we let go of while choosing the most appropriate one
- Feel fair about the margin: People typically think about the margin or income they receive before investing in a specific project with their money or resources.
- People respond to stimulus: Decisions to be made highly depend on incentives related to a product, service, or activity. Negative incentives discourage people, while positive incentives encourage them.
2. Principles of How People Interact
Communication and the market impact business transactions. Let us take a look at the following related principles to justify the statement:
- Trade could benefit anyone: The theory states that trade is a way to share. Everyone gets an opportunity to offer the good products or services they make and buy the products or services that other people are good at manufacturing.
- Markets usually represent a well-organized economic activity: Markets serve as a means of customer and product interaction. Consumers express their desires and expectations (demands), while producers determine whether or not to manufacture necessary products or services.
- Governments may often boost market performance: During adverse market conditions or for the benefit of society, the government intervenes in business operations. An example of such a circumstance is when the government agrees on minimum wages for the benefit of workers.
3. Principles on How Economy Works
The following theory outlines the economic role of an organization’s functioning:
- A country’s standard of living depends on its capacity to generate goods and services: Companies must be productive enough to produce products and services to develop a country’s economy. Ultimately, it meets the customer’s demand and enhances GDP to increase the standard of living in the country.
- Prices increase when the government prints lots of money: Suppose surplus money is available to citizens, and their capacity to spend increases. Eventually, it would lead to a rise in demand. Inflation takes place when manufacturers are unable to satisfy market demand.
- Society faces a short-term correlation between unemployment and inflation: The government introduces numerous economic policies to reduce unemployment. In the short term, such policies target improving the economy and what kind of practice contributes to inflation.
Top Career Options in Managerial Economics
Management economics is an important method for assessing the company’s priorities and objectives, the organization’s current role, and what the management can do to fill the void between the two.
Deriving from the definition of managerial economics, we have listed the best options you can pursue in this field.
1. Banking Sector
Banking sector job profiles are financial analysts, consultants, financial advisers, investment bankers, environmental policymakers, development officers, or part of Research and Development. The job in banking sector comes on top when we think about the scope of managerial economics
2. Business Economist
They deal with various sectors and companies, and their main role is to serve as an intermediary between the corporate world and the outside world.
3. Higher Studies
There are several programs and courses to procure a degree in managerial economics. You can acquire in-depth knowledge in this field by doing higher studies in this subject. Many renowned institutions offer such programs along with good placements. Having high-level knowledge can fetch you impeccable opportunities.
4. Credit and Risk Manager
They analyze the company’s financial details and calculate the associated default risk to help the lender and the buyer.
5. Financial Controller / Economist
A financial controller, or economist, is concerned with analyzing the day-to-day financial operations of an organization. He/she supervises the finance and accounting department and prepares financial reports.
6. Market Analyst
A market analyst analyses the market so that their employers can make a better decision concerning product launches or rendering services.
7. Operations Manager
From output to the review of statistics to educating new staff, an operations manager manages all day-to-day activities in the company and needs to ensure that the organization runs optimally.
8. Teaching
If you want to be a lecturer or become a senior economics teacher in private schools, apply for the NET / CTET exam in the field of education. After completing an M.A in Economics with a mark of at least 55 percent, an applicant can either seek a Ph.D. at any college or appear for UGC-NET. The exam is administered by the NTA.

9. Equity Analyst
An equity analyst extracts equity information for investment purposes and explores stock market insights to identify where to invest or whether to proceed or sell on the market.
10. Cost Accountant
A Cost Accountant plans, studies, and records the costing concepts of an organization. He/she analyzes the fixed and variable costs to obtain the company’s total cost. A cost accountant is one of the exciting career options under the scope of managerial economics.
11. Economic Services of India
You can join the Economic Services of India. To join this service, you have to appear for the Indian Economic Service Exam. You should have completed a M.Sc. or MA. in economics with at least 55 percent marks. The age range is 21-30 years. UPSC administers the test.
12. Public Sector Banking Services
The Reserve Bank of India also recruits banking-sector economists through various recruitment exams. The age limit is 21-28 years.
13. Private and Foreign Banks
An Economics degree holder can try for both private and foreign banks. The Banking job categories are branch managers, clerks, economic analysts, planning and development officers, etc.
14. Agricultural Economist
Agricultural Economics is an advanced branch of Economics. An agricultural economist optimizes the production, distribution, and consumption of food and fiber products.
15. Agencies Worldwide
Experienced and professional economists in well-known international organizations such as the World Bank and the International Labor Organization (ILO) can get great employment opportunities.
16. Work as an Advisor
Graduates in Economics can work as economic consultants independently. In the case of various scientific research and consulting in the private sector, companies can ensure optimal job opportunities. The position include Economic Researcher, Business Economist, Investment Analyst, etc.
17. Entrepreneurship
Economists possessing a profound understanding of the market can create their own start-ups. They can evaluate the industry dynamics and competitive business sectors and, thereon, design their business processes. Ultimately, they can achieve exponential growth by starting their own business. Besides, it will also aid the unemployment problems in the country by generating work opportunities.
18. Mass Media and Journalism
You can also join the news media by becoming an economic or editorial journalist. You can complete your graduation or post-graduation in mass communication and head towards joining mass media. Even if your educational discipline is different, you can take advantage of this option. By having the required knowledge and skills relating to this field, you can grow in your career exceptionally.
Also, Read: Career Options in Economics
Importance of Managerial Economics
Managerial economics holds great importance in various management processes. The main importance of managerial economics in an organization is Demand Analysis & Forecasting, Profit management, and Capital Management. It assists an organization in its decision-making process by integrating the tools and techniques of economic theories with multiple business activities.
Managerial economics deals with the optimum utilization of scarce resources. It ensures the proper functioning of the firm by using the resources effectively. It guides the management in rational decision-making, implementing both economic theories and econometrics. With the help of factual data solutions, several economic problems are curated.
Learn Economics with Chegg
Learn with Chegg and get expert help for your studies online. Chegg is a globally recognized educational provider. It is highly acknowledged by students across the world.
Students worldwide trust Chegg for helping them with their studies. You can simplify your complex topics with the help of experts at Chegg. Chegg comprises an efficient team of Subject-Matter Experts (SMEs) who assist in clearing your concepts. They break down complex topics into simple terms and create easy explanations with the help of definitions, videos, illustrations, and many more.
Are you interested in the subject of Economics? Do you want to learn more about it? Our experts will help you out. Get wide exposure to the world of economics and clarify various concepts from your home. All you need to do is sign up.
Managerial Economics at a Glance
- Managerial Economics amalgamates economic theories with managerial practices. It is a tool used by organizations to formulate various managerial decisions. It aids the organization in numerous decision-making processes.
- Business organizations curate strategies for management planning by using the various tools and techniques of economics.
- Managerial economics can be defined as the branch of economics which combines economic theories with business and management practices. It helps business organizations make various managerial decisions.
- The characteristics of managerial economics are art as well as science, microeconomics, macroeconomic usage, multi-disciplinarity, prescriptive discipline, management-oriented, and pragmatic.
- The concepts of managerial economics include Liberal Managerialism, Normative Managerialism, Radical Managerial, and Managerial Economic Values.
- Principles of how to decide, how to interact, and how an economy works.
- The scope of managerial economics includes business analysts, jobs in the banking sector, cost accountants, economic analysts, financial controllers, risk managers, professors, government services, and many more.
- Profit management, capital management, and demand analysis & forecasting are the main areas of importance of managerial economics.
Here are some related resources:
- Bachelor of Economics: Top Courses and Careers
- Scope of Economics & Top 10 Careers in Economics
- Major Differences Between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
- Tips to Succeed in Indian Economic Services Exam
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the three types of managerial economics?
The three types of managerial economics are:
1. Liberal Managerialism
2. Normative Management
3. Radical Managerialism
What is the role of managerial economics?
Managerial economics applies economic theory and quantitative methods to business management. It aids in decision-making by analyzing market trends, optimizing resource use, and forecasting financial outcomes, ultimately helping firms achieve their objectives efficiently.
What is managerial economics in short notes?
Managerial economics is a stream of management studies that focuses primarily on solving business problems and making decisions by applying the theories and principles of microeconomics and macroeconomics.
What is managerial economics?
Managerial economics is a stream of management studies that focuses primarily on solving business problems and making decisions by applying the theories and principles of microeconomics and macroeconomics.
Who is the father of economics?
Adam Smith is widely regarded as the “father of economics.” His seminal work, “The Wealth of Nations” (1776), laid the foundations for classical economics and introduced key concepts like the invisible hand and free markets.
To read more related articles, click here.
Got a question on this topic?