
Quick Summary
In today’s competitive world, strong communication and interpersonal skills are vital for academic, professional, and social success. Whether you are preparing for campus placements, competitive exams, or corporate meetings, the ability to express your ideas confidently and logically can make a significant difference.
Two of the most common formats used to evaluate such communication abilities are group discussions and debates. While they may seem similar on the surface both involve multiple people expressing opinions on a particular topic they are fundamentally different in purpose, structure, and outcome.
In this guide, we will explore the difference between group discussion and debate, how each works, their objectives, and when to use them effectively.
A Group Discussion (GD) is a structured form of conversation where participants share their opinions, ideas, and perspectives on a given topic in a collaborative manner. It encourages group communication, teamwork, and analytical thinking.
Group discussions are commonly used in educational institutions and corporate recruitment processes to evaluate a candidate’s ability to think critically, communicate clearly, and work as part of a team.
Topic: “Should social media be banned for students?”
Participants in a group discussion would analyze both pros and cons, share relevant data, and attempt to reach a balanced conclusion.
A Debate is a structured argument where individuals or teams present opposing viewpoints on a specific issue. The primary aim of a debate is to prove one side right and disprove the other through reasoning, evidence, and persuasive communication.
It emphasizes debate skills and strategies, logical thinking, and strong articulation. Debating is common in schools, universities, and public forums, and it is an essential component of competitive exams and professional interviews.
Topic: “Artificial Intelligence is a threat to human employment.”
In a debate, one team argues for the statement, while the other argues against it, each presenting strong evidence and rebuttals.
The following table shows the difference between group discussion vs debate:
| Parameter | Group Discussion | Debate |
| Definition | The group communication process includes sharing information and ideas on a specific topic. | Two groups are involved in the official discussion: one opposes the motion, and the other favors it. |
| Nature | It is cooperative and collaborative. | It is competitive. |
| Aim | It aims to learn about and understand a topic. | It tries to support or prove an idea. |
| Taking Turns | The opportunity to speak out during group discussions is always available. | Participants have to wait for their turn to speak. |
| Competition | It is not competitive but collaborative. | It is competitive. |
| Opposition | It can be done without generating opposing viewpoints. However, one may express different points of view if they so choose. | It requires an opposition team to be conducted. |
| Audience | It may or may not have an audience. | It mostly has an audience. |
| Structure | Given that the time limit is not seriously applied, it is semi-structured. The participants may speak at their own pace as long as it is consistent with what is being discussed. | It is structured because there is a set time limit and everyone must wait their turn to speak. |
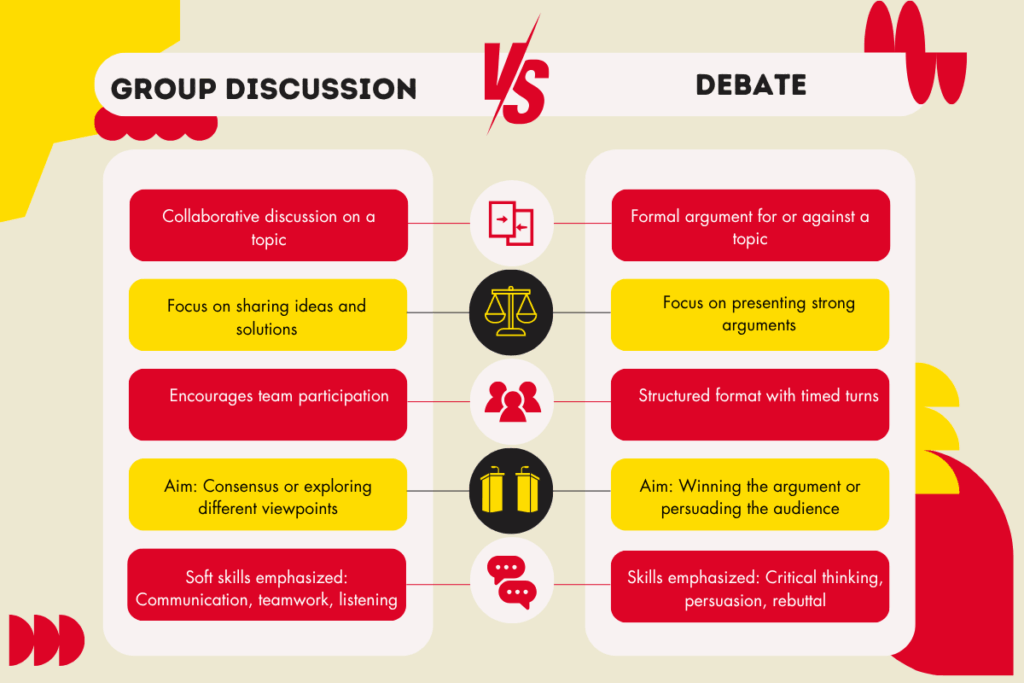
The difference between debate and group discussion lies primarily in their purpose and interaction style. A GD promotes group harmony and decision-making, whereas a debate promotes individual confidence and argumentative clarity.

What is the difference between group discussion and debate? In a group discussion, many individuals contribute their ideas collectively, and participants can speak up at any moment to share their opinions. In contrast, a debate follows a structured format where each candidate is given a defined amount of time to present their arguments. While both involve a natural desire to establish one’s viewpoint and challenge others, a group discussion focuses on collaborative problem-solving. Participants must argue their position with relevant data, facts, and figures, emphasizing constructive dialogue rather than outright opposition.
A major difference between group discussion and debate lies in the structure of the arguments. In a debate, the arguments must focus on a fixed issue, and participants take opposing sides to support their viewpoints. The objective is to defend a specific position and win over the audience or judges by providing strong reasoning and evidence.
On the other hand, a group discussion is more flexible and open-ended. Arguments can shift as participants contribute their thoughts, leading to the exploration of new perspectives and ideas. Group discussions encourage collaboration, allowing individuals to refine and evolve their opinions through shared dialogue and critical analysis of different viewpoints.

Both group discussion and debate have their own rules and set of instructions. Let us take a look.
When exploring the difference between group discussion and debate, it’s important to understand the key elements that define a group discussion. The following are the essentials:
Understanding these elements will help highlight the difference between group discussion and debate and prepare participants for effective participation.
The following are the essentials of the debate:
The following are the do’s and don’ts of the group discussion:

Group conversations entail learning from the experiences and knowledge of others while developing a discourse from similar viewpoints. You can learn more about a subject or improve your understanding by carefully listening to what others say. Difference between Group Discussion and Debate: Because people can see that you value what they say, it also demonstrates respect to the other group members.
Make eye contact with the group members when you’re speaking during a conversation in a group setting. Before moving on to the next person, try to make each feel significant by giving them a few seconds of your attention. Maintaining eye contact while speaking also conveys that you value their attention.
Allowing people to speak during a debate is crucial because it enables them to express their opinions, Difference between Group Discussion and Debate includes any points on which they agree or disagree. Try to mentally create speaking time limitations for yourself, such as 30 to 40 seconds before allowing someone else to speak.
Carefully planning your entry point in a group conversation is essential for making meaningful and confident contributions. It allows you to decide not only what to say, but also the most appropriate moment to say it, ensuring your input adds value to the discussion. Rather than interrupting or speaking randomly, observe the flow of conversation and look for a natural pause or a shift in topic. A strategic approach is to speak up after someone has finished sharing their thoughts on a subject that aligns with your area of knowledge or expertise. This creates a smooth transition, shows you’re actively listening, and increases the chances of your points being well-received by the group.
By timing your contribution effectively, you can communicate more clearly, maintain the group’s attention, and enhance the overall quality of the discussion.
Knowing when to conclude your participation in a group discussion is essential, and this can be achieved by identifying your exit point. An exit point refers to when you choose to stop speaking to allow the conversation to flow naturally and include other participants. If your points are short, clear, and concise, you can briefly share your thoughts and leave the discussion open for further input.
Understanding the difference between group discussion and debate can also help in planning your exit points. In a group discussion, the goal is to foster teamwork and exchange ideas, so knowing when to step back and let others contribute is vital for maintaining balance. On the other hand, debates are more structured and focused on presenting arguments. Recognizing these distinctions will allow you to adapt your communication style to the context while ensuring you contribute effectively without dominating the discussion. Also, understanding the do’s and don’ts of group discussion is essential for effective participation—stay respectful, listen actively, contribute meaningfully, and avoid interrupting or dominating the conversation.
To make a strong impression in a group discussion, ensure that you join the conversation promptly. Pay attention to what others are saying, stay engaged, and look for the right moment to contribute your thoughts. Waiting for an opportunity to speak demonstrates active listening and ensures your input is relevant and timely.
Make sure what you add is pertinent to prevent the conversation from deviating from its main topic. Before you talk, consider whether it is relevant to the wider debate.
Wait until others have finished speaking before adding your comments. The difference between group discussion and debate lies in their purpose and approach. Group discussions emphasize active listening and respecting others’ viewpoints, fostering collaboration and understanding diverse perspectives. In contrast, debates focus on defending a position, persuading others, and often involve opposing viewpoints.
Negative body language might convey apathy in a conversation. Instead, adopt a pleasant attitude and try to adopt the other group members’ body language. By doing so, you may demonstrate that you are listening and are interested in what is being said.
Conversely, the difference between group discussion and debate is evident in the skills required. In a debate, persuasive speaking, critical thinking, and the ability to construct strong arguments are essential, as the focus is on defending one’s position and countering opposing viewpoints. Recognizing these differences helps individuals prepare effectively for each format, whether for collaboration in discussions or strategic argumentation in debates.
Members must have a specific set of abilities to participate and engage in group conversations effectively. Here are the key skills required for both group discussions and debates:
Active listening is essential in group discussions because it helps members understand the ideas and perspectives of others. It involves giving the speaker your full attention, maintaining eye contact, nodding, and responding appropriately. The difference between group discussion and debate is evident here—group discussions rely on active listening to foster collaboration and group communication, while debates focus more on presenting and defending arguments.
To express ideas, thoughts, and opinions in a group conversation, it is necessary to have clear and effective communication skills. Participants should be able to express themselves confidently, using precise language. Effective communication ensures that ideas are promoted clearly and reduces the risk of misunderstandings. Whether in a debate vs group discussion, the ability to articulate thoughts persuasively is key to making a strong impression.
The difference between group discussion and debate also lies in the approach to decision-making and problem-solving. In group discussions, participants focus on identifying problems, brainstorming innovative ideas, and suggesting practical solutions through collaboration. Unlike debates, which emphasize winning an argument, group discussions encourage teamwork and open dialogue to reach the best possible outcomes.
Group discussions are team-oriented activities where participants contribute their thoughts and ideas toward a shared goal. Collaboration involves respecting others’ viewpoints, actively listening, and valuing diverse opinions. It also includes building on each other’s ideas to foster innovation and problem-solving, emphasizing the strength of collective effort over individual perspectives.
Understanding the difference between group discussion and debate is crucial here, as group discussions focus on teamwork and shared exploration of ideas, while debates are more competitive and structured. Effective collaboration in group discussions allows participants to work together to uncover solutions, generate insights, and develop a deeper understanding of the topic through open communication.
Group discussions and debate foster the development of critical leadership abilities. A well-organized debate aids in critical thinking and opinion defense. Discussions in groups encourage cooperation and teamwork. Effective leaders strike a balance between these abilities by understanding when to voice their opinions and when to solicit feedback. People who know how to argue well and have candid conversations make better decisions.
A leader who is proficient in both approaches is better equipped to communicate concepts clearly and adjust to various circumstances. Before involving teams in discussions to improve decisions, business executives frequently discuss strategic directions. Both formats are beneficial for students getting ready for leadership roles.
In summary, while group discussions and debates both enhance communication and confidence, they differ significantly in their goals and execution.
A group discussion encourages collaboration, idea exchange, and teamwork, while a debate focuses on persuasion, logic, and competition. Understanding the difference between group discussion and debate helps you prepare better for competitive exams, interviews, and corporate communication scenarios.
By mastering both, you develop well-rounded communication skills that open doors to leadership, career growth, and personal excellence.
So, whether you are preparing for a group discussion vs debate round in an interview or simply want to polish your debate skills and strategies, remember success lies in expressing ideas with confidence, clarity, and respect.
Ace your job interviews with tailored tips for a great first impression! Explore more Interview Tips with us.
Recommended Read:
The difference between group discussion and debate lies in their structure and purpose. A debate is a formal contest of arguments between two individuals or teams, where one side supports the topic while the other opposes it. In contrast, a group discussion is an open exchange of knowledge, ideas, and information among participants, focusing on collaboration rather than competition.
The difference between group discussion and debate is also evident in their approach to emotions and interpersonal dynamics. Debate focuses on countering the opposing position, often without regard for feelings or relationships, sometimes even belittling the other side. In contrast, discussion centers on content rather than emotions, where emotional responses may arise but are usually not the focus and may even be discouraged.
Group discussions are structured interactions where group members come together to solve problems or make decisions. The main aim of group discussions is to get a proper understanding and agreement of all the group members. Conversations on the topics chosen by group members are friendly and the conversations are designed to be interesting.
Difference between Group Discussion and Debate: During both debates and group discussions, members share ideas and viewpoints. Both these exercises allow participants to express their opinions freely and offer their views on a particular topic. Arguments and convincing are common in debate and group discussions.
To kick off a debate effectively, start by capturing the audience’s attention with an engaging opening statement. This could be a relevant story, a thought-provoking question, a surprising statistic, or a powerful quote that both introduces the topic and clearly presents your position. Be sure to define key terms if needed and take a moment to acknowledge the audience and introduce yourself.
The four main types of debates are:
Formal Debate: Structured with strict rules and time limits, often in a competitive setting.
Informal Debate: Casual and flexible, with less structure and rules.
Public Debate: Involves a larger audience, with panelists discussing public issues.
Team Debate: Involves multiple debaters on each side, working together to present arguments.

Authored by, Rashmi Jaisal
Career Guidance Expert
Rashmi is a Content Strategist who creates research-driven content focused on education, higher education policy, and online learning. She brings an energetic blend of expertise in technology, business, and literature, sparking fresh perspectives and engaging narratives. Outside of work, she’s a passionate traveler who enjoys journaling and curating visual inspiration through Pinterest boards.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.