

Quick Summary
In today’s fast-paced, interconnected world, digital communication has become the cornerstone of personal, professional, and global interaction. With the widespread use of smartphones, social media platforms, and instant messaging apps, people can connect across time zones and geographic boundaries in real-time. This immediacy not only fosters stronger personal relationships but also enables faster collaboration and decision-making in the workplace. Whether it’s a video conference, an email, or a tweet, digital communication tools have transformed how we share information, solve problems, and maintain engagement in an increasingly digital society.
Beyond convenience, the importance of digital communication lies in its ability to bridge gaps, democratize information, and drive innovation. Businesses leverage digital channels to reach broader audiences, build brand identity, and enhance customer experience, while educators and governments use them to ensure access and inclusivity. In a world where remote work, e-learning, and online services are rapidly becoming the norm, mastering digital communication isn’t just an advantage—it’s a necessity. Its role in shaping modern life continues to expand, reinforcing its value as a vital skill and tool in the digital age.
Digital communication refers to the process of transmitting information—text, voice, image, video, data—using discrete signals (1s and 0s) over a channel. It’s the backbone of modern telecommunications, powering everything from internet browsing and VoIP calls to streaming and IoT devices.
Why It Matters
Analog systems transmit continuous signals that directly reflect sounds or images—like classic AM/FM radio or older TV formats. While natural sounding and simple, analog suffers from noise, interference, and signal decay over distance.
Catalyzed by improvements in computing power and digital electronics, the switch began in late 20th century with digital telephone, internet protocols, and digital TV. The result? Better sound, clearer images, and more reliable long‑range transmission.
| Feature | Analog Communication | Digital Communication |
| Signal Type | Continuous variations | Discrete binary pulses (0s and 1s) |
| Noise Resilience | High susceptibility to interference | Strong immunity; error correction mechanisms (geeksforgeeks.org) |
| Bandwidth Needs | Lower bandwidth, but lower efficiency | Higher bandwidth but much more data throughput |
| Hardware Complexity | Generally simpler | Requires more processing power, routers, etc. |
| Cost | Lower upfront costs | Higher initial cost, but cheaper long‑term |
| Multiplexing | Frequency‑based (FDM) only | Supports advanced forms like TDM, CDM, packet multiplexing |
| Error Management | Hard to detect/correct | Built‑in error detection and automatic correction |
| Portability & Power | Less portable, higher power required | Compact, low‑power and portable |
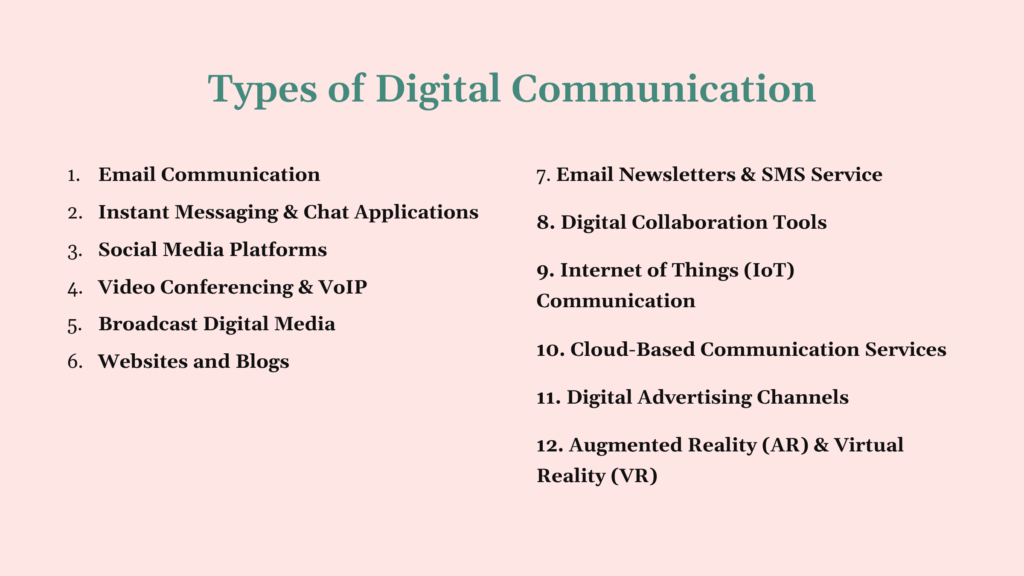
Email is one of the earliest and most enduring forms of digital communication. It allows users to send text, files, links, and multimedia across the internet.
Apps like WhatsApp, Telegram, Slack, and Microsoft Teams allow real-time, short-form communication.
Social platforms like Facebook, Twitter (X), Instagram, and LinkedIn are powerful digital communication tools combining text, video, voice, and interactive media.
Apps like Zoom, Google Meet, Skype, and Microsoft Teams use Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and video transmission over digital networks.
This includes digital television, YouTube, podcasts, and internet radio, all of which distribute content to wide audiences using digital signals.
Websites offer static and dynamic content as a form of one-to-many digital communication.
Automated digital communication through platforms like Mailchimp or SMS APIs delivers scheduled messages to subscribers.
These include platforms like Google Workspace, Notion, Trello, and Asana.
IoT devices use sensors and microcontrollers to send and receive digital signals—without human intervention.
Cloud technologies host applications and data, enabling flexible and scalable communication services.
Digital ads on search engines, social media, mobile apps, and websites communicate brand messages to targeted users.
AR/VR are immersive digital communication methods, increasingly used in gaming, virtual meetings, education, and simulations.
One of the most common and essential applications, digital communication powers mobile networks like 4G and 5G, enabling voice calls, video calls, SMS, and internet browsing.
Television, radio, and online content are now transmitted using digital signals, resulting in clearer quality, efficient bandwidth usage, and interactive capabilities.
Digital communication tools are essential for businesses and teams operating remotely or in hybrid work environments.
Education has become accessible and flexible thanks to digital communication platforms that deliver learning content to students worldwide.
Digital communication bridges the gap between doctors and patients, especially in remote or underserved areas.
From order confirmation emails to live chat support, digital communication drives customer engagement in online business ecosystems.
The fintech revolution relies heavily on secure digital communication to provide seamless and secure transactions.
Governments across the world are implementing e-governance initiatives powered by digital communication.
Smart home and industrial automation systems rely on real-time machine-to-machine (M2M) communication using digital protocols.
Critical applications like defense communication and space exploration depend on encrypted, high-bandwidth digital systems.
Brands use digital tools to enhance user experience through personalized and responsive communication channels.
Brands communicate with their audience through targeted and trackable digital ads.

Digital signals regenerate cleanly via repeaters—addressing signal degradation issues inherent in analog systems
Digitally encoded info remains intact even with some interference, thanks to threshold‑based decoding and forward error correction .
Digital communication enables real-time sharing of information across the globe, reducing delays and improving decision-making in both personal and professional settings.
Unlike traditional methods, digital communication tools such as email, video conferencing, and cloud platforms significantly lower communication costs—especially for remote teams and international businesses.
With digital communication, organizations can connect with a global audience instantly, allowing brands, educators, and service providers to expand their reach far beyond geographical boundaries.
Digital communication supports flexible work environments by allowing people to communicate from anywhere, anytime—making it ideal for remote work, freelancing, and hybrid teams.
Excessive use of digital communication platforms—especially video calls and instant messaging—can lead to digital fatigue, reducing productivity, focus, and mental well-being. Constant connectivity often blurs work-life boundaries, leading to burnout.
Not everyone has equal access to digital tools or high-speed internet, creating a digital divide that limits participation in remote education, work, and healthcare—especially in rural or economically disadvantaged communities.
Digital communication raises ethical concerns such as data privacy, consent, and information integrity. Whether it’s recording virtual meetings or mining user data, ethical practices must ensure transparency and respect for users’ rights.
Inclusive digital communication must accommodate people with disabilities through features like screen readers, subtitles, and voice commands. Designing with accessibility in mind ensures that digital spaces are usable for all, regardless of physical or cognitive ability.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) plays a major role in modern digital communication by enabling real-time content personalization. From adaptive email marketing campaigns to smart assistants tailoring recommendations, AI helps organizations deliver the right message to the right audience at the right time—improving engagement and customer satisfaction.
Chatbots have become vital in automating support and FAQs on websites and social platforms. Brands like H&M and Swiggy use AI-powered chatbots to handle high volumes of customer queries instantly, cutting response times and improving service quality. This trend reflects how digital communication is moving toward 24/7, self-service engagement.
Voice-based digital tools like Amazon Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant are reshaping how users interact with content. Voice communication enhances accessibility for visually impaired users and enables hands-free operation—creating more inclusive digital environments across education, home automation, and business operations.
Predictive analytics uses historical data and behavior patterns to forecast future actions—allowing businesses to optimize message timing, channel choice, and content. For example, Netflix and Spotify leverage it to recommend content, while marketers use it to increase open rates and conversion in their outreach campaigns.
One of the most common and essential applications, digital communication powers mobile networks like 4G and 5G, enabling voice calls, video calls, SMS, and internet browsing.
Television, radio, and online content are now transmitted using digital signals, resulting in clearer quality, efficient bandwidth usage, and interactive capabilities.
Digital communication tools are essential for businesses and teams operating remotely or in hybrid work environments.
Education has become accessible and flexible thanks to digital communication platforms that deliver learning content to students worldwide.
Digital communication bridges the gap between doctors and patients, especially in remote or underserved areas.
From order confirmation emails to live chat support, digital communication drives customer engagement in online business ecosystems.
The fintech revolution relies heavily on secure digital communication to provide seamless and secure transactions.
Governments across the world are implementing e-governance initiatives powered by digital communication.
Smart home and industrial automation systems rely on real-time machine-to-machine (M2M) communication using digital protocols.
Critical applications like defense communication and space exploration depend on encrypted, high-bandwidth digital systems.
As we look toward the future, digital communication will continue to evolve and shape the way we live, work, and connect. With advancements in technologies like artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and 5G networks, the possibilities for more immersive, efficient, and personalized communication are expanding rapidly. These innovations will not only enhance how we interact but also redefine expectations in areas such as customer service, remote collaboration, and global networking. Digital communication will remain at the heart of progress, ensuring that individuals and organizations can adapt quickly in an increasingly dynamic and digital-first world.
Moreover, the importance of digital communication will grow as society becomes even more reliant on virtual environments for learning, commerce, and social interaction. Those who embrace and refine their digital communication skills will be better equipped to thrive in future workplaces and communities. Ensuring accessibility, cybersecurity, and digital literacy will be critical to maximizing its potential and minimizing its risks. Ultimately, digital communication is more than just a tool—it is a driving force behind global innovation, inclusion, and connection in the years to come.
Read More: Digital Marketing Skills: A Comprehensive Guide

Digital communication means sharing information using digital technologies and electronic devices like computers, smartphones, and the internet. It includes emails, social media, instant messaging, video calls, and other online platforms that help people and organizations communicate quickly and effectively.
Example: A Mumbai-based company connects with clients through email, WhatsApp, and Zoom calls to share updates, reports, and presentations digitally.
Tip: Focus on understanding different digital tools and platforms. This will make communication faster, more efficient, and more accessible.
Digital communication includes any exchange of information using digital tools or platforms.
Example: A Mumbai-based company sends emails to clients, holds Zoom meetings with team members, shares updates via WhatsApp, and posts announcements on LinkedIn. All of these are forms of digital communication.
Tip: Focus on using the right digital platform for the audience and purpose. This ensures messages are effective and reach the intended recipients.
Digital communication is important because it allows for fast, efficient, and widespread information exchange. It enables real-time collaboration, remote work, global connectivity, and easy documentation. Businesses, students, and professionals rely on digital communication to save time, improve productivity, and maintain effective relationships.
Example: A Mumbai-based company uses emails, Zoom meetings, and WhatsApp to coordinate teams, share reports, and communicate with clients instantly.
Tip: Focus on mastering digital tools and platforms. This improves efficiency and ensures clear communication.
Digital communication can be classified into two main types:
Synchronous Communication, real-time communication where participants interact instantly.
Example: Video calls on Zoom or Google Meet, instant messaging on WhatsApp.
Asynchronous Communication, communication where responses do not happen right away.
Example: Emails, discussion forums, or recorded video messages.
Tip: Understand when to use synchronous versus asynchronous communication. This ensures messages are timely and effective.
Yes, digital communication is essential in today’s work and personal life. It means using digital tools and platforms to share information, work with others, and connect with people. Strong digital communication skills boost productivity, teamwork, and professional credibility.
Example: A professional in Mumbai effectively uses email, WhatsApp, and Zoom to coordinate projects, share updates, and maintain strong client relationships.
Tip: Focus on mastering digital platforms, being clear in your messages, and responding promptly. This makes digital communication a very valuable skill.
The five basic digital skills essential in today’s professional and personal life are:
Digital Communication, using emails, messaging apps, and video calls effectively.
Basic IT Literacy, operating computers, software, and mobile devices.
Online Research, finding, evaluating, and using information from the internet efficiently.
Data Management, organizing, analyzing, and presenting data using spreadsheets or databases.
Cybersecurity Awareness, understanding safe online practices and protecting personal or organizational data.
Example: A Mumbai-based professional uses emails for digital communication, Excel for data management, internet research for online research, operates office software for IT literacy, and follows strong password and antivirus practices for cybersecurity.
Tip: Focus on practicing these skills regularly; they are foundational for career growth in the digital age.

Authored by, Mansi Rawat
Career Guidance Expert
Mansi crafts content that makes learning engaging and accessible. For her, writing is more than just a profession—it’s a way to transform complex ideas into meaningful, relatable stories. She has written extensively on topics such as education, online teaching tools, and productivity. Whether she’s reading, observing, or striking up a conversation while waiting in line, she’s constantly discovering new narratives hidden in everyday moments.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.