Home » Full Forms » Unlocking LPA Full Form: Making Sense of Earning a Lakh per Annum
Unlocking LPA Full Form: Making Sense of Earning a Lakh per Annum

Table of Contents
LPA Full Form
LPA Full Form is Lakh Per Annum. Lakhs Per Annum (LPA) is a unit used in India to describe an individual’s yearly income. LPA is one of the most vital factors when it comes to employment offers. You should know that the LPA is not the same as the salary that you will get. It indicates an employee’s annual revenue in lakhs earned within a yearlong business cycle. For example, if an employee earns 15 LPA, he makes 15 lakh rupees per year.
Understanding the Value of a Lakh Per Annum
Knowing what is LPA is essential to understanding its purchasing power and overall economic impact. Several factors influence the amount of an LPA’s income. Let’s think your income is INR 1.45 LPA. Here is the breakdown.
The whole of your Basic Salary, Employee Provident Fund (EPF), Employer Contribution to your EPF, House Rent Allowance (HRA), and Ex-Gratia for the entire year is INR 1.45 lakhs. Let’s look at the pay breakdown below:
- Basic Salary = INR 72,500
- EPF (Mandatory 12% of Basic Salary) = INR 8,700 Employer’s Contribution (Mandatory 12% of Basic Salary) = INR 8,700
- HRA (approx. 15% of total salary) = INR 21,750
- Rest Amount of salary = INR 33,350
Budgeting for Financial Success
Making a budget is one of the simplest to improve the financial situation. Without a budget, it is difficult to manage the multiple parts of personal finances, such as credit, insurance, saving, and investing. Budgeting is a fundamental financial planning activity.
Here are some helpful hints for making budgeting easier when you have an LPA income:
- Track your expenses
- Set financial goals
- Invest wisely
- Reduce debt and prioritize savings
Saving and Investing Strategies
There are several simple investing and saving options available in India. It is for people who make up to several lakhs annually. It can help them increase their wealth while lowering their risk. Here are some effective tactics:

Recurring Deposits (RD)
Recurring Deposits are a special type of term deposit provided by Indian banks. It is a mechanism for investing that enables consumers to make consistent deposits and receive respectable returns. The owner of an RD account has the option to invest a certain sum each month while receiving an interest rate of 3 to 7.50%. A recurring deposit has a minimum term of six months and a maximum term of 10 years. RDs are a great combination of investment and savings tools.
Systematic Investment Plan (SIP)
SIP stands for Systematic Investment Plan. A SIP plan is a common investing technique that allows you to invest and deploy a modest amount of money into a specified ULIP fund or mutual fund scheme at regular intervals (such as monthly or quarterly). The instalment payment is akin to a recurring deposit and might be as small as INR 500 per month. It’s convenient since you can direct your bank to automatically deduct the specified amount each month.
Low-Risk Mutual Fund
Investments in mutual funds are all risky. However, each fund will be linked to a particular degree of risk, such as low risk, moderate risk, high risk, etc. Every mutual fund’s risk-o-meter uses product labelling to communicate this information. It shows how risky a strategy is. Comparing low-risk equity schemes to high-risk equity schemes, low-risk funds are investment alternatives with lower risk. A low-risk mutual fund is preferable.
Tax Planning Made Easy
India has progressive income tax rates. It means the more you make, the more you have to pay. The maximum exemption amount is now 3 lakh, and the next slab rate will apply to any income over 3 lakh. You can save money on taxes by taking advantage of applicable deductions and exemptions. Here are some common deductions and exemptions in India:
Section 80C
Deduction up to Rs. 1.5 lakh for investments like EPF, PPF, ELSS, NSC, tax-saving FD, life insurance premiums, home loan principal, and tuition fees.
Section 80D
Deduction for health insurance premiums for self, spouse, children, and parents – up to Rs. 25,000 and an additional Rs. 25,000 for parents.
Section 24(b)
Deduction up to Rs. 2 lakhs on home loan interest for self-occupied property, unlimited for let-out property.
Section 80TTA
Deduction up to Rs. 10,000 earned from savings accounts.
Section 80G
Deduction for donations to specified charitable organizations, ranging from 50% to 100% of the donated amount.
Section 80E
Deduction on interest paid on education loans for higher studies, available for up to 8 years.
Securing Your Future
Knowing that you and your loved ones are financially protected against a variety of unanticipated circumstances would give you more peace of mind. The insurance lump sum award will assist them in covering the expenses of maintaining the family.
You purchase protection from unanticipated financial losses when you purchase insurance. The insurance company will reimburse you or a chosen beneficiary if something terrible occurs to you. So, it is always a good idea for every individual to think about health insurance.
Embracing Opportunities for Growth
Earning a few lakhs each year is just the start of your financial journey. Seize growth opportunities and upskill for a brighter, more fulfilling future. Enhance your skills and effort to boost your salary. Understand the meaning and significance of LPA. Here is a highlight of the potential for professional growth and increased earning potential:
- Continuous learning and upskilling provide doors to new prospects for professional progress.
- Promotions may be obtained through demonstrating great leadership abilities and taking on tough assignments.
- Developing a diversified skill set improves employability and attracts higher-level positions.
- Networking and mentorship provide vital insights and professional development assistance.
- Exploring business or freelancing gives individuals greater independence and possible income development.
CTC vs LPA: Key Differences
LPA meaning is Lakh Per Annum. It displays your yearly income in lakhs, which means LPA full form in salary. CTC stands for the cost to a company and refers to how much the firm invests in you. Your pay, allowances, and other internal costs are all included.
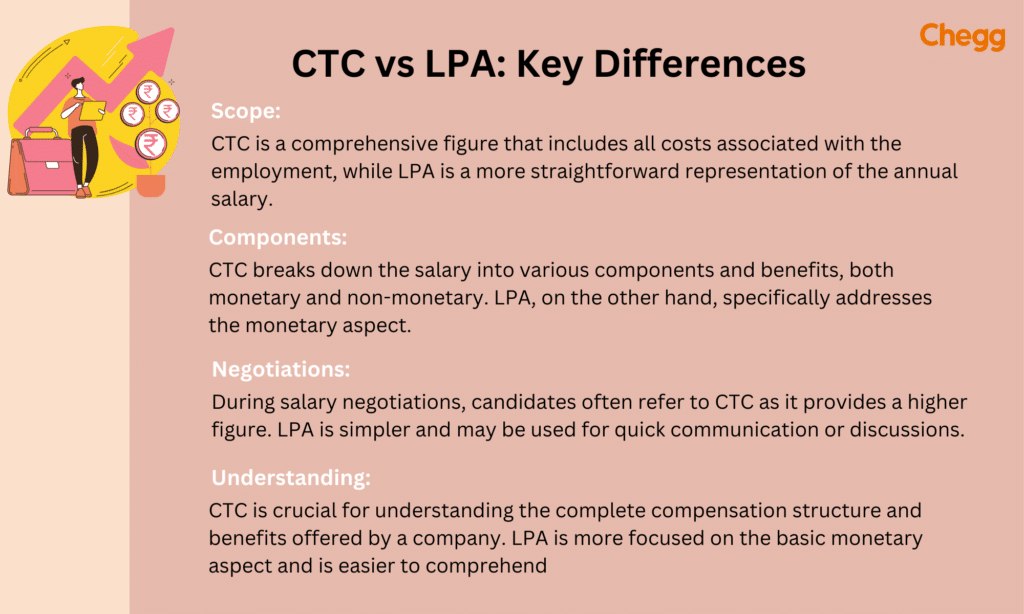
If you have 6 LPA packages, then you may expect approx. 40000/- in hand (per month) after deducting EPF, Taxes, gratuity, etc. So, in essence, LPA is a monetary value that firms use every year to convey CTC data to applicants.
CTC is often distributed in the form of LPA. For example, if a person receives a CTC of 20 LPA each year, this indicates that the firm invests a total of 20 Lakh per year in that individual, from which he receives his pay, allowance, and other services. It’s a summation of many components offered in terms of financials or benefits during the offer letter.
Component may be:
- Fixed Salary (Basic + HRA + DA + Other Fixed Allowance) : Guaranteed payable
- Variable Salary: Not Guaranteed, depends on your and the Company’s Performance
- Employer EPF Contribution: Employers need to contribute 12% EPF along with your contribution
- Gratuity: 4.81% of basic salary
- Cost of Medical Insurance
- Cost of Food expenses, benefits given by the company
- Cost of Travel expenses, benefits given by the company
Conclusion
Earning 2.5 lakh per year is a solid starting point in India because it is the average LPA. It provides individuals with several chances to protect their future and fulfil their financial goals. The goal is to be proactive in terms of financial planning and optimizing the usage of this revenue. Individuals may manage their costs more effectively and save for emergencies and long-term objectives by embracing smart budgeting. Exploring appropriate investment possibilities can assist in growing wealth and making the most of their hard-earned money. It is critical to be knowledgeable about tax-saving tactics and to take advantage of available deductions and exemptions to lower your liabilities.
| USSR Full Form | CNF full form |
| RAC full form | USA full form |
| BBC full form | RSA full form |
| USP full form | CPC full form |
| RPM full form | MCWG full form |
LPA Full Form: FAQs
The full form of LPA is lakh per annum. Lakhs Per Annum (LPA) is a unit used in India to describe an individual’s yearly income.
Here is the difference between CTC vs LPA. LPA is Lakh Per Annum. It just displays your bundle in Lakhs. CTC stands for the cost to a company and refers to how much the firm invests in you. Your pay, allowances, and other internal costs are all included.
5 LPA means the individual’s income is 5 lakh per annum.
Lakhs Per Annum (LPA) is a unit used in India to describe an individual’s yearly income. LPA is one of the most vital factors when it comes to employment offers. You should know that the LPA is not the same as the salary that you will get.
CTC stands for the cost to a company and refers to how much the firm invests in you. Your pay, allowances, and other internal costs are all included.
Got a question on this topic?