Home » Full Forms » LAN Full Form: Local Area Network
LAN Full Form: Local Area Network
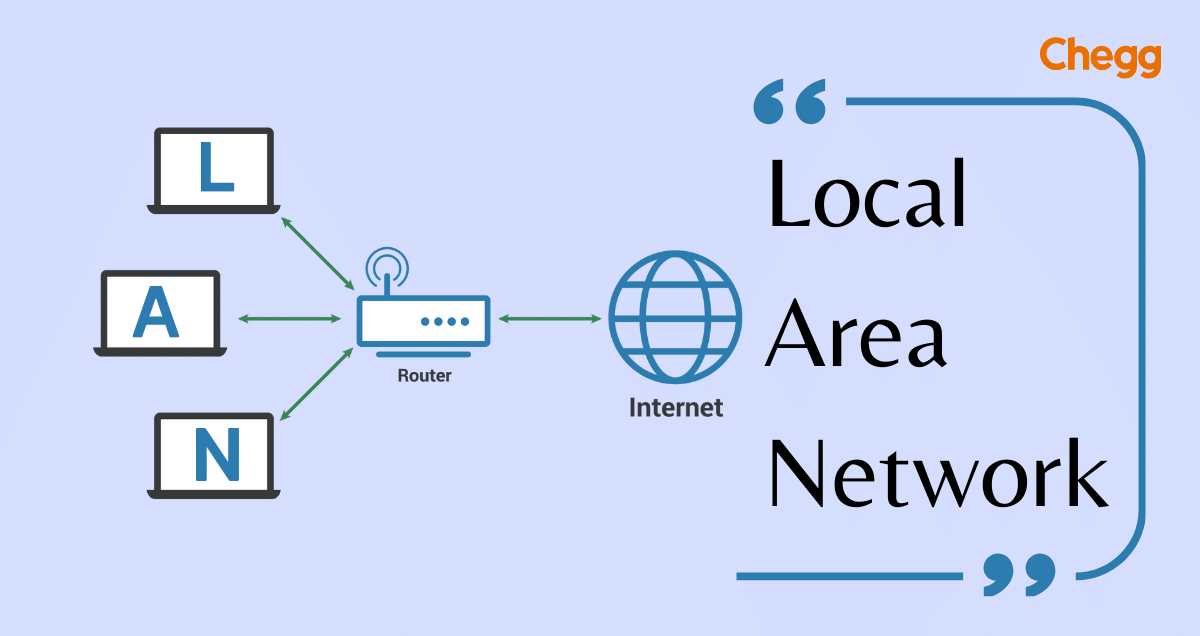
Table of Contents
What is LAN full form
Local Area Network (LAN full form) is a phrase that is commonly used in the area of computer networks. It is a network of networked computers and devices within a certain geographical region, such as a house, business, or college. The LAN full form, “Local Area Network,” emphasizes its limited nature, distinguishing it from wide area networks (WANs), which cover broader territories.
The LAN full form in the computer is Local Area Network. The network architecture enables linked devices to communicate and share resources in real time, encouraging efficient data transport and cooperation.
LAN in modern computer networks is a critical component, enabling resource sharing, communication, and the building of sophisticated computing environments.
The notion of local area networks – LAN full form developed in the 1970s when academics investigated ways to connect computers close to one another, leading to substantial advances in networking technologies.
LAN meaning
LAN is a network of interconnected devices such as computers, printers, servers, and switches located within a relatively small geographical region. This localized network enables smooth communication, effective resource sharing, and collaborative actions among connected devices.
Components of a LAN: Nodes, Devices, and Infrastructure
A LAN’s architecture includes critical components that ensure flawless data transmission. The LAN’s backbone comprises nodes, which are connected devices such as PCs, printers, and servers. These nodes work together to exchange data and resources efficiently.
Routers connect various LANs, allowing communication between networks. Modems, on the other hand, allow digital signals to be converted for transmission via telephone lines.
Types of LANs
It is important to know the types in addition to LAN full form in computers.
Wired LANs
Wired LANs have long been the backbone of local area networks, relying on physical wires such as Ethernet cables or fiber optics to connect devices. These types of LANs are appropriate for fixed installations that require regular and uninterrupted data transfer due to their dependable and high-speed connectivity. Because cables provide low interference and good data integrity, wired LANs are preferred for locations requiring a solid and secure network architecture.
Wireless LANs
The introduction of wireless technology resulted in a major shift in LAN communication. Wireless LANs, often known as Wi-Fi networks, use radio waves to connect devices without cables. Because wireless freedom provides exceptional flexibility and mobility, they are becoming increasingly common in homes, cafes, airports, and companies.
History of LANs
The History of Local Area Networks (LANs) is one of innovation and growing connection. Here’s a glimpse into their evolution:
- 1970s: Sharing Takes Center Stage: The concept of LANs emerged, aiming to share resources and enhance communication within limited areas.
- 1973: The Birth of Ethernet: Robert Metcalfe, a future tech giant, laid the groundwork for Ethernet, the dominant network technology to come.
- 1976: Xerox PARC Delivers the First LAN: The first true LAN technology, Ethernet, arrived courtesy of Xerox Corporation’s Palo Alto Research Center.
- 1980s: Businesses Embrace LANs: As personal computers became more affordable and widespread, LANs gained traction in the business world.
- 1983: Standardizing Ethernet: The IEEE 802.3 standard solidified the use of Ethernet over coaxial cable.
- 1985: Planning for Wireless: The IEEE 802.11 committee was formed to develop a standard for wireless LANs, paving the way for Wi-Fi.
- 1990s: Beyond Businesses: LANs transcended the business world, finding homes in schools, institutions, and even households.
- 1997: Wi-Fi Takes Flight: The first IEEE 802.11 standard for wireless LANs (Wi-Fi) was published, ushering in a new era of connectivity.
- 2000s and Beyond: A Wired and Wireless Future: Wired and wireless LANs continued to evolve, boasting increased speed, reliability, and robust security features.
LAN Components and Devices
Network Interface Cards (NIC)
NICs are necessary components for connecting devices to a LAN. They handle data conversion between the internal format of the computer and the layout suited for network transmission.
Switches and Hubs
Switches and hubs aid in the forwarding and distributing of data packets inside a LAN. While switches are more efficient at the data-link layer, hubs are less sophisticated at the physical layer.
Routers and Gateways
Routers connect various LANs and allow data to flow across them. Gateways act as network entry and exit points, allowing LANs and WANs to connect.
Modems and Access Points
Access points provide wireless device connectivity within a LAN, whereas modems convert digital signals to analog for transmission over telephone lines.
LAN Cables and Connectors
Various cables and connectors, such as Ethernet and RJ-45 connectors, establish wired connections in LANs.
LAN Protocols
Ethernet Protocol
Ethernet is a popular LAN protocol that specifies how data is delivered across a LAN using frames. Its speed versions, such as Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet, have evolved.
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
TCP/IP is a protocol suite for data transfer over networks such as LANs and the Internet. It enables end-to-end communication between devices.
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
UDP is a connectionless protocol that allows quicker data transmission but does not ensure delivery.
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
ARP translates IP addresses to MAC addresses within a LAN, allowing devices to interact.
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
Within IP networks, ICMP is in charge of sending error messages and operational information.
LAN Management and Administration
LAN management and administration are critical to ensuring the network’s smooth operation. Network administrators continually monitor LAN performance, assessing data flow and usage patterns. This proactive strategy enables them to identify potential faults or bottlenecks impeding ideal performance.
Network Performance Optimization
LAN administrators are dedicated to optimizing network performance to ensure optimal data flow and decrease delay. They rigorously fine-tune network setups, upgrade hardware as needed, and put Quality of Service safeguards in place to prioritize vital data traffic. Furthermore, managers monitor bandwidth utilization and proactively distribute resources to ensure that bandwidth-hungry applications or devices do not interfere with other critical network processes.
User Access Control and Authentication
Maintaining the LAN’s security and integrity is critical, and user access control is crucial. LAN administrators create comprehensive access control methods that define user privileges and permissions to prevent unauthorized access to important resources.
LAN Documentation and Asset Management
Comprehensive documentation and asset management methods are required for effective LAN management. Administrators keep meticulous records of network settings, equipment inventories, and IP address assignments. This well-organized documentation supports streamlining troubleshooting operations, simplifying network expansion or alterations, and facilitating disaster recovery activities.
LAN Advantages and Disadvantages
The LAN definition talks about the advantages and disadvantages of it.
Advantages of LANs
LANs are crucial for modern organizations and families because they provide fast data transfer, resource sharing, collaboration, and cost-effectiveness.
Disadvantages of LANs
Security issues, scalability limits, and the necessity for periodic maintenance and upgrades are all potential drawbacks.
Overcoming LAN Limitations
Technological advances and effective management practices can assist in overcoming LAN limits and improving performance.
What is a Virtual LAN?
Imagine dividing your apartment Wi-Fi into two separate networks, each with its own devices. But wait, you only need one router!
That’s the magic of VLANs. They create virtual sub-networks within a single physical network. This is especially useful for large organizations:
- Improved Network Management: Think of it as organizing your messy cables. VLANs let network admins segment the network, making control and monitoring much easier.
- Security Boost: By separating devices (e.g., guest computers vs. work computers), VLANs can enhance network security.
LAN Future and Emerging Trends
Gigabit Ethernet and Beyond
Faster Ethernet variations, such as 10 Gigabit Ethernet and beyond, will continue to improve data transfer rates on LANs.
Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
SDN enables centralized network management, increasing the flexibility and programmability of LANs.
Internet of Things (IoT) and LAN Integration
Integration of IoT devices with LANs will enable smart homes and companies to have greater automation and connectivity.
Conclusion
It’s important to acknowledge the crucial role of LANs in modern computing. They facilitate smooth communication, resource sharing, and efficient data movement within confined areas. As technology advances, LANs will continue to evolve, offering faster connections, stronger security, and better integration with emerging technologies. Ultimately, the success of organizations and individuals in interacting and sharing resources depends on the criticality of LAN in computer networks.
Learn more about some other full forms:
| DHCP Full Form | RDBMS Full Form | ENIAC Full Form |
| GPU Full Form | PHP Full Form | PDA Full Form |
| RADAR Full Form | CFL Full Form | IDE Full Form |
LAN Full Form: FAQs
LAN full form is Local Area Network. LAN definition states that this local network connects local devices in a particular area.
LAN in computer networks covers a small geographical area, whereas. WANs cover bigger regions or even the entire globe.
Nodes (devices) and infrastructure such as switches, routers, and cables.
Faster and more reliable data transport with reduced interference.
LAN security can be guaranteed through strict access controls, encryption, firewalls, and regular updates.
Improve performance, security, and integration with upcoming technologies such as IoT and SDN.
In residential LAN setups, a primary choice is a single router, tasked with establishing the network and managing all linked devices. Functioning as a central hub, the router facilitates network communication among computers, tablets, and smartphones.
Got a question on this topic?