
Quick Summary
Macroeconomics encompasses the study of numerous topics, such as national income, employment, economic growth, inflation, aggregate demand and supply, monetary policy, fiscal policy, and international trade. It identifies the impact of larger-level phenomena on a society’s economic well-being and how these variables impact its citizens’ financial and day-to-day lives.
The scope of macroeconomics includes analyzing these broad economic factors to understand how economies function. Macroeconomics also lays a foundation for governments and other groups/organizations to make evidence-based decisions in pursuit of economic growth and stability.

The social science of economics examines how people, organizations, governments, and societies decide how best to use scarce resources to meet their needs and desires. It focuses on producing, distributing, and consuming goods and services.
Economics can be divided into two broad categories: microeconomics and macroeconomics.
The study of microeconomics focuses on the decision-making processes of individual economic agents, including businesses and consumers. It investigates pricing, market equilibrium, and supply and demand. Macroeconomics, on the other hand, examines the economy as a whole, including national income, inflation, unemployment, and fiscal policies.
Ragnar Frisch introduced the term macroeconomics in 1933. However, its approach to economic problems originated with mercantilists in the 16th and 17th centuries.
This branch of economics deals with the economy as a whole or as a whole, including macro factors. The economy studies the total and average of the entire economy. The major factors include national income, total employment, total savings and investments, aggregate demand and supply, and the general price level, which make up the features of macroeconomics.
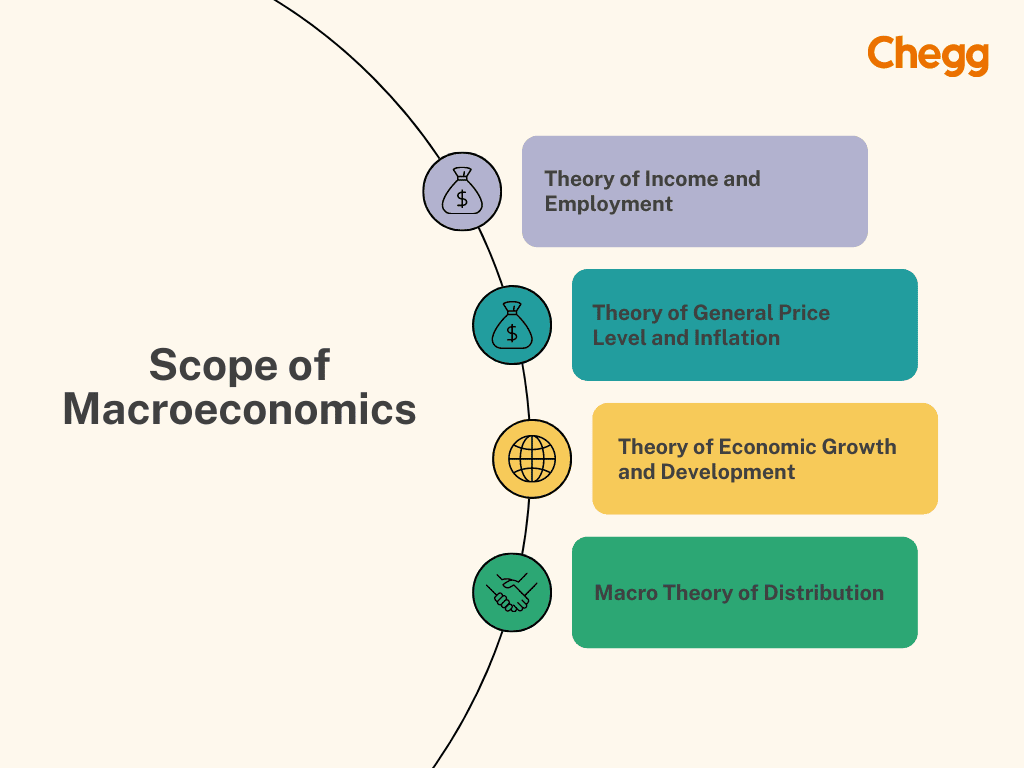
Macroeconomics focuses on how income and employment are determined. As a result, it is referred to as the “theory of income and employment,” which mainly consists of the true meaning of macroeconomics.
We now know that macroeconomics is a subfield of economics. It focuses on the economy by calculating the total impact of individual units on the entire country. This idea is the foundation of all significant policies and initiatives. For instance, national income is determined by the per capita income, which represents the mean income of all the people in the country.
The following table will help you get a good understanding of the two branches of economics:
| Basis of Distinction | Microeconomics | Macroeconomics |
| Meaning | It is the study of individual units in a country’s economy | It is the study of a nation’s economy and its aggregates |
| Nature | Static | Dynamic |
| Area of Action | It is applied to the internal environment | It is applied to the external environment |
| Scope | Deal with several issues related to Income, Employment, Distribution Money General Price Level | Deal with several issues related to Income, Employment, Distribution of Money, and General Price Level |
| Focus | Studies individual market segments in the economy | Studies the entire economy of a country as a whole |
Understanding a nation’s overall economic health requires understanding macroeconomics, a vital field of study. Its scope is broad because it aids governments, financial institutions, and researchers in analyzing national issues and economic health. Macroeconomics mainly focuses on the fundamental elements of economic theories and policies that affect a country’s performance.
Economic growth, national income, money, employment, international trade, and the general level of prices are all included in macroeconomics. These fields aid in comprehending the larger economic picture and the interactions between different economic sectors. Macroeconomics also examines a country’s long-term growth and prosperity to help shape policies that promote stability and growth.
Furthermore, macroeconomics revolves around macroeconomic policies, such as monetary and fiscal policies. This field looks at things like inflation, unemployment, and balance of payments (BOP) imbalances. By researching these issues, economists can suggest solutions to enhance a country’s economic circumstances and guarantee stability and sustainable growth.
Recommended read: Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
The scope of macroeconomics covers numerous subject matters. Some of these are as follows:
A big car manufacturer chooses to start producing motorcycles, electric scooters, and bicycles in addition to cars. The business produces these extra vehicles using its current workforce, supply chain, and infrastructure rather than constructing new facilities.
Through economies of scope, the company reduces its overall production costs by pooling resources like factories, distribution networks, and technology. Compared to manufacturing each product independently, this strategic expansion enables the business to diversify its offerings while preserving efficiency and cutting costs.
The government is essential to managing the economy, emphasizing elements that affect people’s lives. To analyze these factors, one must have a solid understanding of macroeconomics. Studying important topics like GDP, unemployment, and inflation is part of macroeconomics’s nature and scope. The nature and scope of macroeconomics encompass six primary theories that aid in explaining economic dynamics and serve as a framework for policy decisions. These theories influence how the economy as a whole is understood.
There are six theories under the scope of macroeconomics –
The growth of an economy also comes under the study of macroeconomics. The resources and capabilities of an economy are evaluated based on the scope of macroeconomics. It influences the increase in national income and output at the environmental level. They have a direct impact on the economic development of an economy.
Macroeconomics assesses the impact of the reserve bank on the economy, the inflow and outflow of capital, and its effects on job rates. The frequent change in the value of money caused due to inflation and deflation has adverse effects on a nation’s economy. They can be cured by taking monetary and fiscal policies and direct economic control measures.
It includes different topics related to measuring national income, including revenue, spending, and budgeting. The macroeconomic study is vital for assessing the economy’s overall performance in terms of national income. At the onset of the Great Depression of the 1930s, it was essential to investigate the triggers of general overproduction and unemployment. This led to the creation of data on national income. It helps forecast the level of economic activity and income distribution among various citizens.
It is an area of study focusing on exporting and importing products or services. In brief, it points out the effect on the economy through cross-border commerce and customs duty.
This scope of macroeconomics assists in determining the level of unemployment. It also determines the causes that lead to such conditions of unemployment. Hence, this affects the production, supply, consumer demand, consumption, and expenditure behaviour.
This refers to studying commodity prices and how specific price rates fluctuate due to inflation or deflation.
The Government of India and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) collaborate to carry out macroeconomic policies meant to promote the growth and development of the country. Understanding the larger economic variables that affect national prosperity is central to the study of macroeconomics. Both the government and the RBI work together to address different facets of the nature and reach of macroeconomics, including fiscal stability and inflation control. Their cooperation is crucial to determining the character and application of macroeconomics and guaranteeing long-term economic growth.
It is classified into the following two sections –
It is one of the effective tools of macroeconomics that helps ensure a country’s economic stability. It refers to how the expenditure meets the deficit income, which is explained as a form of budget decision under the scope of macroeconomics.
The Reserve Bank establishes monetary policy in coordination with the Government. These policies regulate interest rates to maintain economic stability and growth.
The nature of macroeconomics is as follows:
We have investigated the nature and application of macroeconomics to comprehend how significant economic factors affect a country. The study of macroeconomics centers on ideas important in determining the economy’s direction, such as GDP, unemployment, and inflation.
The nature and application of macroeconomics aid in developing policies regarding employment, economic growth, and fiscal stability. With a solid understanding of macroeconomics, governments and corporations can make well-informed decisions that propel national development and enhance people’s quality of life.
Now, let us understand the importance of macroeconomics in multiple areas:
The nature of macroeconomics covers a wide range of subjects, including inflation, GDP, unemployment, and fiscal policies. It is essential to comprehend how economies operate on a broader scale, impacting domestic and international economic patterns. Understanding how different sectors interact and affect economic growth and stability is made possible by the nature and application of macroeconomics.
However, some limitation of macroeconomics prevent the economy from reaching its full potential. Variables such as political unpredictability, global economic uncertainties, and unexpected events can impact economic analysis and policy-making. These restrictions influence how macroeconomics can be used to solve problems in the real world.
An economist needs to analyze the following limitations of macroeconomics –
The comprehensive study of a country’s whole economy is known as macroeconomics. The distribution of resources is determined by its tenets. Every aspect of life, including daily life and industrial settings, involves macroeconomics. It is dynamic and addresses the ongoing shifts in an economy. It plays a significant role in a nation’s financial model and assists the government in formulating solutions for a range of economic issues. It is essential for achieving a nation’s economic stability and has many applications. It affects people as well as the financial structures of the government.
Many economic policies are also based on macroeconomics. Macroeconomics establishes the framework for a country’s regional decision-making system and sheds light on how a nation’s economy functions.
Nonetheless, this concept’s underlying policies typically have a widespread effect. It calls for an incredible, logical, and observational approach.
As an expert, you have to answer queries from students worldwide in subjects like Economics and more. You can work from home or anywhere in the world. All you have to do is sign up with Chegg!
Read more:

Macroeconomics helps understand the overall economy, guides policies, controls inflation and jobs, supports growth, and explains global trade.
Example: RBI changing interest rates to control inflation is a macroeconomic move.
Tip: Follow major economic updates, they impact daily life more than you think.
The scope of microeconomics covers how individuals, firms, and markets make decisions about prices, demand, supply, and resource use.
Example: Deciding the price of a product based on demand is microeconomics.
Tip: Use it to understand everyday choices in business and spending.
The economics scope covers how resources are used to meet needs through production, consumption, and distribution.
Tip: Economics helps you make better everyday choices.
Macroeconomics is the study of the overall economy, focusing on factors such as national income, inflation, unemployment, and economic growth.
Example: When the government changes interest rates to control inflation, that’s macroeconomics in action.
Tip: Understanding macroeconomics helps you see how national policies affect daily life.
Scarcity – Resources are limited, but wants are unlimited.
Opportunity Cost – Choosing one thing means giving up another.
Supply and Demand – Prices depend on how much is available and how much people want it.
Marginal Utility – The added satisfaction from consuming one more unit of something.
Equilibrium – The point where supply equals demand in a market.
Tip: Keep these basics in mind; they guide almost every economic decision.
The scope of macroeconomics includes national income, inflation, unemployment, economic growth, and government policies that affect the whole economy.
Example: How inflation impacts prices is studied in macroeconomics.
Tip: Understanding it helps you follow significant economic changes that affect everyday life.
Microeconomics studies individual choices, such as those of consumers and businesses, while macroeconomics examines the economy as a whole, including national income and inflation.
Tip: Knowing both helps you understand everyday decisions and significant economic trends.

Authored by, Gagandeep Khokhar
Career Guidance Expert
Gagandeep is a content writer and strategist focused on creating high-performing, SEO-driven content that bridges the gap between learners and institutions. He crafts compelling narratives across blogs, landing pages, and email campaigns to drive engagement and build trust.
Editor's Recommendations
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.
Chegg India does not ask for money to offer any opportunity with the company. We request you to be vigilant before sharing your personal and financial information with any third party. Beware of fraudulent activities claiming affiliation with our company and promising monetary rewards or benefits. Chegg India shall not be responsible for any losses resulting from such activities.